This is an automatically translated article.
Laparoscopic radical nephrectomy is indicated for patients with benign or malignant renal tumors that are less than 4cm in size, located in the periphery and protruding out. This is an effective method of treating kidney tumors for patients to help limit open surgery with long incisions, limit postoperative pain, and speed up recovery.Laparoscopic radical nephrectomy is contraindicated in patients unable to adapt to general anesthesia, patients with severe cardiovascular disease, uncontrolled coagulopathy, and hypovolemic shock.
1. Preparing for laparoscopic radical nephrectomy
The urologist will be the one to perform the surgery, with a full range of surgical facilities including the common means of endoscopes, surgical instruments and vascular clamps: Hemolock, Clip, Right angle, Surgicel . ..For patients who need to perform routine tests before surgery, computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast. At the same time, patients need to fast from the night before, intravenous broad-spectrum antibiotics before entering the operating room.

Trước khi phẫu thuật, bệnh nhân cần nhịn ăn từ tối hôm trước
2. Perform laparoscopic radical nephrectomy
Step 1: Peritoneal approachAfter placing the urethral catheter and nasogastric tube, the patient is placed in a lying position or tilted 30-45 degrees, the bearing points on the patient's body must be covered to no neuromuscular damage.
Trocar position: 1 trocar 12mm in the umbilicus, 1 trocar 12mm across the umbilicus outside the rectus muscle, and 1 trocar 5mm between the sternal tip and the navel.
Location of trocar for laparoscopic radical nephrectomy:
Open the Toldt fascia to move the colon to the middle. Perform the Kocher maneuver to expose the duodenum and inferior vena cava (right nephrectomy). Renal peduncle dissection to find renal vein, renal artery;
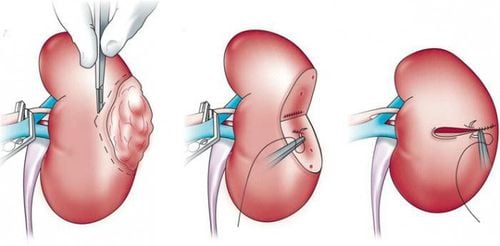
Renal tumor removal: Using Bulldog or Stansky laparoscopically clamp the renal artery, remove the whole kidney tumor with 5mm surgical margin. Suture the renal section: insert the Surgicel roll between the cut and suture the section; It should be noted that warm ischemia time < 30 minutes.
Take the specimen into the bag and remove it through a small incision in the midline below the umbilicus or the Pfannenstiel line.
Step 2: Retroperitoneal approach
The patient lies on his side 90 degrees, fold the operating table to widen the hip area between the lower costal margin and the iliac crest like in open nephrectomy. The bearing points on the patient's body must be covered.
Trocar position: 1 trocar 12mm at the tip of 12th rib for bronchoscope placement, 2 trocars with 10mm operation at the anterior axillary line 2cm above the iliac crest and 1 5mm trocar at the dorsal rib angle or in the posterior axillary line above the iliac crest.
Location of trocar for laparoscopic retroperitoneal nephrectomy:
Creating retroperitoneal space: Using a 14F Plastic catheter and gloved finger to create a retroperitoneal space. Through the small incision at the tip of the 12th rib, inflate the balloon about 700ml. Place 3 trocars, 2 12mm trocars and 1 5mm trocar into the retroperitoneal space. Open the Gerota fascia, dissect the renal peduncle to find the renal artery and vein.
Renal tumor removal: Using Bulldog or Stansky laparoscopically clamp the renal artery, remove the whole kidney tumor with 5mm surgical margin. Suture the renal section: insert the Surgicel roll in the middle of the cut and suture the section. It should be noted that warm ischemia time < 30 minutes.
Take the specimen into the bag and remove it through a 12mm trocar wide incision.
Patients after laparoscopic radical nephrectomy need to have nasogastric tube removed immediately. The urethral and retroperitoneal drainage tubes were withdrawn within 24 h after surgery. In addition, the patient is given oral or intravenous infusion to maintain for several days. Conventional analgesics for pain control taken orally or intramuscularly.
Bệnh nhân sau khi phẫu thuật nội soi cắt thận tận gốc cần được rút ống thông mũi dạ dày ngay
3. Management of laparoscopic radical nephrectomy complications
Bleeding: Intraoperative bleeding at the cut site can be controlled by hemostasis, suturing the section with a surgicel roll inserted in the middle of the cut. Late bleeding after surgery is often due to pseudoaneurysm or renal arteriovenous fistula, occlusion gives good results in most cases Postoperative urine leak: The drain has a lot of fluid or there is a collection of fluid after surgery, suggesting injury. pyelonephritis, requiring drainage and retrograde catheterization Other complications: Infection of trocar hole, retroperitoneal hematoma, persistent wound pain ... Vinmec International General Hospital with facilities With quality, modern medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured that they will be examined and treated at the Hospital.To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MORELaparoscopy Robot complete nephrectomy Laparoscopic nephrectomy for malignant kidney disease How is laparoscopic nephrectomy performed?