This is an automatically translated article.
Autoimmune hemolysis is a dangerous disease with an unknown cause in about 50% of cases. In addition, the disease may also be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic lymphocytic leukemia or systemic lymphoma.
1. What is autoimmune hemolytic disease?
Autoimmune hemolysis is an anemia caused by the appearance of anti-erythrocyte antibodies that shorten the life of red blood cells.
2. How is autoimmune hemolysis diagnosed?
Autoimmune hemolytic disease causing very rapid anemia in the patient can be life-threatening. Symptoms used to diagnose autoimmune hemolysis include:
Patient complains of fatigue, may have pre-cardiac attack or congestive heart failure Anemia syndrome: Dizziness, lightheadedness, pale skin, pale mucous membranes Jaundice syndrome (jaundice): More or less jaundice, often combined with tanning, yellowing mainly in the mucous membranes, especially the mucous membranes of the eyes, mouth and tongue. Dark urine, yellow like turmeric.
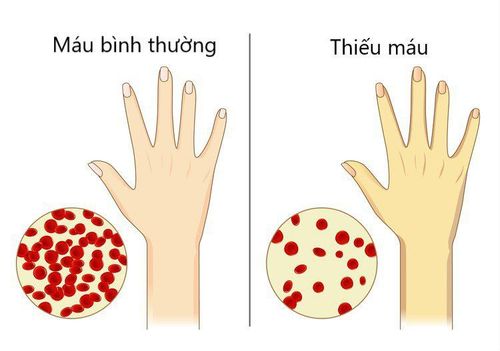
Bệnh tan máu tự miễn gây ra tình trạng thiếu máu rất nhanh
Examination may show hepatomegaly, splenomegaly If the patient has an etiology such as systemic lupus erythematosus or chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the specific features of these diseases may be seen.
3. Subclinical diagnosis of autoimmune hemolysis
In addition to the clinical examination, autoimmune hemolytic disease also needs the following laboratory tests to confirm the diagnosis:
Peripheral blood tests: Decreased red blood cell count, normal or enlarged red blood cells , the more severe the anemia, the larger the red blood cell size tends to be. Hematocrit decreased by less than 10% in severe cases. Often there are increased reticulocytes and erythrocytes on the peripheral blood smear Blood chemistry: Bilirubin is increased, mainly indirect bilirubin, LDH is increased, haptoglobin is decreased. Vigorous, reticulocytes increased, granulocyte count and platelet count were normal. Positive direct Coombs test The indirect Coombs test can be positive indicating a large number of saturated autoantibodies sites of erythrocyte binding and thus appear in serum. Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as if you want to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online. online HERE.