The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Bui Minh Phuc, Grade II Specialist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.
Jaundice is a phenomenon of red blood cells being broken, the liver's bilirubin metabolism function is not yet complete. Pathological jaundice in newborns can cause complications of kernicterus, which can cause death or leave sequelae of slow development in children. Therefore, mothers should recognize some signs to distinguish physiological neonatal jaundice from pathological jaundice.
1. Distinguishing physiological jaundice from pathological jaundice
Newborns can have physiological jaundice or pathological jaundice. Physiological jaundice will usually disappear after a short time. Meanwhile, if there is pathological jaundice, it canwill be hazardous ashazardousas it may lead to coma, seizures, so parents need to know how to detect jaundice in newborns because the child can be comatose and have convulsions, so parents need to know how to detect jaundice in newborns.
1.1. Physiological jaundice
Physiological jaundice can be mild, in full-term babies, jaundice is normally considered physiological when jaundice appears after 24 hours of age, and usually disappears within 1 week in full-term babies and 2 weeks in premature babies.
Mild jaundice is simply jaundice (jaundice only in the face, neck, chest and abdomen above the navel) without other abnormal symptoms (anemia, enlarged liver and spleen, refusal to feed, lethargy, ...). Bilirubin concentration/blood is not more than 12mg% in full-term babies and not more than 14mg% in premature babies, ... The rate of increase in Bilirubin/blood is not more than 5mg% in 24 hours. In addition, the newborn's urine is dark or yellow (newborns' urine is usually colorless) and the stool is pale.
The cause of physiological jaundice in newborns is the accumulation of Bilirubin, a yellow substance produced when red blood cells are broken down and released. This phenomenon is common in newborns because they have many red blood cells, which are constantly broken down and replaced. Meanwhile, the baby's liver is not mature enough to filter all the Bilirubin from the blood, causing jaundice. When the baby is about 2 weeks old, the liver has developed more fully and is strong enough to process Bilirubin, so jaundice will go away on its own without causing any danger.
Trắc nghiệm: các chỉ số cần chú ý về sự phát triển thể chất của trẻ
Chiều cao, cân nặng của bé ở từng giai đoạn nên là bao nhiêu là bình thường, bao nhiêu là bất thường? Cùng ThS.BS Ma Văn Thấm điểm lại xem bạn đã nắm được các chỉ số phát triển thể chất của bé chưa nhé!The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Ma Văn Thấm , Nhi , Phòng khám Đa khoa Vinmec Dương Đông(Phú Quốc)
1.2. Pathological jaundice
In some cases, jaundice can be a sign of an underlying disease. When this occurs, jaundice may appear early, within 24 hours after birth. Pathological neonatal jaundice is characterized by a dark hue that emerges early and does not resolve after one week in full-term infants or two weeks in premature infants. The yellowing can affect the entire body, including the palms, soles, and conjunctiva. In addition to jaundice, other abnormal symptoms may be present, such as lethargy, refusal to breastfeed, convulsions, etc. A blood test typically reveals a bilirubin level higher than normal. If pathological neonatal jaundice is not identified and treated promptly, it can lead to serious complications, including neurotoxicity. This occurs when elevated indirect bilirubin enters the brain, potentially causing death or lifelong brain damage.Some common causes of pathological neonatal jaundice include:
Incompatibility between the mother's and baby's blood groups (such as ABO or Rh incompatibility), hemolytic diseases (like G6PD deficiency or sickle cell anemia), infections, subcutaneous hemorrhage, slow passage of meconium, fetal viral infections, and congenital hepatobiliary diseases (including biliary atresia and biliary dilation).
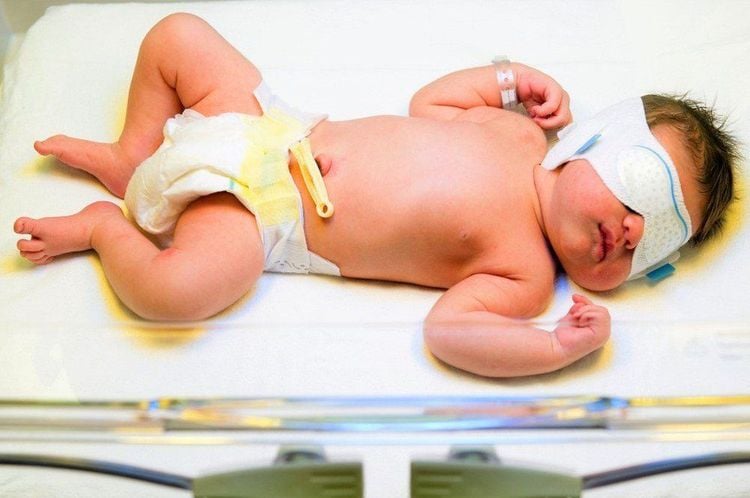
2. Signs that the child needs to see a doctor
When a child exhibits any of the following signs, parents should take them to a medical facility for examination to determine the cause of jaundice and ensure prompt treatment:
- Jaundice appears early, within 48 hours after birth.
- Jaundice covers the whole body, including yellowing of the palms and soles.
- Jaundice lasts more than one week for full-term babies and more than two weeks for premature babies.
- Babies with jaundice manifestdisplay additional concerning signs such as poor feeding, convulsions, fever, or pale stools.
Jaundice can be easily recognized by the naked eye in well-lit areas. Therefore, mothers should observe their baby's skin color daily in bright conditions. In cases where it is difficult to detect (for example, if the baby's skin is pink or dark), gently press your thumb on the baby's skin for a few seconds and then release it. If the baby has jaundice, the area where you pressed will appear clearly yellow. If any signs of jaundice are suspected, parents must take the baby to the doctor for examination.

3. Preventing Neonatal Jaundice
- Take good care of your health during pregnancy and attend regular prenatal checkups to detect and treat any illnesses early. This can help avoid premature birth, low birth weight, and infections from mother to child.
- Breastfeed your baby immediately after birth and ensure they are kept warm to prevent hypothermia, hypoglycemia, and early meconium stools.
- Ensure the nursery has adequate lighting to easily monitor the baby's skin color.
There are two methods to treat pathological neonatal jaundice due to increased indirect bilirubin:
- Phototherapy: This is a simple, safe, and effective treatment method that uses light energy through the skin to convert free bilirubin in the blood into non-toxic substances, which are then excreted in the stool and urine. During treatment, the baby will be unclothed (except for protective coverings for their eyes and genitals) and positioned to maximize skin exposure to the light.
- Exchange Transfusion: This medication/treatment/methodapproach is used if onlywhen the baby's jaundice is severe and does not respond to phototherapy or if there are accompanying neurological symptoms.
Note: Exposing the baby to morning sunlight is not effective for treating pathological jaundice, as the light intensity is too weak and prolonged exposure to sunlight is not advisable.
To treat pathological neonatal jaundice caused by increased direct bilirubin, different treatment strategies may be necessary depending on the underlying cause, such as surgery for biliary atresia or congenital biliary dilation.
See more: Instructions for diagnosis and treatment of pathological newborns
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.











