This article was professionally reviewed by Dr.Le Thi Thu Hang, Grade I Specialist, a dermatologist at the Department of Examination & Internal Medicine at Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
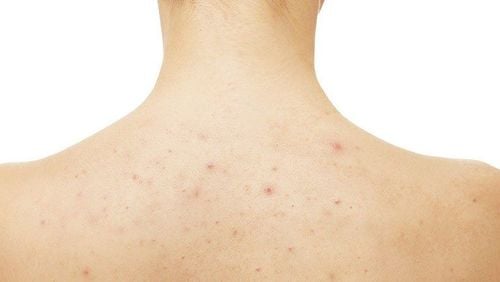
Folliculitis can occur anywhere on the body, including in the genital area, where it is often referred to as pubic folliculitis. Patients may notice small pustules that appear around the hair follicles in this region.
1. Causes of Folliculitis in the Genital Area
Both men and women can experience folliculitis in the genital area due to various factors:
- Infections: caused by bacteria (commonly Staphylococcus aureus), viruses, or fungi.
- Folliculitis may develop due to ingrown hairs, which occur when hair follicles become blocked by sweat and dead skin cells. This condition is more prevalent in areas with coarse hair that are frequently shaved. In the genital area, the hair is coarser, the skin is more sensitive, and the risk of bacterial infection from razors or hair removal products is higher than in other parts of the body
- Tight clothing and elastic underwear increase friction between the skin and fabric. When combined with sweat from physical activity or simply walking, these conditions create an ideal environment for folliculitis.
- Using dirty hot tubs can lead to folliculitis, as bacteria thrive in warm water. It’s important to clean the genital area after sexual activity or hot tub use to reduce the risk.
- Some women may experience a higher incidence of vulvar folliculitis during their menstrual periods due to hormonal changes.
2. Symptoms of Genital Folliculitis

Vaginal folliculitis may present as pimples on the inner thighs, labia, and pubic area.
Common signs and symptoms include:
- Clusters of small red bumps or whiteheads around hair follicles.
- Larger, painful lumps.
You should visit a healthcare professional if inflammation spreads or if symptoms do not subside within a few days.
3. Complications of Folliculitis in the Genital Area
If left untreated, folliculitis can develop into boils or carbuncles, which are larger infections beneath the skin that may lead to abscesses. While infections in individuals with normal immune systems can sometimes resolve on their own, squeezing the lesions or immunocompromised individuals can facilitate the spread of the infection, resulting in larger abscesses.
4. Treatment of Folliculitis in the Genital Area
The treatment for folliculitis varies depending on its type and severity.
Mild cases usually require treatment with topical antiseptics or antibiotics. Severe cases with complications may necessitate systemic antibiotics.
For other cases, the additional treatments are required, include:
- Minor Surgery: In cases with complications like boils or abscesses, a doctor may make a small incision to drain the pus. This can alleviate pain and expedite recovery. The area will then be covered with sterile gauze to manage ongoing drainage.
- Laser Hair Removal: If other treatments are ineffective, laser hair removal or IPL therapy may help reduce recurrence. This method can be costly and requires multiple sessions. This method will reduce the density of hair in the treated area. Potential side effects include skin discoloration and herpes.
5. Preventing Folliculitis in Men and Women

Practicing proper hygiene in the genital area to prevent folliculitis.
To prevent folliculitis in the genital area, it is essential to practice proper hygiene. Wash the area regularly with mild soap and warm water. Avoid sharing towels and change them frequently to reduce bacterial buildup. Women should pay special attention to vaginal hygiene during their menstrual period, as hormonal changes can increase skin sensitivity and the likelihood of hair follicle infections.
If you shave, ensure the area is clean before shaving, use a disposable razor, and apply lotion afterward. You might also consider alternative hair removal methods, such as hair removal gel or laser hair removal.
With proper hygiene and care, folliculitis in the genital area can be easily prevented. However, it is important to note that some sexually transmitted diseases may resemble the bumps associated with folliculitis or genital warts. If you experience recurrent symptoms or if the lesions are painful and take a long time to heal, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist.
Dr. Thu Hang has over 10 years of experience in dermatology, specializing in skin conditions affecting both adults and children, including sexually transmitted diseases, autoimmune disorders, and rare skin diseases. She holds several qualifications, including a Grade I Specialist of Dermatology from Hanoi Medical University and a DFMS Degree in Dermatology from the University of Paris XIII in France. Dr. Hang currently practices at the Department of Internal Medicine at Vinmec Hai Phong Hospital.
Resource: Flo.health and Mayoclinic.org
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
References: Flo.health and Mayoclinic.org