Many patients live with gallbladder sludge without knowing it until they experience severe pain. So, is gallbladder sludge treatable, and how can it be prevented?
1. Overview of Gallbladder Sludge
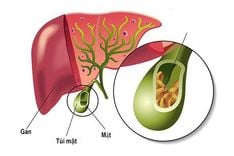
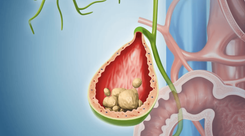
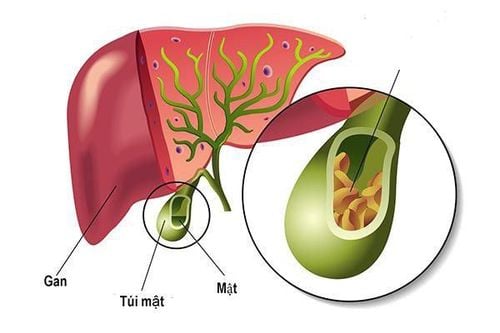
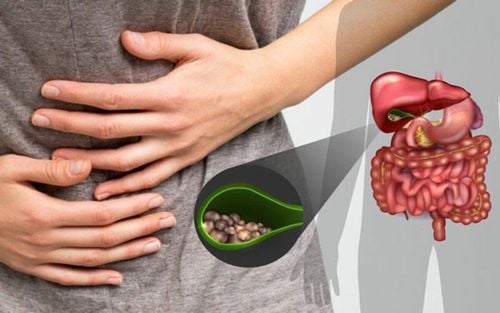
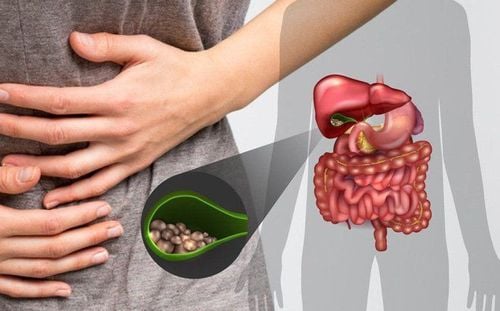
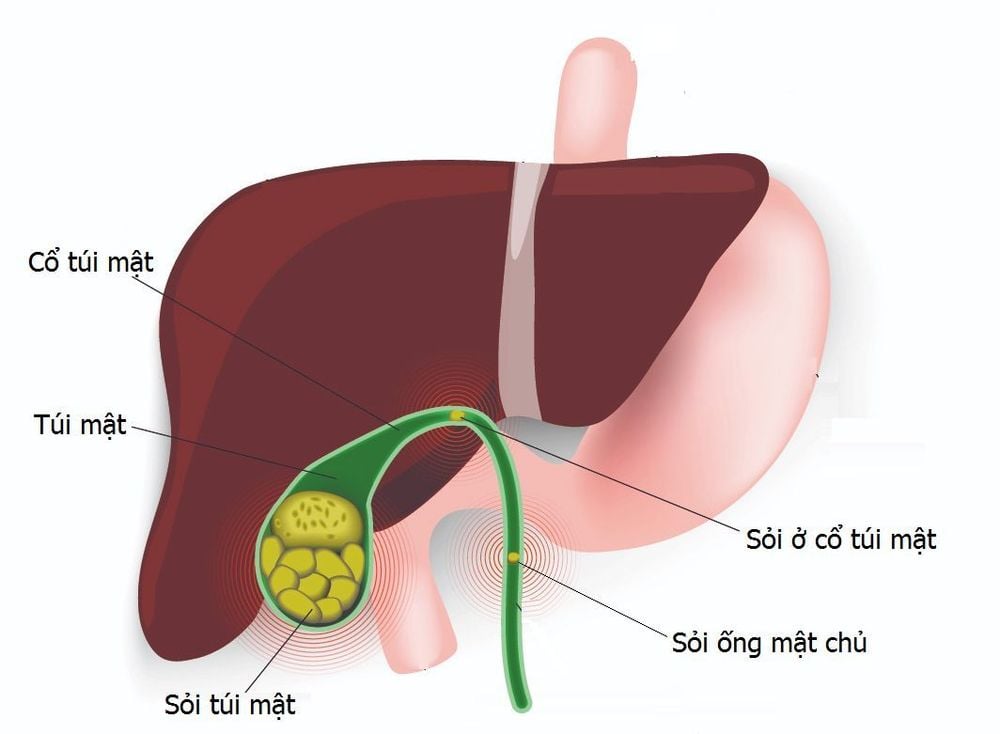
Gallbladder sludge consists of tiny, grainy particles that accumulate within the gallbladder. These particles are composed of cholesterol, calcium bilirubinate, mucus, and bile salts. Over time, these deposits can harden into cholesterol gallstones, commonly known as gallstones.
Often, gallbladder sludge is asymptomatic, meaning people may not know they have it until they experience pain. In some cases, the sludge can naturally disintegrate or be expelled by the gallbladder's contractions. However, untreated gallbladder sludge may lead to complications such as gallstones, acute pancreatitis, and other related conditions.
