This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Nguyen Van Khanh - Pathologist, Laboratory Department - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
After a breast biopsy, the specimen will be examined under a microscope by a doctor called a pathologist. The results of the pathology will be sent back to your treating doctor. The information in the pathology results will help monitor and treat you. The questions and answers below will help you understand more about the medical terms you see in your pathology results.
1. Explanation of terms
What do the following terms: glandular disease, fibroadenoma, apocrine metaplasia, cyst, columnar cell change, columnar cell hyperplasia, collagen bridge, ductal dilatation or cystic fibrosis change? All of these terms are noncancerous (benign) changes seen under the microscope by the pathologist. They are not important when biopsies show invasive breast cancer.
What is Fat Necrosis?
Fat necrosis is a benign lesion with no risk of cancer. Most are caused by trauma to the breast, although it can also occur in people without any trauma to the breast.
What is common tube hyperplasia?
Catheter hyperplasia is usually a benign lesion that has a low risk of causing cancer. There is no need for surgery or other treatment if only this lesion is present.

Một số bệnh lý tuyến vú có thể gây ra triệu chứng đau vú ở chị em phụ nữ
These features are benign (not cancerous). If these features are present on the open biopsy specimen, no further treatment is required. However, if you see them on a core biopsy, it's not that simple. If the lesion is small, completely removed on the core biopsy, or unrelated to what is seen on the mammogram, no further treatment is necessary. However, with larger or incomplete lesions on the core biopsy. , surgery is needed to remove more tissue from that area because they are sometimes found nearer more serious lesions. You should talk to your treating doctor to choose what is best for you.
What does papilloma mean?
A papilloma is a benign (non-cancerous) growth. If a papilloma is detected on an open biopsy, no further treatment is usually needed. When a papilloma is diagnosed on a core biopsy, it's not straightforward. If the papilloma is small and the mammogram features are similar to a papilloma (and there are no more serious lesions), no further treatment is needed.
However, doctors often recommend surgically removing more tissue to make sure there aren't any more serious injuries nearby. You should talk to your treating doctor to choose what is best for you.
What is a flat epithelial atypical lesion?
Atypical flat epithelial lesions are not cancerous. Sometimes, it is found near other, more serious lesions. If atypical flat epithelial lesions are seen on an open biopsy, no further treatment is usually needed.
However, if atypical flat epithelial lesions are seen on a core biopsy, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove more surrounding tissue. The best way to treat atypical flat epithelial lesions is unclear. If your biopsy shows atypical flat epithelial lesions, it is best to speak with your treating physician to discuss what further action should be taken.
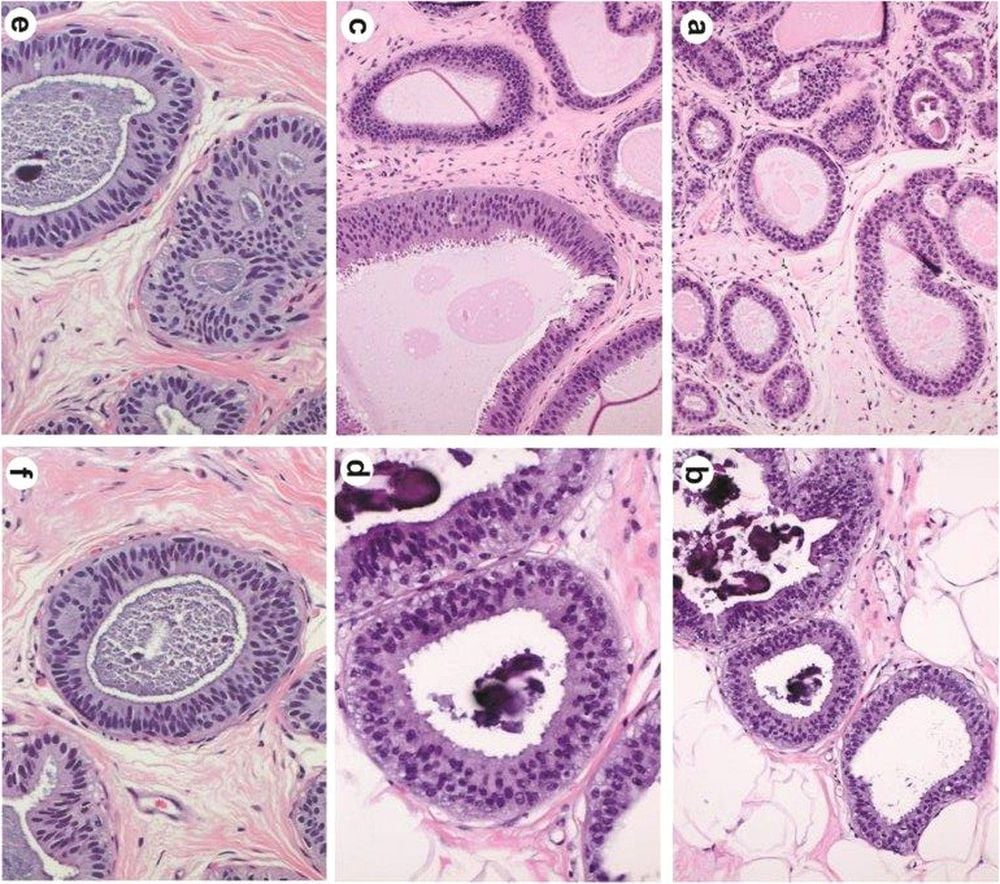
Hình ảnh tổn thương không điển hình biểu mô phẳng
What is fibroadenoma or phyllodes tumor?
