This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor II Cao Thi Thanh - Pediatrician - Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Osteogenesis imperfecta or brittle bone disease in children is a rare but troublesome clinical disease. The disease is characterized by a decline in bone quality due to a lack of collagen in the body, so children with the disease often have spontaneous fractures without trauma or fracture many bones at the same time.
1. What is osteogenesis imperfecta?
Osteoporosis is also known as vitreous bone disease or brittle bone disease. This is an autosomal dominant genetic disease, characterized by a decline in bone quality due to a lack of collagen and connective tissue. Genetic damage in the genes that regulate collagen synthesis is implicated as a direct cause of the disease. Children with osteogenesis imperfecta are very susceptible to fractures or bone deformities after even mild trauma because the bones become brittle and have reduced bearing capacity. Some cases can even appear after coughing or sneezing or not experiencing any trauma.Brittle bone disease or osteogenesis imperfecta in children is relatively rare in the community with an incidence of about 1/20000. The incidence and severity of the disease did not differ across geographic regions, races, or sexes. Currently, not many studies have been conducted to find out the standard regimens for the treatment of osteogenesis imperfecta. Scientists are working hard to understand many other aspects of the disease, including the genes responsible for osteopenia, drugs that increase bone strength, and surgical aids.
2. Causes of osteogenesis imperfecta in children
Childhood osteogenesis imperfecta is a chromosomally inherited disease. Mutations in the gene responsible for collagen production in the human body lead to disorders and loss of bone quality. Collagen is one of the components that make up the skeleton, plays a role in maintaining bone stiffness, making bones strong. When collagen is not produced in sufficient quantity or quality, bones become "brittle" and more prone to fracture. Having a parent with the disease increases the risk of the baby being born with the disease. Usually, children with brittle bone disease receive only one gene for the disease from one parent, rarely simultaneously from both. However, not all cases of children with osteogenesis imperfecta are due to inherited disease genes from previous generations. Gene mutations present shortly after conception are also responsible for brittle bones in some situations.3. Clinical signs of osteogenesis imperfecta in children
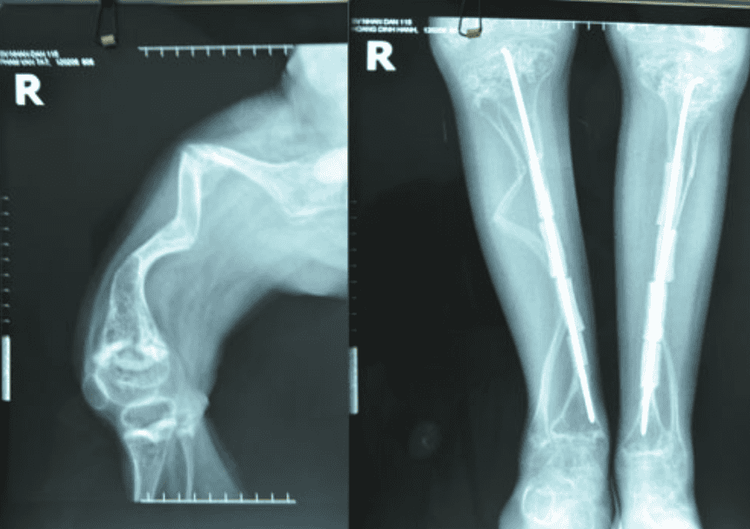
Unfortunate children with osteogenesis imperfecta often have a clinical presentation that coincides with repeated fractures or multiple fractures. The clinical presentation of osteogenesis imperfecta varies from patient to patient. Bone damage occurs after minor trauma or even without a history of trauma in many cases. This is also the most common symptom that prompts parents to bring their children to the hospital, and is the first symptom that helps doctors orient the diagnosis of osteogenesis imperfecta in children. Other bone abnormalities that can be encountered in children with the disease are bone deformities, deformed faces, barrel-shaped deformed rib cage, curved spine, underdeveloped small skeleton that makes children short and loose joints.Abnormalities in collagen production make the manifestations of the disease varied because collagen is a component of many different organs in the body, including: skin, ligaments, teeth, sclera of the eye. Children with brittle bone disease may also face other symptoms such as tooth deformities, brittle teeth, blue eyes, hearing loss.
4. Methods of treatment of osteogenesis imperfecta in children
Osteoporosis is caused by abnormalities in the gene that regulates collagen synthesis in the body, so there is currently no specific treatment to completely cure the disease. Correcting faulty genes is a resource-intensive method that has not yet been widely adopted. Children with osteogenesis imperfecta are often treated with primary care to help improve and control symptoms.Principles of treatment of osteogenesis imperfecta need to ensure the following:
Treatment of broken bones Care for broken teeth Control pain symptoms with drugs or interventions Physical therapy Rehabilitation for children with aids in walking and moving, most commonly a wheelchair Treatment of broken bones is usually carried out by surgery. The doctor fuses the broken pieces of the bone by means of support such as nails, screws. Choosing a surgical method, in addition to helping to fix the bone, also plays a role in correcting deformities or abnormal bone formation.

Maintain a good weight for the child. An overweight or obese child increases the risk of fracture because the child's fragile skeleton is not able to bear the weight. Exercise: many parents are often afraid and do not want their children to exercise when they are diagnosed with osteogenesis imperfecta. However, a reasonable exercise regimen such as walking, swimming can help bones become stronger. Provide adequate nutrients Do not use corticosteroids because they degrade bone quality.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.