Bartholin's cyst is a gynecological disease in women of reproductive age. Treatment of Bartholin's cyst is relatively simple, however, if the patient is negligent and does not treat it, it will cause many effects in daily life.
1. Where are the Bartholin glands located?
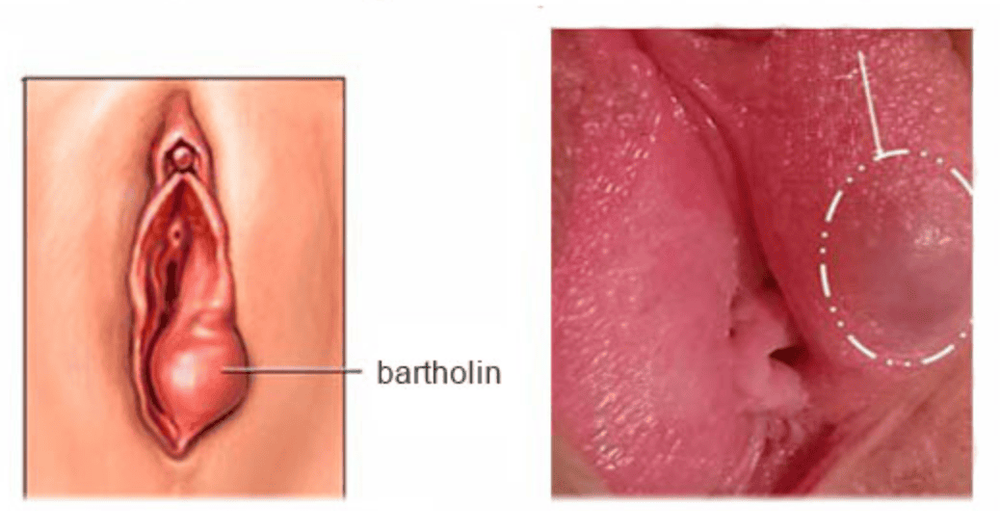
The Bartholin glands are glands of the external genitalia, located under the skin on both sides of the vagina. They are very small in size, so they are difficult to see when the glands are normal. The glands are spherical, 1cm in diameter, and are made up of mucus-secreting columnar cells. The Bartholin glands are responsible for secreting mucus into the surface of the labia minora surrounding the vagina, keeping the area moist and lubricated during intercourse.
2. What is a Bartholin's cyst?
A Bartholin's cyst is a cystic lesion, measuring 1.5 - 3cm in size, most commonly found in the vulva. The cyst is formed due to blockage of the glandular duct, while the gland continues to secrete mucus, forming a thin-walled cyst. The cause of the blockage of the glandular duct can be due to infection and edema that compresses the glandular duct, or due to trauma, chronic infection that blocks the glandular duct opening.
3. Treatment of Bartholin's cyst
Bartholin's cyst is usually only on one side of the vulva and does not show any symptoms, so no treatment is needed, the Bartholin's cyst can disappear on its own. Treatment of Bartholin's cyst is indicated in cases where the cyst increases in size, sometimes 5 - 10cm or is infected and causes pain in the vulva area.
Bartholin's cyst excision is a procedure used to treat Bartholin's cyst with or without fistula, Bartholin's cyst. This surgery is contraindicated in patients with Bartholin's cyst in the inflammatory stage (swelling, heat, redness, pain).
Bartholin's cyst excision is performed as follows:
• Step 1: Skin incision
• Step 2: Gland dissection: The outer upper edge of the gland is often adherent, making it more difficult to dissect than the inner surface under the mucosa. The gland is dissected very carefully to avoid breaking the inflammatory mass or allowing pus to escape.
• Step 3: Hemostasis.
• Stage 4: Mucosal suture
Bartholin's gland cyst enucleation
Bartholin's gland cyst enucleation
After Bartholin's gland cyst enucleation surgery, the patient is prescribed antibiotics for at least 5 days after the procedure, perineal hygiene with betadine solution or other antiseptic solutions, and monitoring for the risk of post-procedure hematoma and infection.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.