This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by resident Doctor Le Thanh Tuan - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Nha Trang International Hospital. The doctor has extensive experience in examination, treatment and surgery of abdominal diseases.Laparoscopic colostomy has many advantages over traditional surgery. Although it is not a difficult technique, the surgery to make an ostomy needs to be done very carefully, because the patients participating in the surgery are often terminal cancer, the body is thin and exhausted.
1. What is colostomy?
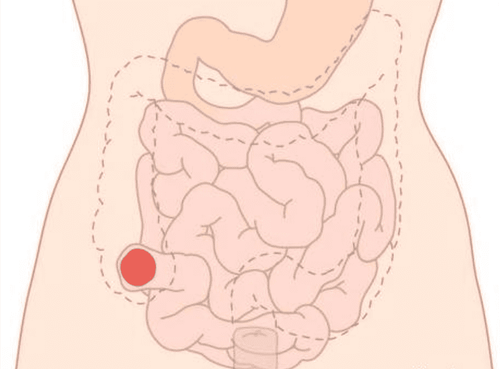
The large intestine is a part of the alimentary canal connecting the small intestine, consisting of two parts, the colon and the rectum. The colon helps to absorb and reabsorb water from waste, the rest forms stool, which will be contracted to push down the rectum and excreted through the process of defecation. An colostomy is an active opening in the colon (or jejunum) to the skin to allow stool to pass. Stool will pass directly through this opening and into a fecal bag. Because these stomas have no valves or muscles, stools cannot be controlled. An ostomy is indicated when:The large intestine is damaged, blocked. Patient has cancer of the lower part of the rectum, ulcerative proctitis, profuse bleeding, colon diverticulum, rectal-vaginal fistula, or rectal-bladder fistula, rectal rupture causing intra-abdominal infection, trauma, and complex anal fistula. Transsphincter or other dysfunctions The colostomy consists of two types: temporary colostomy and permanent colostomy. A temporary colostomy is used to drain stool for a short time, about 3-6 months, to help the lower large intestine rest and heal the intestinal anastomosis. When the injury or disease recovers, the stoma will be closed, and the normal flow of stool through the real anus will be restored.
Permanent colostomy is often used in colorectal cancer, patients have to use ostomy for the rest of their lives.

2. Classification of colostomy
The placement of the colostomy is determined before surgery for both standing and sitting positions. Depending on the medical condition, the doctor will specify the position of the patient's colostomy. Placement must be on a straight abdominal wall to make it easy to stick the bag and easy to observe, not right at the waist of the pants, not near the old scar, the hump of the bone.There are many ways to make a colostomy, each type of colostomy is named after the part of the colon it opens:
sigmoid colostomy: the sigmoid colon is the part closest to the colon and anus. , which functions to store waste in the stool before it is expelled. The sigmoid colostomy gives hard stools and is more physiologically suitable than other colostrums. This is the most commonly performed colostomy. Transverse colon colostomy: The stool of the transverse colon colostomy is usually soft because only a small part of the colon participates in water absorption. In the transverse colon, three types of colostomy can be performed: + Loop colostomy: a hole is made for stool to pass out, while the colon is still connected to the rectum, so it is sometimes stool and gas pass through the rectum.
+ Gun barrel-type colostomy: divides the colon into 2 parts, forming 2 openings, stool will exit through the upper hole, mucus from the colonic mucosa exits the remaining hole.
+ End-to-end colostomy: this is a permanent colostomy, the surgeon will remove the large intestine including the rectum and the colon below the anal opening.
3. How is laparoscopic colostomy performed?
There are two methods of colostomy surgery: open surgery and laparoscopic surgery. Laparoscopic surgery has many advantages such as less invasive, less pain for patients, faster recovery time. Although not a difficult technique, but ostomy surgery is often performed on terminal cancer patients, exhausted, in poor health, so the process must be performed with great care.Before surgery, the patient will be examined and carried out tests to evaluate the cardiovascular, respiratory as well as gastrointestinal tract function. Patients should fast for at least 6 hours before surgery.
The procedure for endoscopic colostomy takes place as follows:
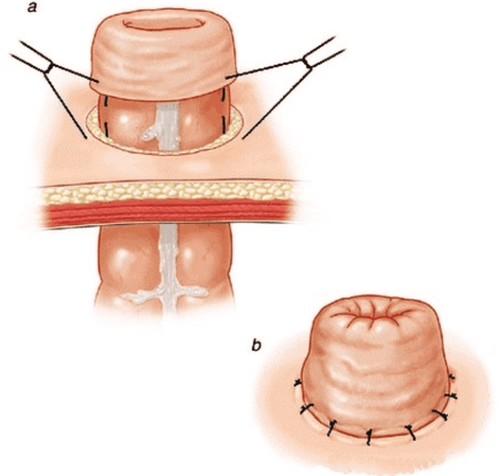
The patient lies on the operating table, supine position, arms closed, under endotracheal anesthesia. If making a descending colostomy, the laparoscope is placed on the left, the surgeon goes to the right. If making colostomy of ascending colon or ileum, the laparoscope is placed on the right, the surgeon stands on the left. Place a 10mm trocar below, inflate the abdomen, the doctor observes the entire abdomen, determines the segment of intestine that needs to be taken out to make an ostomy, then uses a clamp to clamp the intestine to fix it. The doctor cuts a circular section of skin, 2.5cm in diameter, longitudinal incision to the fascia, without removing fatty tissue (because this will be the stromal tissue for the artificial anus). After separating the muscle fibers to the two sides, make an incision in the outer diagonal fascia, and then make an incision on the posterior rod. Upon reaching the parietal peritoneum, carefully shallow the abdominal wall with fingers to create the jaw line. Use Bancock to bring the colon out of the abdominal wall. The terminal colon was brought out 2cm from the abdominal wall. Stitch the colon to the fascia of the abdominal wall. Continue to fix the colon to the prosthesis so that the colon protrudes 0.5-1cm from the abdominal wall.
