This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Specialist Doctor II Tran Lien Anh - Head of Neonatology Department - Vinmec Times City International HospitalUp to now, in advanced countries, neonatal jaundice and neurological sequelae due to hyperbilirubinemia are no longer a problem to focus on research. Experts are well aware that if a newborn has excessive jaundice for any reason, but if detected early, diagnosed and treated promptly, the prognosis will be very good.
1. Causes of Newborn Jaundice So why do babies get jaundice? How does jaundice and elevated blood bilirubin levels cause brain damage? To what extent is jaundice dangerous? How to detect early and promptly treat cases of excessive (unusual) jaundice?... These are the questions that have been answered by medical staff, as well as families. Newborn babies need to know in the process of taking care of babies.
The majority of newborns present with jaundice due to increased levels of bilirubin in the blood, related to the red blood cell replacement process similar to adults and due to the newborn's poor ability to excrete bilirubin. . This is a yellow pigment, if formed in large quantities and in free form (not bound to Albumin), it can penetrate into the tissues causing jaundice. But because this is a manifestation of the vast majority of newborns, it is called physiological jaundice. And because of physiological jaundice, the child still eats and sleeps normally, still has yellow stools. Without treatment, the baby's jaundice will clear up in 7-10 days. For premature babies, jaundice may last longer and become darker.
In addition to the reasons mentioned above, there are many other risk factors that can make the baby more jaundiced than usual such as hemolysis due to incompatibility of mother-child blood group Rh and ABO system; or not due to immunity such as: postpartum asphyxia, premature birth, infection, blood clotting disorder, hematoma under the scalp, familial disease...
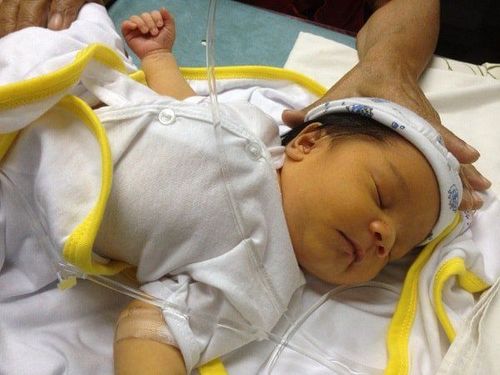
So to know if the baby has jaundice or not, To distinguish physiological or pathological jaundice, mothers need to carefully observe the skin areas on the child's body under natural light (daytime) as soon as the baby is 1-2 days old. If it is physiological jaundice, the baby will only have yellow from the face to the navel, usually appearing from the 3rd to 5th day after birth, the yellow skin color is also very pale like the color of a ripe lemon, the baby does not have any abnormal manifestations of the lesions. Central nervous system injury, still eating well, sleeping peacefully.
Pathological (excessive) jaundice usually appears earlier after birth (possibly within the first 24 hours after birth). The skin has a dark yellow color like turmeric, straw color, appears first on the face, can increase rapidly, then spread to the body, limbs, and is accompanied by unusual symptoms such as lethargy, stop feeding (this is the alarm phase of brain damage). If the child is detected early at this stage and treated promptly with phototherapy, not only can blood transfusion be avoided, but also has a very good prognosis. On the contrary, if the child has darkening of the whole body, accompanied by abnormal symptoms due to severe brain damage, such as: refusing to breastfeed, having generalized spasticity, twisting limbs, lying on the back, If you stop breathing, have a high fever, you will have a very bad outcome if you are taken to the hospital. Most of the children die at this stage if the blood is not changed. As for the children who come late, although they are treated with blood changes or phototherapy, it is difficult to avoid neurological sequelae later.

Vàng da ở trẻ sơ sinh
There are 3 main methods to treat jaundice in babies. That is medication, light therapy, and blood exchange. Depending on the case, it may be necessary to combine all 3 methods to treat 1 child with severe jaundice.
Phototherapy: Light therapy is widely used in the treatment of children with jaundice very effectively
Bilirubin in the blood is a yellow crystal, capable of absorbing light (cold-spectrum light, skin irradiation). Under the action of light, bilirubin will be converted into a water-soluble compound and quickly eliminated from the body through feces and urine. Lighting is very safe (if the eyes are protected), easy to do, babies can still breastfeed when having to shine. There are many types of projectors suitable for each jaundiced object that needs to be illuminated: crib-type lamps (the child lies directly on top, double-projected lights above and below (used in cases where positive illumination is required), blanket lamps , bag wrapped around the young (very convenient for mothers when taking care of the baby: can be picked up to breastfeed, lighted at the same time)
Blood change Blood change is the last resort in the treatment of severe jaundice when the light is not When the blood is changed, we can quickly get the bilirubin circulating in the blood vessels, leading to a decrease in bilirubin in the blood and thereby also reducing bilirubin.
Currently, thanks to advances in science, blood transfusions are not only performed after birth but also before the baby is born (cases of hemolytic jaundice due to disagreement Rh) has helped bring happiness to many infertile families
By exchanging blood we can quickly remove a lot of bilirubin from the veins. It is difficult to determine how much bilirubin has entered the brain and caused brain cell damage. Therefore, in order to avoid brain damage due to hyperbilirubinemia, experts not only need to predict cases of severe jaundice, but also guide families on how to monitor after discharge from the hospital such as: mother-child with blood group incompatibility, infant asphyxia, premature birth, postpartum infection, mother taking fertility drugs, etc., but also must know how to detect cases of excessive jaundice so that the child can receive light in time. time.