This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Truong Thanh Tam - Pediatrician - Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. Dr. Tam has 15 years of experience working in the field of Pediatrics.Ear bleeding is a common symptom in otolaryngology, caused by many different causes such as: skin damage, head trauma, ear infection, perforated eardrum, ear cancer or pressure changes capacity on airplanes, diving,...
1. General structure of the ear:
The ear is made up of three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The outer ear is divided into two parts: the outer cartilaginous ear canal and the inner bony ear canal. The outer cartilaginous ear canal has hairs and hair glands as well as earwax-producing glands to prevent and push out impurities. The remaining parts from the eardrum enter and play an important role in the body's mechanism of hearing and balance. Therefore, bleeding in the ear can come from any ear area and should be given proper attention to avoid unfortunate complications.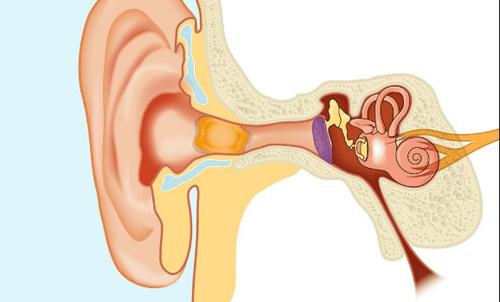
Chảy máu có thể xảy ra ở bất cứ vùng nào của tai
2. Is ear bleeding dangerous?
Bleeding from the ear that is not caused by trauma is usually not an emergency, but the causes of this condition can lead to long-term consequences such as a perforated eardrum or infection, and even hearing loss. permanent force if not treated properly. Common complications of ear bleeding include:Changes in language perception Hearing loss Tinnitus Frequent headaches Dizziness Imbalance problems.

Ù tai chóng mặt có thể là biến chứng của chảy máu tai
3. Causes of ear bleeding:
Causes that can lead to ear bleeding include:Superficial trauma to the skin: wounds, cuts or abrasions of the ear skin caused by cotton swabs, hard objects, usually only mild pain in the ear. Damaged area Foreign object in the ear: common in children when children put small objects such as candy, toys in the ear, in addition, there may be small insects crawling into the ear causing bleeding, infection Injuries Head from falls, accidents or sports Ear infections: otitis media, otitis externa Perforation of the eardrum: often causes pain, ringing in the ears, discharge and dizziness, hearing changes Barotrauma : trauma caused by rapid changes in pressure and altitude from activities such as flying or diving Ear cancer: usually the result of skin cancer outside the ear causing hearing loss, ear pain, swollen lymph nodes, facial paralysis, headache.
4. How to treat ear bleeding?
The primary treatment of ear bleeding is to stop the bleeding and address the underlying cause. Once the underlying cause is addressed, the bleeding will stop. Possible treatments include:Antibiotics: use only when there is evidence of infection because viral infections will not respond to antibiotic therapy.

Chảy máu tai do nhiễm vi trùng có thể điều trị bằng kháng sinh
Children who do not eat properly are at risk of micro-mineral deficiency causing anorexia, growth retardation, malabsorption,... If they notice the above signs, parents should supplement their children with products. The supplement contains lysine, essential micro-minerals and vitamins such as zinc, chromium, selenium, and B vitamins to help fully meet the nutritional needs of children. At the same time, these essential vitamins also support digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, help improve anorexia, and help children eat well.
Parents can learn more:
Signs of zinc deficiency in children
Micronutrient deficiency and failure to gain weight in children
Please regularly visit Vinmec.com website and update useful information to take care of your child. Take care of the baby and the whole family.