4. Follow-up of patients after laparoscopic surgery for colostomy
During the first 24 hours after surgery, it is necessary to monitor the patient's general condition, pulse, blood pressure, and breathing rate. Administer intravenous fluids, use pain relievers, use antibiotics to prevent infections,...In the following days, continue to give patients drugs as prescribed by the doctor. When the patient has a bowel movement, give the patient a light meal such as porridge or milk. If the condition of the incision and the whole body is stable, the patient should be mobilized soon.
Most of the cases after surgery have favorable progress, good bowel circulation, convenient eating,... It is necessary to continue monitoring to detect and handle early complications that may occur after surgery such as:
Intestinal obstruction: occurs when the tunnel on the abdominal wall is too narrow, there is damage to the colon above the stoma, the stoma is twisted, turned upside down or due to a hernia near the stoma. These cases need re-operation, treat the cause. Inflammation of the skin around the artificial anus: treated by sticking a patch bag to limit the outflow, taking care of the skin with neutral soap, applying ointment, and using antibiotics if necessary. Abscess around the artificial anus: treated by cutting the thread, separating part of the colostomy mouth from the edge of the skin to drain pus, changing the wound dressing daily. Artificial anal necrosis: if the necrosis extends beyond the fascia of the abdominal wall or anal torsion is suspected, re-operation is required. The stoma has been retracted into the peritoneal cavity: surgery and reconstruction of the stoma. If it is a temporary colostomy, when it is time to close the anus, surgery to close the anus is performed. Artificial para-anal hernia: treated by suturing to narrow the opening of the abdominal wall or attaching the colon wall to the abdominal wall. Prosthetic colostomy: perform the colostomy again.
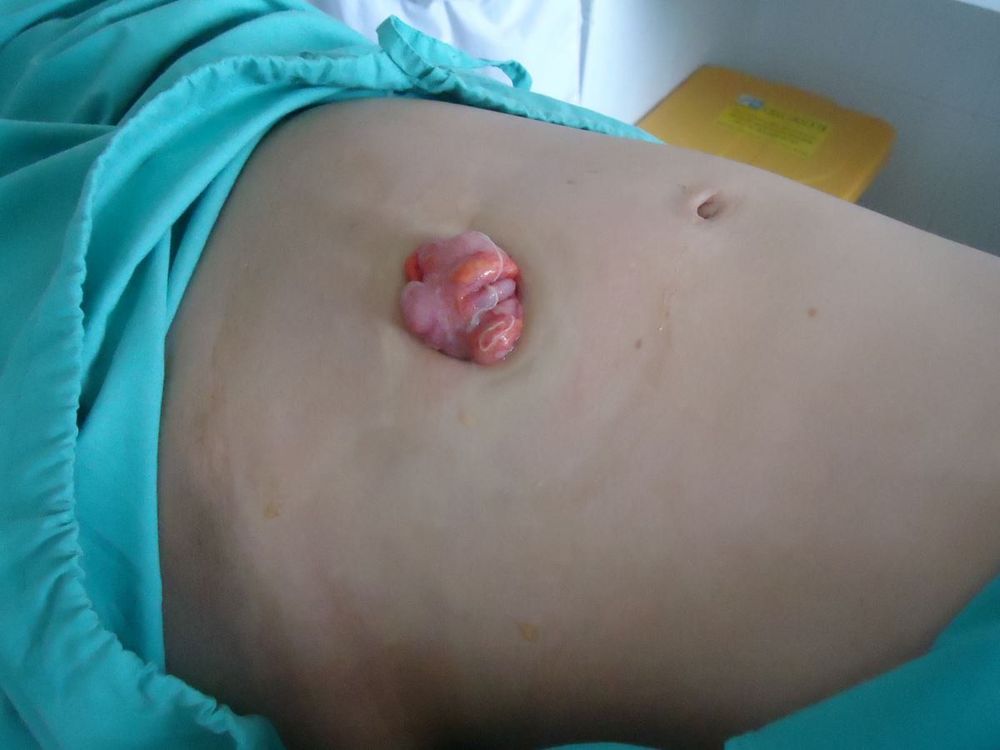
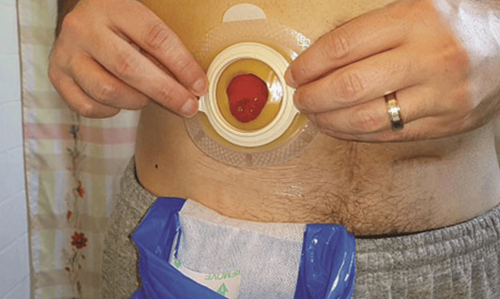
5. Care of the colostomy
The patient needs to clean the colostomy several times a day, keeping the anal sac less than half full at all times. Choose a bag with a deodorizing filter and air vents, which limit the chance of the bag becoming too tight and popping out of the abdomen. Keep the skin around the anus clean to avoid infection.Most patients after artificial surgery are very worried about their ability to continue working and living as well as fear of being alienated because of the bad smell from the artificial anus. Therefore, in addition to physical care, patients after surgery for colostomy need family and loved ones to care and help spiritually. Encourage the patient to participate in outdoor activities to improve health and help keep the mind comfortable, reasonable exercise will not affect the colostomy. Encourage patients to join groups of people with colostomy to share difficulties in living with colostomy, this will help provide psychological support for the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Recommended video:
Periodic health check at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
SEE MORE
Common complications and how to take care of an ostomy What are the types of colostrum commonly used How to treat anal fistula?