This is an automatically translated article.
Pityriasis rosea is a rash that usually begins as a large round or oval spot on the skin. Pityriasis rosea can affect any age group. It usually goes away on its own within 10 weeks. Rosacea can cause itching. Treatment can help relieve symptoms.1. Symptoms
Pink psoriasis often begins with a large, slightly raised, scaly patch called a plaque on the back, chest, or abdomen. Before plaque appears, some people experience headaches, fatigue, fever, or sore throat. A few days to a few weeks after the patches appear, you may notice smaller scaly spots on your back, chest, or abdomen that resemble pine tree patterns. The rash can be itchy, sometimes severe.
A dermatologist can usually diagnose it by eye. To be sure, your doctor may order blood tests, or a biopsy. These tests can rule out other types of skin problems, including eczema, ringworm, and psoriasis.
Main symptoms of pityriasis rosea
Feeling unwell: Some people feel unwell for several days before they develop a rash, with symptoms such as headache, high temperature, and joint pain. Plaques: A scaly, oval-shaped pink or red patch called a plaque usually appears at least 2 days before the rash spreads further. The plaques range in size from 2cm to 10cm. It can appear on the abdomen, chest, back, or neck and is less common on the face or scalp or near the genitals Widespread rash: Until 2 weeks after the plaque appears, the rash is more widespread, may continue to spread for the next 2 to 6 weeks. This rash is small, raised, scaly patches usually up to 1.5cm in size. Most plaques appear on the chest, back, abdomen, neck, upper arms, and upper thighs. The face is usually not affected.
In light-skinned people, the patches are usually pinkish-red in color. In dark-skinned people, the patches can sometimes be gray, dark brown, or black. Both the plaque and the rash usually last 2 to 12 weeks, although they can last up to 5 months. After the rash has gone, you may have some areas of skin that are darker or lighter. They should return to normal within a few months and will leave no permanent scars.
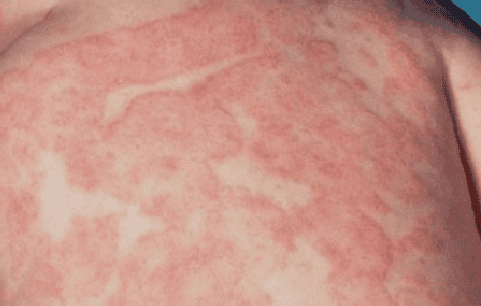
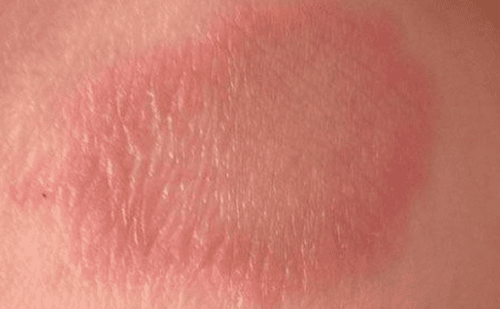
Vẩy phấn hồng thường xuất hiện các mảng thường có màu đỏ hồng.
2. Cause
Currently, the exact cause of roseola is unknown. Some evidence suggests that the rash may be triggered by a viral infection, especially by certain strains of the herpes virus. But it's not related to the herpes virus that causes cold sores. Psoriasis is not thought to be contagious.
Although the cause of psoriasis is not clear, several factors suggest that it causes them to be an infection. First, outbreaks of the condition occur in clusters, suggesting that an infectious agent is circulating. Second, recurrence of pityriasis rosea beyond the acute phase is rare, suggesting long-term immunity after infection. Third, up to 69% of patients with pityriasis rosea have prodromal disease prior to the appearance of plaque. Finally, some patients with pityriasis rosea have an increase in B lymphocytes, a decrease in T lymphocytes, and an increased deposition rate.
Unfortunately, although electron microscopy shows some changes to the virus and possible viral particles. But antibody and polymerase chain reaction tests for known viruses failed to identify the virus.
Virus herpes có thể là nguyên nhân gây bệnh
3. Complications
Complications of roseola psoriasis rarely occur. If they do occur, they can include intense itching and, on dark skin, brown spots that linger long after the rash has healed.
In most cases, pityriasis rosea is harmless and doesn't come back after it goes away. If your case lasts more than 3 months, check with your doctor. You may have another condition or are reacting to a medication. Pregnant women are in a group that has a higher risk of serious complications from this condition. In one small study, the majority of women who had a rash during the first 15 weeks of pregnancy had miscarriages.
Vẩy nến hồng có thể gây ngứa dữ dội
4. Treatment of Psoriasis
Psoriasis usually gets better without treatment within 12 weeks. Treatment is not necessary unless you experience discomfort and itching.
Possible treatments for rosacea include:
Emollients : Creams that hydrate and soothe the skin. Several emollients can be used as soaps, and are often recommended, because regular soap can irritate a rash. You can buy them over the counter from most pharmacists Steroid creams or ointments, like hydrocortisone and betamethasone creams. They are prescribed by a doctor and can reduce swelling and relieve itching Antihistamines: If you have trouble sleeping because of the itching, your GP may prescribe an antihistamine that will make you feel drowsy, such as hydroxyzine or chlorphenamine. Antihistamines, commonly used for allergies, in some forms also treat rashes and itching In some cases, your doctor may want you to take prescription medications, such as corticosteroids, to reduce itching and swelling, or acyclovir (Valtrex, Zovirax), an antiviral medicine that causes cold sores. UVB light therapy: If other treatments don't work, you may be treated with UVB light therapy. However, light carries its own risks, such as leaving dark spots behind. Psoriasis is not contagious and cannot be spread to others through physical contact.
Petrification Vers Colored is another common skin condition that can be confused with pityriasis rosea, as the rash can look similar. But there is an important difference between these two conditions. Pityriasis versicolor is caused by a yeast infection and can be treated with antifungal medications, including antifungal creams and antifungal shampoos.

Bệnh vẩy nến hồng có thể điều trị bằng dầu gội chống nấm
Psoriasis is a common, acute case. Viral and bacterial causes have been searched, but convincing answers have not been found. Psoriasis usually affects children and young adults. It is characterized by a plaque, followed by the development of a diffuse rash. The patches are often misdiagnosed as eczema. Psoriasis is difficult to identify until the appearance of smaller secondary lesions that are characteristic of the Langer line (split line).
Some drugs can cause a rash similar to that of pityriasis rosea, and some diseases, including secondary syphilis, are included in the differential diagnosis. The resolution of the rash can be accelerated with UV therapy but is not without the risk of hyperpigmentation. Topical or systemic steroids and antihistamines are often used to relieve itching.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at the Hospitals of the National Health System, please book an appointment on the website for the best service.
Articles refer to sources: mayoclinic.org, nhs.uk, webmd.com, aafp.org
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.