This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Le Duc Hoang - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Electric shock is a treatment that helps to quickly extinguish and stabilize cardiac arrhythmias. There are two methods of electric shock being used, including: cardioversion and defibrillation.
1. What is electric shock?
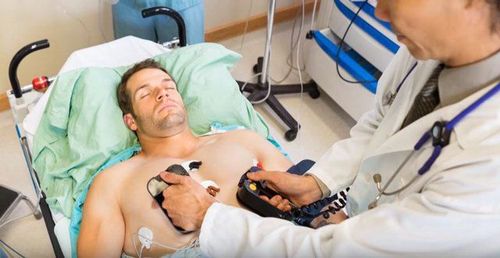
Electric shock is a method of using electrical energy to restore a patient's normal heart rhythm. This is a simple and fast-acting method in the treatment of some cases of tachyarrhythmia: Atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation,... Specifically, electric shock has the role of extinguishing the tachyarrhythmias that are taking over the rhythm of the sinus rhythm, helping the sinus rhythm return to the role of the rhythm master.*Note: It should not be misunderstood that electric shock is a method of using electric current to stimulate the heart to beat.
The equipment used for electric shock technique is an electric shock machine. The electric current released by the electric shock machine to treat arrhythmias is direct current. Some commonly used types of shock machines include:
Manually controlled external thoracic shock machine; Semi-automatic external thoracic shock machine; Automatic external thoracic shock machine; Electric shock machine with electrodes applied to the heart when performing open heart surgery; Cardiac cardioversion - implantable vibration defibrillator; Electric shock vest outside the chest. In pregnant women, electric shock is completely safe, does not affect the heartbeat and other health problems of the fetus. Shocks in people who have implanted pacemakers or automatic defibrillators can also be performed safely, as long as there are a few things to keep in mind when performing the procedure, such as the electrode plate needed to keep pace with the pacemaker. at least 12cm,...
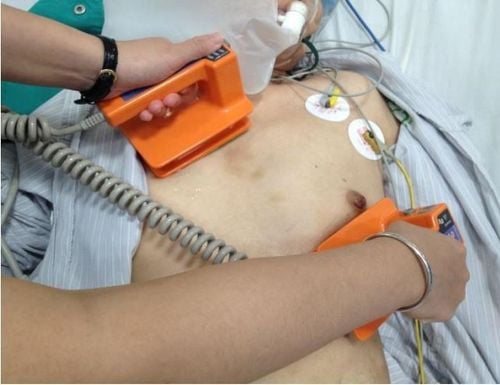
Ở phụ nữ có thai, sốc điện hoàn toàn an toàn, không gây ảnh hưởng tới nhịp tim và các vấn đề sức khỏe khác
2. Overview of cardioversion and defibrillation shocks
There are 2 types of electric shocks including:Cardioversion: Discharge of electrical current synchronized with the patient's QRS complex for cardioversion; Defibrillation: Discharge of electrical current at any of the patient's cardiac cycles (asynchronous). 2.1 Vibration Shock
Vibration Shock is an asynchronous electric shock. Current from the capacitor is released through the shock plate as soon as the doctor pushes the discharge button.
Indication of shock-defibrillation in the following cases:
Ventricular fibrillation; Pulseless ventricular tachycardia. Contraindications to defibrillation electric shock:
Asystole; Discrete ventricular rhythm; Circuitless electrical operation. Note that when the shock breaks the vibration, absolutely do not press the Sync button because if you press this button, the current will accumulate in the capacitor and not discharge.
Energy level of shock shock:
Single phase electric shock: 360J; 2-phase electric shock machine: 120J - 200J depending on the type of machine (follow the manufacturer's recommendations and instructions of the treating doctor). If the first shock fails, the energy level should be increased on subsequent shocks if the machine allows. 2.2 Cardiac cardioversion
Cardiac cardioversion is a synchronous electric shock. When pressing the sync button (Sync) on the shock machine, the machine will automatically detect the QRS complex, marking the location where the electric shock will be discharged. When the discharge button is pressed, energy will accumulate in the capacitor, waiting for the right time to have the QRS complex to discharge. When the discharge button is pressed, the technician performing the shock should hold the live pole until the shock is released and avoid tilting the plate.
Indications for cardioversion:
Atrial fibrillation; Atrial flutter; Atrial tachycardia ; Supraventricular tachycardia due to re-entry circuit; The ventricular tachycardia is hemodynamically stable. Contraindications to cardioversion:
Relative contraindications in patients with Digitalis toxicity because this method has the potential to cause additional arrhythmias for the patient. However, in the case of patients with ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia with indications for electric shock, it should be combined with treatment with Lidocaine, potassium supplementation,... in accordance with the standard regimen.
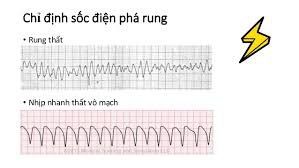
Sốc điện phá rung
Depending on the electric shock machine (1 phase or 2 phases) and the type of tachyarrhythmia (atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia) there will be an appropriate energy level. fit.
Complications of cardioversion:
Hypotension; Respiratory depression due to sedation; Transient ST-T wave changes; Atrioventricular block or sinus bradycardia; Ventricular arrhythmia or atrial arrhythmia; Damage to the heart muscle; Thromboembolism; Pulmonary edema ; Skin burns. When indicated to perform cardioversion and defibrillation in cardiovascular emergencies, patients need to strictly follow the doctor's instructions to ensure the success of the technique.
Master - Doctor Cao Thanh Tam has many years of experience in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases; Performing transthoracic echocardiography in the field of internal medicine and interventional Cardiology; Perform other non-invasive functional investigations in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Currently working as a cardiologist at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital since November 2015.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
SEE MORE
What is an electrocardiogram Holter And what does it mean in the diagnosis of arrhythmia? How is arrhythmia diagnosed? Stress electrocardiogram helps detect many dangerous cardiovascular diseases