This is an automatically translated article.
Pulmonary coagulation syndrome is one of the most common lung diseases and can leave many dangerous complications. Depending on the cause of the thickened lung, there will be an appropriate treatment for the patient.1. What is a condensed lung?
The lung parenchyma of a healthy, normal person is spongy. When the lung parenchyma becomes inflamed, in areas of lung injury the congested alveoli become more densely filled with secretions, increasing the density of the lung parenchyma known as pulmonary consolidation syndrome.2. Causes of thickened lung
Lungs coagulate due to many causes such as:
Pneumonia: Non-tuberculosis pneumonia in general and pneumococcal pneumonia in particular, is the main cause of pulmonary consolidation with typical symptoms is sudden high fever, accompanied by chills, chest pain, coughing up purple or rusty sputum. Lung Abscess: Certain types of anaerobic or aerobic bacteria inflame the lung parenchyma and cause festering. Pulmonary TB : Pulmonary TB can lead to lung consolidation and chronic progression in one or more areas of the lung, leaving the patient exhausted and often with persistent fever. Atelectasis due to bronchial compression: Enlarged lymph nodes can compress the bronchus and cause collapse of a segment of the lung. Atelectasis can also occur when the bronchi are suddenly compressed by a foreign body or blood clot. Pulmonary artery infarction: In some vascular diseases such as coagulopathy, mitral stenosis, or in some patients after surgery, postpartum maternal occlusion may occur in a pulmonary artery branch.
Áp xe phổi có thể dẫn đến phổi đông đặc
3. Symptoms of thickened lung
The common symptoms of congested lungs caused by the above causes are:
Difficulty breathing, wheezing, especially when the degree of lung consolidation increases, the patient will have more difficulty breathing. Rapid breathing, shallow breathing, unable to breathe when speaking. Severe pain in the chest. Pale, pale skin. Coughing more or less, coughing up sputum, maybe coughing up blood. Fever, profuse sweating (especially at night), fatigue, weakness.
4. Diagnosis of congestive lung
To make a diagnosis, the doctor will rely on the medical history and physical examination. Clinically, lung consolidation can be detected through the following manifestations:
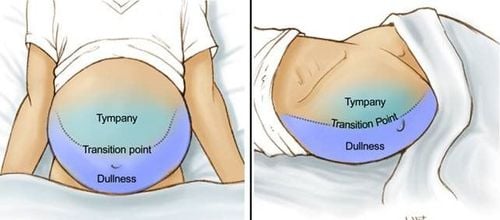
Increased vibrato: When the lung parenchyma is frozen, the vibration of the sound is more resonant and conducts farther. Turbid percussion: The alveoli are filled with secretions, so when percussion, a more turbid sound will be heard. Reduces alveolar murmur: The alveoli become inflamed and secrete fluid that interferes with air circulation. If the clinical manifestations are not obvious, the doctor will order a chest X-ray. Condensed chest X-ray images show the following features:
Location, size, and characteristics: Pulmonary solids are opacities of irregular or even density, which can be difficult to delineate if the borderline is demarcated. unknown, scattered or concentrated in an area in the lung field, possibly a segment or an entire lung. Neighboring organs: To distinguish from syndromes and other respiratory diseases, it is necessary to observe nearby organs and areas. Pulmonary consolidation syndrome on chest X-ray with opacity on one affected lung, accompanied by signs of diaphragm, intercostal space, and mediastinal retraction. Meanwhile, pleural effusion can cause these areas to be pushed out. In order to determine and conclude exactly what cause lung consolidation is causing, the doctor will ask the patient to perform other tests.

Bác sĩ sẽ chỉ định phù hợp
5. Treatment of thickened lung
Depending on the cause of the thickened lung, the doctor will prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Pneumonia: Treatment of pneumonia is mainly medical methods, using drugs including antibiotics or antivirals, fungi and drugs to relieve symptoms such as cough, fever, chest pain. Lung Abscess: Can be treated with medication or surgery, when the abscess becomes more severe. Pulmonary tuberculosis: Treatment with drugs in combination with a healthy lifestyle, abstain. Atelectasis due to bronchial compression: Depending on the cause of the atelectasis such as enlarged lymph nodes, tumor or foreign body compressing the bronchi, the patient will be prescribed drug treatment or surgery. Pulmonary consolidation syndrome has many causes. A physical examination, combined medical history, X-rays and other necessary tests help the doctor determine the cause of the disease and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a general hospital with the function of examining and treating common respiratory syndromes and diseases such as pneumonia, bronchitis, asthma, pleural effusion, coagulation syndrome pneumonia and many other diseases. At Vinmec, we have also performed endoscopic diagnosis and treatment with modern medical methods for respiratory diseases, not only bringing high efficiency but also minimizing complications of recurrent disease. The great success is because Vinmec is always fully equipped with modern facilities, examination and treatment procedures are carried out by a team of experienced and qualified doctors that bring optimal treatment results. advantage for customers.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.