This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Specialist Doctor II Phan Thi Minh Huong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Congenital gastrointestinal vascular lesions can cause acute or chronic gastrointestinal bleeding. These lesions are responsible for 7% of upper GI bleeding cases.
1. Some common gastrointestinal vascular lesions
1.1. Gastric antral vasodilatation disease
Gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE) is also known as Watermelon gastric disease. The characteristic image of the disease is the large varicose veins running along the stomach, creating a striped appearance similar to the image of a watermelon rind. This is a rare but important cause of severe gastrointestinal bleeding that is difficult to control. Gastric antral vasodilatation accounts for 4% of cases of upper gastrointestinal bleeding due to esophageal varices. The disease occurs mainly in elderly women and the cause is unknown.1.2. Hereditary hemorrhagic vasodilatation syndrome
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, also known as Rendu-Osler-WEber syndrome, is an autosomal dominant inherited disorder that causes damage to blood vessels in many different parts of the body. It has gastrointestinal blood vessels.The most common sign of the disease is dilated capillaries in the nose and causes repeated nosebleeds. Nosebleeds can happen as often as daily or several times per month. Signs of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia usually occur only during puberty or adulthood.
Along with nosebleeds, other signs of the disease are small red-purple lesions that appear on the face, lips, oral mucosa, fingertips, and gastrointestinal tract. The disease causes the risk of frequent gastrointestinal bleeding, anemia, increased risk of stroke, ...
1.3. Dieulafoy injury
Dieulafoy's lesion is a dilated, unstable submucosal artery that can erode the GI mucosa and cause severe bleeding. Dieulafoy's lesions were 10 times larger than the normal size of mucosal capillaries in similar locations. Dieulafoy lesions cause about 1.5% of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding and 3.5% of jejunal bleeding. 70% of Dieulafoy's lesions occur in the stomach, other common sites are the duodenum (15%), esophagus (8%).Gastrointestinal bleeding due to Dieulafoy lesions is more common in men than in women. Most common in the elderly, people with cardiovascular diseases, kidney failure, diabetes, using anticoagulants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs),...
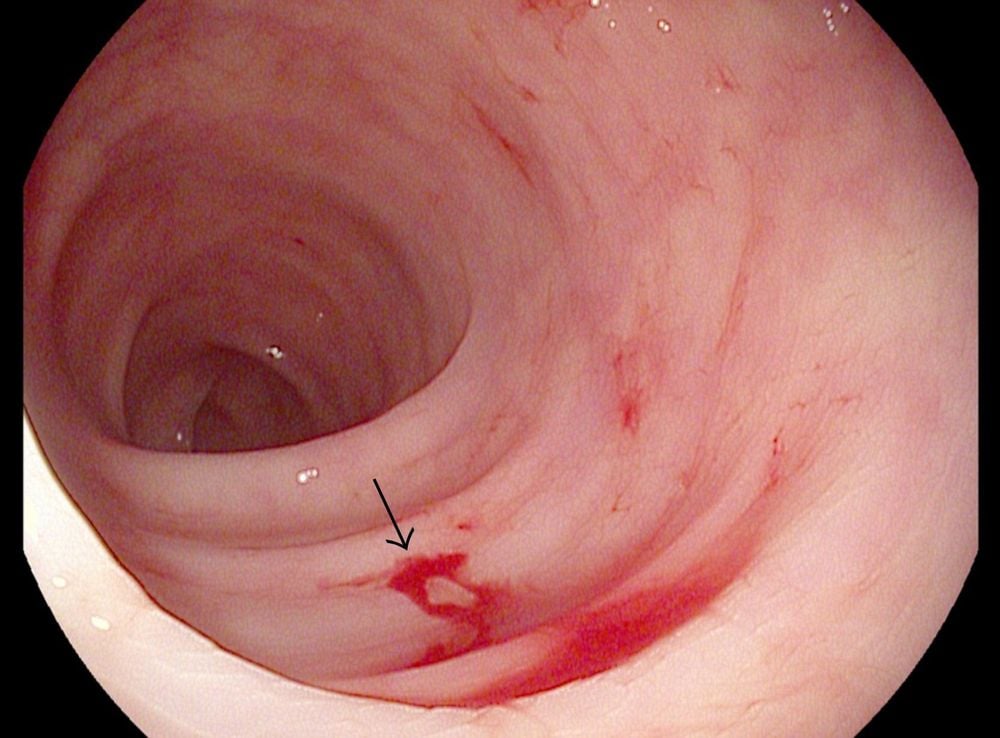
Xuất huyết tiêu hóa do thương tổn Dieulafoy
1.4. Arteriovenous malformation and benign hemangioma
Arteriovenous malformation is a congenital disease of blood vessels in which arteries and veins communicate directly without passing through the capillary system. Arteriovenous malformations can occur in the gastrointestinal tract causing gastrointestinal bleeding but are rare.Hemangioma is a congenital benign tumor, caused by abnormal growth of blood vessels. Hemangiomas usually appear as a red lump on the skin, but can appear on any part of the body, including blood vessels in the gastrointestinal tract.
1.5. Gastrointestinal varicose veins
Varicose veins often appear in the distal esophageal and gastric aneurysms due to portal hypertension. Varicose veins are the result of a number of diseases, mainly cirrhosis of the liver. Varicose veins usually appear suddenly, in large numbers in the upper gastrointestinal tract.2. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal vascular injury
To diagnose gastrointestinal vascular lesions causing gastrointestinal bleeding, the doctor will rely on clinical signs such as vomiting blood, black stools, signs of acute blood loss,... Usually done through endoscopy. If routine endoscopy is not diagnostic, depending on the specific clinical situation, the doctor will prescribe techniques such as single-balloon small bowel endoscopy, capsule endoscopy, intraoperative endoscopy, imaging Visceral vasculature, red blood cell scintigraphy,...Treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding due to vascular damage, can use one or a combination of endoscopic hemostasis procedures such as endoscopic clipping, laser, plasma argon,... If endoscopic hemostasis procedures are unsuccessful, the doctor may switch to surgical options to stop bleeding.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.