1. What is Tinea?
Tinea is a skin condition caused by a fungal infection. It can appear on various parts of the body, including the scalp, feet, between the toes, thighs, and nails. Tinea is most prevalent during the transition between winter and spring or spring and summer. This is because the warm and humid weather during these seasons creates ideal conditions for fungi to thrive and multiply.
2. Causes of Tinea
Tinea is caused by fungal infections, most commonly by three types:
- Trichophyton
- Microsporum
- Epidermophyton
The primary causes of tinea stem from poor hygiene, contaminated water sources, and unsanitary living environments, which create favorable conditions for fungi to grow and cause infection. Specific causes of tinea include:
- Poor personal hygiene, infrequent bathing, and excessive sweating, which provide a breeding ground for fungi.
- Wearing damp or wet clothing, creating a moist environment for fungi to thrive.
- Bathing in contaminated water, allowing fungi to easily enter the body and cause infection.
- Transmission from infected individuals through shared clothing, swimming or bathing together, or direct contact with infected skin.
3. Signs of Tinea
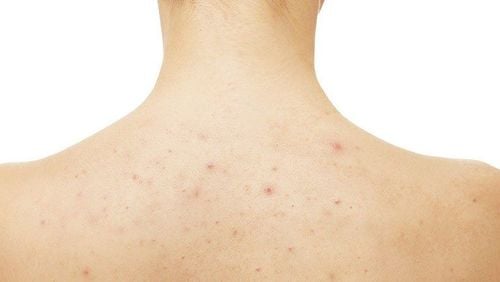
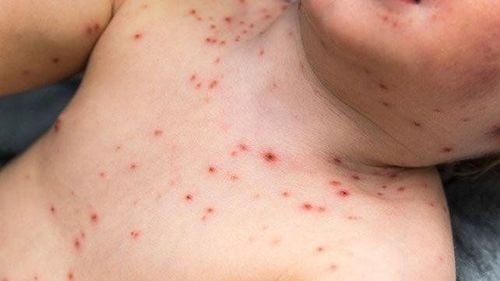
The most noticeable characteristic of tinea is a red rash with many small blisters forming in a ring-like pattern. Patients experience itching and discomfort in the affected area, especially at night or in hot weather. Excessive scratching can break the blisters, leading to bacterial infections and the formation of yellow pus or blisters.
Patients with tinea may initially develop a red rash in one area, which can then spread to other parts of the body such as the face, neck, chest, groin, etc. If left untreated, the condition can spread throughout the body, causing skin lesions or eczema.
4. Is Tinea Dangerous?
Tinea can cause itching, discomfort, and can be unsightly, especially if it appears on visible areas like the face, neck, hands, or feet. This can lead to self-consciousness and a negative impact on self-esteem. If left untreated, tinea can spread to other parts of the body, causing skin lesions or eczema, and may leave scars.
However, tinea is generally a benign skin condition and is not life-threatening. It's a common condition and is easily treatable.
5. How to Treat Tinea
Treatment for tinea involves both topical and systemic medications.
5.1. Topical Treatment
Anti-fungal creams are applied directly to the affected area. Common options include:
- Ketoconazole
- Miconazol
- Clotrimazol
These creams help to reduce itching and prevent the spread of the infection. Patients should apply the medication to the affected area regularly to reduce itching, prevent the spread of the infection, and avoid contaminating other parts of the body. When you have tinea, avoid scratching the affected area to prevent infection.
5.2. Systemic Treatment
In some cases, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed, such as:
- Itraconazole
- Nizoral
Antihistamines can also be used to relieve itching. If a secondary bacterial infection develops, antibiotics may be prescribed.
It's important to follow the full course of treatment as prescribed by your doctor to prevent the infection from recurring.
6. Preventing Tinea
Tinea is contagious and can easily spread from person to person. To prevent tinea or prevent it from recurring, follow these tips:
- Avoid sharing clothing or personal items with others.
- Do not wear damp or wet clothing.
- Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing.
- Maintain good hygiene by bathing regularly and choosing soaps and shampoos that are suitable for your skin type.
- If you have tinea, follow your doctor's treatment plan to prevent recurrence.
- Keep your pets clean.
- Exercise regularly to boost your immune system, eat a balanced diet, and get enough rest.
- Limit close contact with others to prevent the spread of infection.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.