While anyone can develop gallbladder sludge, certain groups are at higher risk, including:
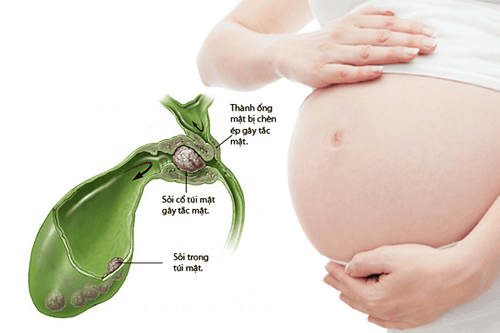
Pregnant women
Diabetics
Obese individuals or those losing weight too rapidly
Patients receiving intravenous feeding
People on long-term medications like lipid-lowering drugs or hormonal treatments
2. Causes of Gallbladder Sludge
Several factors can contribute to the development of gallbladder sludge. These include:
Pregnancy: During pregnancy, the gallbladder is compressed by the growing fetus, affecting its normal functioning. However, this condition usually resolves after delivery.
Rapid Weight Loss and Unhealthy Dieting: Crash diets or extreme weight loss can force the body to burn fat rapidly, increasing cholesterol production in the liver. This heightened cholesterol level promotes the formation of gallbladder sludge.
Gallstones: Blockage of the bile ducts by gallstones can also lead to the accumulation of gallbladder sludge.
Certain Medications: Prolonged use of medications such as lipid-lowering drugs or oral contraceptives can raise the risk of gallbladder sludge.
Intravenous Feeding: Patients relying on intravenous feeding due to gastric surgery or digestive issues often experience bile stagnation, increasing their risk of sludge formation.
Excess Cholesterol in Bile: When the liver produces too much cholesterol, bile becomes oversaturated, causing cholesterol to precipitate and form sludge.
Excess Bilirubin in Bile: Patients with liver conditions such as cirrhosis or biliary infections may produce excess bilirubin, which can lead to sludge formation.
Alcohol Abuse: Chronic alcohol damages liver function, hindering bile flow and increasing the risk of gallbladder sludge.
3. Symptoms of Gallbladder Sludge
Gallbladder sludge often goes unnoticed due to its silent progression. Many symptoms are similar to those of liver or digestive issues, making diagnosis challenging. Studies estimate that up to 80% of cases remain undetected until the condition progresses to gallstones.
However, when gallbladder sludge affects other organs, the following symptoms may appear:
Sudden pain in the upper right abdomen, especially after consuming fatty or greasy foods. Pain intensity can vary from severe to dull and may last for several hours.
Pain radiating from the upper abdomen to the shoulders or lower back.
Digestive discomfort, including bloating, nausea, or vomiting.
Fatigue, chills, excessive sweating, mild fever, or jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
Clay-colored stool or unusual changes in bowel movements.
These symptoms may indicate that gallbladder sludge has become severe and could lead to complications like bile duct obstruction, bile leakage, or acute pancreatitis, which, if left untreated, can result in shock or death.
4. Is Gallbladder Sludge Dangerous?
As mentioned earlier, gallbladder sludge may resolve on its own in some cases. However, if left untreated, it can lead to dangerous complications, such as:
Bile Duct Obstruction: Accumulated sludge can block the bile ducts, causing bile to stagnate, which increases the risk of gallstones, cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) or other gallbladder disease.
Gallbladder Inflammation (Cholecystitis): Prolonged retention of sludge in the gallbladder can lead to inflammation and infection, causing severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Acute Pancreatitis: Gallbladder sludge can migrate into the pancreatic duct, triggering acute pancreatitis, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Gallstones: Sludge can harden into gallstones, leading to intense gallbladder pain and further complications. If untreated, gallstones may severely impact health and even threaten life.
5. Can Gallbladder Sludge Be Treated?
Gallbladder sludge can be diagnosed using the following methods:
Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging is a common, non-invasive way to detect the location of sludge in the gallbladder.
MRI scans: can identify gallbladder sludge and rule out other causes of symptoms and detect whether gallbladder sludge has progressed and caused complications.
Other Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to evaluate liver function, and cholesterol or calcium levels.
Treatment Options
No Treatment (Observation): If no symptoms are present, treatment may not be required. Patients are advised to adopt a healthy diet and exercise regularly to encourage natural sludge breakdown.
Medication: For symptomatic sludge, doctors may prescribe medications to dissolve it.
Surgery: In cases where sludge causes complications, gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy) may be necessary. While surgery eliminates the gallbladder, patients may still experience recurrence of sludge in other parts of the bile duct system.
6. How to Prevent Gallbladder Sludge?
To prevent the development of gallbladder sludge, consider the following:
Healthy Diet: Avoid high-cholesterol foods, fried items, processed snacks, and sugary treats. Instead, eat more fiber-rich vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts, and seeds in your diet.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Exercise regularly to maintain a healthy weight and prevent becoming overweight or diabetic, which lowers the chance of gallbladder disease.
Routine Deworming: Regular deworming helps prevent biliary infections that could contribute to gallbladder issues.
Gallbladder sludge can be treated with medications to dissolve the sludge or through minimally invasive procedures such as laparoscopic stone removal or gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy). However, the best approach is to prevent gallbladder conditions by maintaining a healthy and balanced diet alongside an active, healthy lifestyle.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.