This is an automatically translated article.
The spleen is enlarged and swollen to many times the usual size is a manifestation of abnormal changes in the body. There are many causes for an enlarged spleen, but the direct cause is that the spleen has to work with an excessive frequency.
1. What is an enlarged spleen?
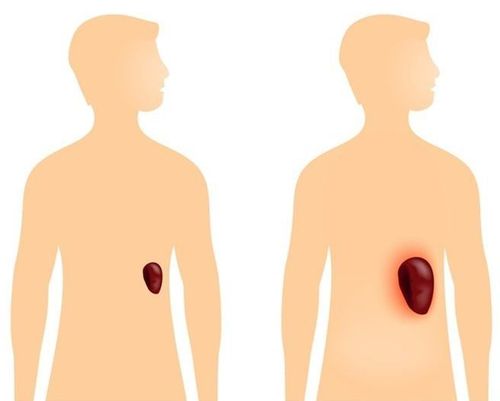
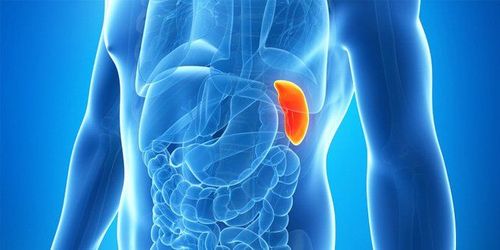
The spleen is a small organ located toward the back in the ribcage. Not only has an important role in the hematologic system, the spleen is also an immune system that produces antibodies against external agents such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites to ensure a healthy body. .
Splenomegaly is a condition where the size of the spleen is beyond normal. Normally the spleen is about the size of a fist. Enlarged and swollen spleen to many times the normal size is a sign of abnormal changes in the body.
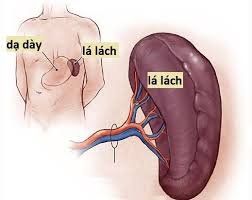
Lá lách là bộ phận nhỏ nằm hướng về sau lưng trong lồng ngực
2. Is an enlarged spleen dangerous?
An enlarged spleen can cause the following symptoms:
Pain or fullness in the upper left abdomen, Pain may spread to the left shoulder, Anemia, fatigue, Frequent infections, In addition, the patient has a spleen also experience bleeding easily. In the event that medical treatment does not improve splenomegaly, and serious complications occur, splenectomy will be considered. If the patient has a history of thalassemia, then after splenectomy can still live a normal healthy life.
However, an enlarged spleen can be considered for radiation therapy, which can help shrink the spleen and avoid surgery for the patient.
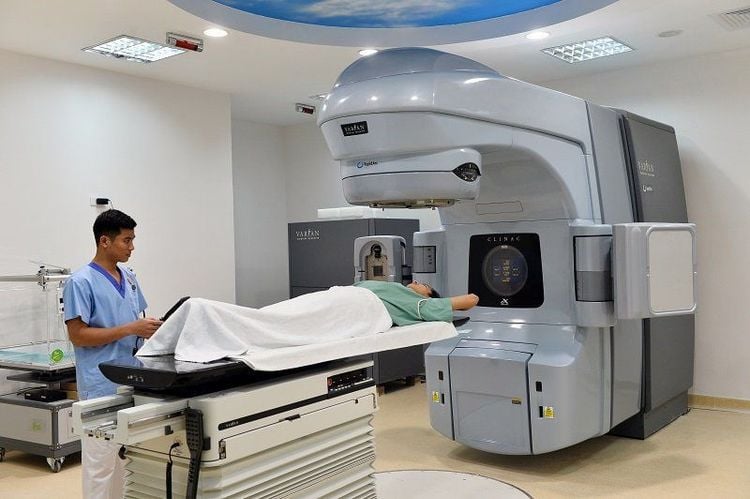
Người bệnh có thể được chỉ định xạ trị thu nhỏ lách để tránh phẫu thuật
3. Causes of Spleen Enlargement
Enlarged spleen can be caused by some of the following:
3.1 Enlarged spleen due to infection Virus, eg mononucleosis Parasite (toxoplasmosis) Some bacteria such as heart valve infection 3.2 Enlarged spleen due to cancer Leukemia Lymphoma Lymphoma (Hodgkin's) 3.3 Other Causes Autoimmune inflammatory diseases such as: Rheumatoid arthritis, sarcoidosis, or lupus Sports injuries Other but metastatic cancers spread to the spleen Cysts Large abscesses due to infection Certain infectious diseases such as Gaucher, increased glycogen storage, or increased protein accumulation.
Có nhiều nguyên nhân gây ra bệnh lách to
4. How to recognize an enlarged spleen?
Usually patients cannot detect an enlarged spleen by themselves, but must be examined through examination. Splenomegaly is detected when the patient undergoes a general examination or is suspected from the above-mentioned signs and is examined on request.
To diagnose an enlarged spleen, doctors usually order some tests such as:
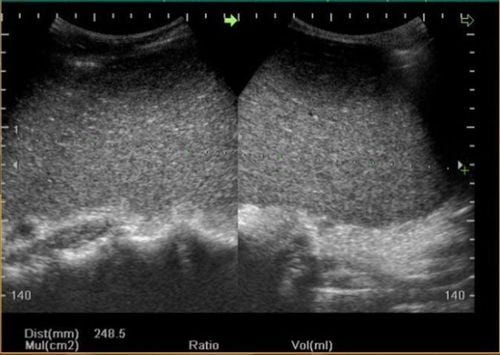
A blood count test to check the number of different types of blood cells Detecting splenomegaly through computed tomography or splenomegaly MRI ultrasound, which helps monitor blood flow through the spleen is also an option to check for an enlarged spleen Sometimes to find out the cause of an enlarged spleen, the doctor may order some other tests such as functional tests liver and bone marrow.
SEE MORE
Splenic abscess: Diagnosis and treatment Spleen Enlarged and painful after malaria, what to do? Spleen rupture: How is it treated?