This is an automatically translated article.
Biopsy is one of the most reliable and accurate testing methods. Biopsy tests are especially useful and often applied in the diagnosis of cancers, helping to prevent unnecessary risks to the patient's health and life.1. What is a biopsy?
A biopsy is a highly accurate medical test performed surgically with the primary purpose of taking a sample of cells or tissue to diagnose most cancers.This is a method that can comprehensively assess the situation of the disease, done if other simple methods such as tests, endoscopy, ultrasound, and photography are not effective.
Doctors can perform biopsies by taking samples of tissue from any location on your body, such as organs, skin, or other structures. Once removed from the body, these tissues will be examined under a microscope for a more accurate and effective diagnosis.
2. Purpose of Biopsy
The main purpose of this method is to check for abnormal function of an organ or abnormal cell structure changes such as swelling, tumor, tumor,... Biopsy procedure usually involves the cancer. However, if your doctor orders you to have the test, it doesn't mean you have cancer. Your doctor simply wants to check if there is anything abnormal in your body due to cancer or other factors. For example, when you have a lump in your breast, an imaging test helps your doctor confirm the lump. A biopsy will help determine if you have breast cancer or another condition.
Nếu bác sĩ yêu cầu bạn thực hiện xét nghiệm thì không có nghĩa là bạn bị ung thư
3. Common types of biopsy tests
Usually, biopsy tests will be classified into many different types and based on the condition and suspicious area on the body, the doctor will choose the type of biopsy that is appropriate for each patient. A common feature of biopsy tests is a local anesthetic to relieve pain in the area being performed. Some common types of biopsies include:3.1 Bone marrow biopsy Bone marrow is the spongy material inside some large bones like the femur, the hip bone, where blood cells are produced. If your doctor suspects that you have a blood problem, a bone marrow biopsy may be done. This type of test helps diagnose cancerous and noncancerous conditions, such as anemia, leukemia, lymphoma, or infection.
A bone marrow biopsy is also done to check if cancer cells from another part of the body have spread to the bones.
During a bone marrow biopsy, your doctor will remove a sample of bone marrow from the back of your hip bone using a long needle. In some cases, your doctor may biopsy marrow from other bones in your body. You will be given a local anesthetic before the bone marrow biopsy to minimize discomfort during the procedure.
3.2 Endoscopic Biopsy An endoscopic biopsy is done to give the doctor access to the body's internal tissue to collect samples from organs such as the colon, lungs, bladder,...
When performing an endoscopic biopsy, your doctor will use an endoscope with a small camera and light attached. The endoscope image will appear on a screen connected to the camera mounted at the end of the endoscope, making sample collection easier.
The process of performing an endoscopic biopsy usually takes about 5-20 minutes. Depending on the type of endoscopic biopsy you have, your doctor may give you sedation or anesthesia before the procedure. After the test is over, you may feel a little uncomfortable, have a sore throat, or have gas.
3.3 Needle Biopsy A needle biopsy is often used on tumors that your doctor can feel through your skin, such as suspicious breast lumps and lymph nodes. When combined with an imaging procedure, such as an X-ray, a needle biopsy can be used to collect cells from a suspicious area that cannot be felt through the skin.
Types of needle biopsies, including:
Core needle biopsy: The doctor will use a medium or large needle to access the central tissue core, such as removing tissue from the central core of a tumor in the breast. Fine Needle Biopsy: Using a fine needle attached to a syringe, the doctor can drain fluid and cells. This method is usually applied to tumors and palpable tumors. Axial biopsy: Usually applied to areas that are not palpable, but can be seen on an X-ray or CT scan, giving the doctor access to specific areas, such as the liver or lungs. and other parts. Vacuum-assisted biopsy: This is a vacuum-assisted test, commonly used for breast testing. This method helps patients less pain and scarring, does not cause breast deformation and does not require hospitalization.
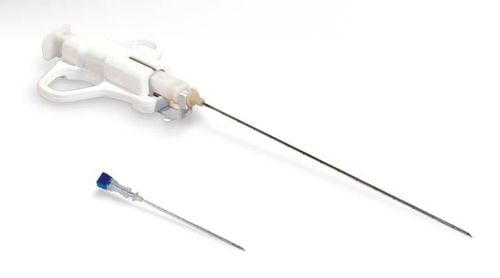
Sinh thiết kim thường được sử dụng trên các khối u mà bác sĩ có thể cảm nhận qua da của bạn
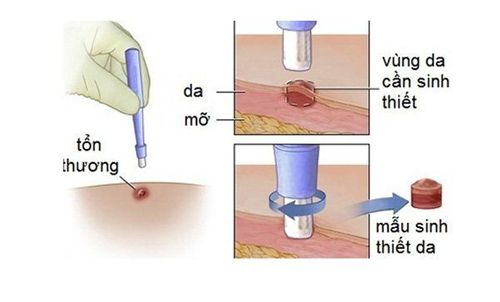
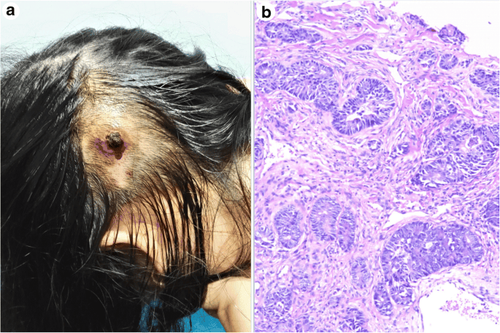
Click biopsy: The doctor will use a 2 to 4mm needle shaped like a small pen to take a biopsy sample from the skin. Once done, the doctor will either stitch it up with 1 stitch or let the wound heal on its own. Excisional biopsy: The doctor will completely remove the lesion and then send the entire biopsy sample to doctors who specialize in pathology. If the results show that the edge of the lesion is free of cancer cells, then the cancer has been completely removed. It can be said that excisional biopsy has both diagnostic and therapeutic effects. 3.5 Surgical biopsy A surgical biopsy procedure may be used to remove part of an area of abnormal cells (incisional biopsy), or to remove an entire area of abnormal cells. (excisional biopsy).
Your doctor may give you a local anesthetic to numb the biopsy area. Some surgical biopsy procedures require general anesthesia so that the patient is unconscious during the procedure. After the surgical biopsy is done, the patient may be asked to stay in the hospital for observation.
To learn more about biopsy methods at Vinmec, you can contact Hotlines of hospitals, or register online HERE.
MORE:
What is a cold biopsy (instant biopsy)? Can a cancer diagnosis ever be wrong? Importance of CEA quantification for cancer markers