Fibroadenoma is the most common benign (non-cancerous) tumor in the mammary gland. If the tumor is diagnosed on core biopsy and the mammogram features are consistent with fibroadenoma (and there are no more serious lesions), surgical removal is not necessary and may only require follow-up. without any further treatment. If the tumor is larger and/or unsightly, it may be surgically removed.
A phyllodes tumor is a very rare breast tumor that develops from cells in the stroma (connective tissue) of the mammary gland. These tumors are usually benign, but they can also recur and cause cosmetic loss of the breast if surgery does not remove the tumor. Sometimes they can be malignant (cancerous). Malignant phyllodes tumors can invade beyond the mammary gland. If a phyllodes tumor is diagnosed on a core biopsy, surgery is required to remove the entire tumor.
In some cases it is difficult to distinguish between a fibroadenoma (benign) or a phyllodes tumor on core biopsies. In those cases, the pathologist calls it a cell-rich fibroepithelial lesion or a benign fibroepithelial neoplasia. Because it could be a phylloderm, it is the type of tumor that requires total surgical removal (usually one of the breast-conserving surgery methods, eg lumpectomy).
What is calcification or microcalcification?
Microcalcification or calcification is mineral deposition that can be present in both noncancerous and cancerous mammary gland lesions. They can be seen either on a mammogram or under a microscope. Since some calcifications are seen in areas containing cancer, their presence on mammograms is an indicator for biopsies of this area. The pathologist then looks at the tissue sample removed and makes sure it contains calcifications. If there is calcification, the doctor understands that the biopsy sample was taken in the correct area of the lesion (that is, the abnormal areas containing calcification on the mammogram).
Microcalcifications and calcifications are important only because they are sometimes found in areas where cancer is present. When they are found alone (without disturbing changes in the tubules or lobules), they are not important.
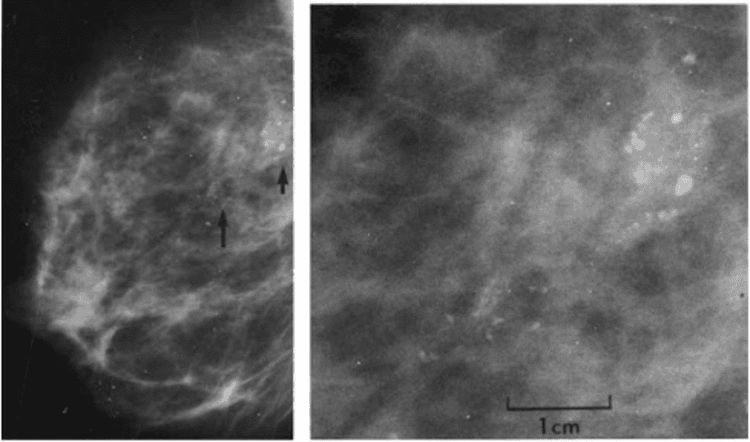
Hình ảnh các vôi hóa to, lành tính với trung tâm sáng (mũi tên ngắn)
What are the special tests like Cytokeratin, CK5/6, p63, SMA?
These are special tests that a pathologist uses to help diagnose invasive breast cancer or identify metastatic cancer in the lymph nodes. Not all cases require these tests. Whether or not your pathology results refer to these tests has no bearing on diagnostic accuracy.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Reference article: American Cancer Society