This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Pulmonary coagulation syndrome is one of the most common lung diseases and can leave many dangerous complications. Depending on the cause of the thickened lung, there will be an appropriate treatment for the patient.
1. What is pulmonary coagulation?
Lung consolidation occurs when the air in the small airways in your lungs is replaced by something else. Depending on the cause, air can be replaced with:A liquid; such as pus, blood, or water. Concentrated ingredients; such as stomach contents or cells. The X-ray picture of your lungs and your symptoms are almost pathologically similar. So usually, you'll need more tests to figure out why your lungs are frozen. With proper treatment, solidification usually disappears and air is re-opened.
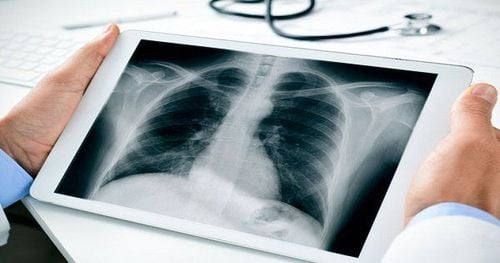
2. Chest condensate on X-ray
2.1. Symptoms Condensation almost always makes it hard to breathe. Air can't pass through the lung condensate, so your lungs can't do their job of bringing in fresh air and getting rid of the air your body used. This can make it hard to breathe. It can also make your skin look pale or bluer due to lack of oxygen. Other symptoms, depending on the cause, may include:Coughing up green or bloody sputum. Hemoptisi . Dry cough. Breathing sound, wheezing. Chest pain or heaviness in the chest. Breathe fast. Fever. Tired. 2.2. Causes Causes of lung consolidation include:
Pneumonia Pneumonia is the most common cause of lung consolidation. When you have an infection in your lungs, your body sends white blood cells to fight it. Dead cells and debris build up creating pus, which fills the small airways. Pneumonia is usually caused by bacteria or viruses but can also be caused by fungi or other unusual organisms.
Pulmonary edema Congestive heart failure is the most common cause of pulmonary edema. When your heart can't pump hard enough to send blood forward, it backs up into the blood vessels in your lungs. The increased pressure pushes fluid from your blood vessels into the small airways.
People who almost drown have pulmonary edema, medically called “drowning on land”. In these cases, fluid enters the airways from outside the body instead of inside.
Pulmonary hemorrhage Pulmonary hemorrhage means you are bleeding in your lungs. According to a review article in Tuberculosis & Respiratory Diseases, the condition is most commonly caused by inflammation of the blood vessels. This makes your blood vessels weak and leaky, so some of your blood moves into the small airways.
Foreign body or aspiration pneumonia Asphyxiation occurs when you breathe in food particles or stomach contents into your lungs.
Inhaling food can cause pneumonia, but infections are often more difficult to treat than common pneumonia. If you can't swallow properly, you're more likely to get food into your airways when you eat. If the swallowing problem is not corrected, you will continue to have aspiration pneumonia.
Stomach acid and other chemicals can also cause inflammation and irritate or damage your lungs.
Lung cancer Lung cancer is a common form of cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, lung cancer claims more lives each year than prostate, colon, and breast cancers. You are more likely to get lung cancer if you smoke.

3. How is pulmonary consolidation different from pleural effusion?
A pleural effusion is a collection of fluid in the space between your chest wall and your lungs. Like consolidation of the lungs, pleural effusions are also white areas on your chest X-ray. Since an effusion occurs in a relatively open space, it will often move due to gravity as you change your position. A frozen lung can also be caused by fluid, but it's inside your lungs, so it can't move when you change positions. This is one way a doctor can tell the difference between the two conditions.Some causes of pleural effusion such as congestive heart failure, pneumonia, lung cancer. As mentioned, this is also the cause of the thickening in the lungs. So you can have both conditions at the same time.
4. How is pulmonary consolidation diagnosed?
Pulmonary consolidation is most easily seen on chest x-ray. The solidified parts of your lungs look white or opaque on a chest X-ray. The location of solidified areas on your X-ray can help your doctor find the cause, but other tests are almost always needed. Includes:Blood test . This test can help determine: Whether you have pneumonia and what caused it. Your red blood cell level is low. You are bleeding into your lungs. You have vasculitis. Your blood oxygen levels are low. Sputum culture. This test can help determine if you have an infection and what is causing it. CT scan . This scan provides better solidified images. Many conditions have characteristic features on CT, making the diagnosis easier for doctors. Bronchoscopy. For this test, your doctor will insert a small fiber-optic camera on a tube into your lungs to look at the solidification, and sometimes, they'll take a sample for culture and study.
5. How is pulmonary coagulation treated?
Pneumonia Pneumonia is treated with medications that target the organism that causes it. Usually, you'll be given antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals. You may also be given medicine to control cough, chest pain, or fever.Pulmonary edema Treatment for pulmonary edema will be based on its cause. Treatment may include medication to remove excess fluid, reduce pressure in your blood vessels, or make your heart pump better.
Pulmonary hemorrhage If you have vasculitis, you are usually treated with steroids and immunosuppressants. You may need to take these medicines regularly to prevent further bleeding.
Aspiration pneumonia If you have aspiration pneumonia, you will be treated with strong antibiotics. You will also be evaluated and treated for swallowing problems, so that you don't continue to inhale.
Aspiration pneumonia is not an infection, so antibiotics don't work. If you are very ill, you may be given steroids to reduce inflammation, but usually you only get supportive care while your body heals.
Cancer Lung cancer is difficult to definitively treat. Removing the tumor with surgery may give you the best chance of a cure, but not all lung tumors can be removed. Once cancer begins to metastasize, it cannot be cured and treatment is given only to help relieve your symptoms. Early detection of cancer is the key to treating this monstrous disease.

6. Prospects for pulmonary coagulation disease
Pulmonary consolidation has many causes. There are causes that can be serious, but many others are easily treatable and curable. Treatment can vary, but regardless of what is causing your lung consolidation, it's important to see your doctor as soon as you develop symptoms. Starting treatment early when sick usually gives you better results.Vinmec International General Hospital is a general hospital with the function of examining and treating common respiratory syndromes and diseases such as pneumonia, bronchitis, asthma, pleural effusion, coagulation syndrome pneumonia and many other diseases. At Vinmec, we have also performed endoscopic diagnosis and treatment with modern medical methods for respiratory diseases, not only bringing high efficiency but also minimizing complications of recurrent disease. The great success is because Vinmec is always fully equipped with modern facilities, examination and treatment procedures are carried out by a team of experienced and qualified doctors that bring optimal treatment results. advantage for customers.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.