This is an automatically translated article.
With autoimmune hemolytic disease, the bone marrow does not make enough red blood cells, or these cells do not function properly. As a result, the body will not receive enough oxygen, making the person feel tired or short of breath.
1. What is autoimmune hemolytic disease?
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia, full name Acquired autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA), is a rare form of anemia. The word "Acquired" in the English name for autoimmune hemolytic disease is similar to that in Acquired ImmunoDeficiency Syndrome - AIDS. Translated as “acquired”, it means that you are not born with this disease. Another disease or other trigger will lead to this autoimmune disorder. Meanwhile, the word "Autoimmune" means that the body's immune system automatically attacks and destroys its own red blood cells.
Red blood cells are made in the bone marrow - located deep inside the bone. These blood cells normally live for about 120 days, carrying oxygen throughout the body. If you have autoimmune hemolytic anemia, your body destroys red blood cells faster than the bone marrow makes new cells. Sometimes these red blood cells only live for a few days.
Normally, the immune system detects foreign "invaders" - like bacteria and viruses, and then produces antibody proteins to attack them. When you have autoimmune hemolytic disease, your immune system makes antibodies that mistakenly attack your own red blood cells.
2. Cause

Hút thuốc lá thường xuyên là yếu tố bị bệnh tan máu tự miễn
You can develop autoimmune hemolytic anemia if you have another autoimmune disease, such as lupus. Subjects susceptible to lupus are:
90% of lupus patients are women, with high levels of hormones such as estrogen, progesterone; African-American, Asian, Hispanic, Native American; Children or siblings of lupus patients (relatively low rates); Working or living in an environment exposed to ultraviolet rays; Regular smoking, stress,... Several other diseases and drugs can also cause autoimmune hemolytic anemia, such as:
Cancer, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma Hodgkin ; Respiratory infections caused by bacteria Mycoplasma pneumonia; Medicines such as: Penicillin, methyldopa (Aldomet), quinine (Qualaquin) and sulfonamides; Viruses such as: Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, HIV and hepatitis.
3. Symptoms

đau ngực là triệu chứng thường gặp của thiếu máu tán huyết tự miễn
People with acquired autoimmune hemolytic anemia often have symptoms that include:
Chills; Fast heart beat; pale skin, which may begin to turn yellow; Short of breath; Weakness and fatigue; Chest pain; Yellow skin or whites of the eyes; Dark urine; A feeling of fullness in the abdomen due to an enlarged spleen.
4. Is autoimmune hemolytic disease dangerous?
Most hemolytic disease is insidious, gradual (chronic) with less prominent symptoms. However, severe autoimmune hemolytic anemia is still a risk factor, adversely affecting other health problems, such as heart and lung disease.
If there is an acute hemolytic situation, such as when the wrong blood group is transfused or the G6DP enzyme deficiency is consumed with large amounts of food, highly oxidizing drugs, etc. The intense hemolytic reaction can be life-threatening. core.
In general, the prognosis of patients with autoimmune hemolytic anemia is quite good. It usually only lasts for a while, but if it occurs in adolescence it can develop into a long-term health problem. Appropriate medical treatment will help reduce adverse effects.
5. Diagnosis
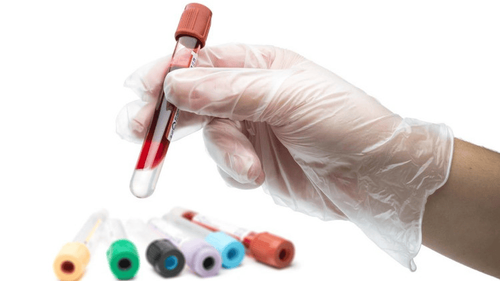
Xét nghiệm máu chuẩn đoán bệnh tan máu tự miễn
If you suspect you have signs of anemia, you should see a doctor who specializes in hematologic diseases to take a medical history, take any medications you have taken and review your symptoms.
The doctor also ordered a complete blood count (CBC) to look for signs of anemia. Specifically, the test will give results on:
Number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets; Size of red blood cells; Protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells (hemoglobin - hemoglobin); Hematocrit, also known as the volume percentage of red blood cells in the blood (hematocrit). A low red blood cell count, as well as low hemoglobin and hematocrit levels are signs of anemia.
If your CBC test results show that you are anemic, your doctor may do a few other common tests for autoimmune hemolytic anemia, including:
Reticulocyte test Measure red blood cell count immature in your body. A high reticulocyte count means that the bone marrow is producing more to replace cells that have been destroyed by the body.
Antiglobulin technique (Coombs test) Helps to detect if your body has made antibodies against red blood cells.
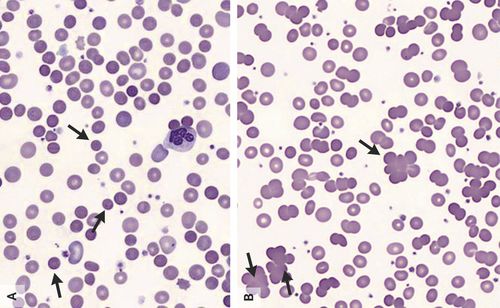
Peripheral smear The doctor will look at the red blood cells under a microscope for evidence of blood cell damage.
Chemical test Helps check the level of bilirubin - a substance that increases when blood cells are destroyed.
6. Treatment
Trường hợp bị lupus dẫn đến thiếu máu tan máu tự miễn cần phải điều trị can nguyên trước
If you have autoimmune hemolytic anemia due to another condition, such as lupus, your doctor will treat the underlying condition first. If a drug is the cause of autoimmune hemolytic disease, you will have to stop taking that drug. If the hemolytic anemia is mild, you may not need treatment.
First, doctors often prescribe steroids, such as hydrocortisone or prednisone, to stop the immune system from attacking red blood cells. Then surgery to remove the spleen and prescribe the drug rituximab. Other drugs such as azathioprine (Imuran) and cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) may also be used to suppress the immune system. In some cases, a blood transfusion is necessary.
Although autoimmune hemophilia cannot be prevented, your doctor will monitor or take certain medications to prevent the disorder. To reduce your risk, you should avoid contact with people who have the infection, wash your hands and maintain good personal hygiene, get a flu shot, and try to stay warm. Pregnant women need to have regular checkups, supplement with adequate nutrition, folic acid and iron, as well as listen to prenatal counseling to reduce the risk to the baby. In addition, do not arbitrarily take western medicine, or use traditional medicine, herbal medicine, because this is a factor that can play a role in disease formation.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.