This is an automatically translated article.
Research into the genome sequence changes and genetic characteristics of seasonal influenza viruses play an important role in public health. As a result, it is possible to determine if vaccines and antiviral drugs are still effective against circulating influenza viruses, and to understand the risk of influenza viruses in animals infecting people.
1. Genome sequence of seasonal influenza virus
Seasonal influenza viruses are constantly changing, in fact all influenza viruses undergo genetic changes over time. An influenza virus genome consists of many genes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) tracks the genome changes of influenza viruses that circulate year-round. This work is done as part of routine influenza surveillance.
The sequence of nucleotides in a gene is the same as the letters of the alphabet. Nucleotides are organic molecules that form the structural units of nucleic acids, such as RNA or DNA. All seasonal influenza viruses consist of single-stranded RNA, instead of the usual double-stranded DNA. Influenza virus RNA genes are made up of nucleotide-linked sequences and encoded with the letters A, C, G, and U - corresponding to adenine, cytosine, guanine and uracil. The full genome sequence of the virus may include about 13,500 characters. Comparing the composition of nucleotides in a gene with the order of nucleotides can reveal variations between two different viruses.
Genetic variants are important because they can affect the surface protein structure of the influenza virus. Proteins are made up of chains of amino acids. Replacing one amino acid with another can affect the properties of the virus, such as the ability of the virus to transmit between people, or the susceptibility of the virus to drugs and vaccines. present.

Virus cúm mùa đều trải qua những thay đổi di truyền theo thời gian
Influenza A viruses and influenza B viruses that mainly infect humans are RNA viruses with eight gene segments. These genes contain "instructions" for making new viruses. Specifically, when the influenza virus infects the human body, they will "trick" the cells to produce more flu viruses, thereby multiplying and spreading.
Each year, CDC studies the entire genome sequence of approximately 7,000 influenza viruses from collected clinical samples. An influenza A virus or influenza B virus genome contains eight gene segments that encode, determine the structure and function of 12 viral proteins. Two major surface proteins, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA), determine important properties of the influenza virus. These include how viruses respond to certain antiviral drugs, comparing genetically similar viruses to current influenza viruses, and the ability of zoonotic influenza viruses to infect human hosts.
2. Genetic characteristics of seasonal influenza virus
CDC and other public health laboratories around the world have sequenced the genes of seasonal influenza viruses since the 1980s. The results of gene sequencing studies allow comparisons of the genes of current influenza viruses. circulating with the genes of the old influenza virus and the virus used to make the vaccine. This comparison process, known as genomics, is used to:
Determine the degree of association between influenza viruses with similar genomes Monitor the evolution of seasonal influenza viruses Identify changes Genetic changes affect viral properties. For example, does the flu virus spread more easily, cause more severe illness, or develop drug resistance Assess the effectiveness of the flu vaccine based on the genetic similarity of the viruses Track change genetics of influenza viruses circulating in animal populations can infect humans. The differences between a group of seasonal influenza viruses are shown in a family tree, showing how closely the individual viruses are related. Viruses are grouped together based on nucleotide homology in their genes. Influenza virus genealogies often show similarity of the viral genes hemagglutinin (HA) or neuraminidase (NA). Each specific influenza virus has its own branch on the tree. The degree of genetic difference (number of nucleotide differences) between viruses is expressed as the length of the horizontal lines (branches) in the phylogenetic tree. The more distant the viruses are from each other, the more genetically distinct they are.
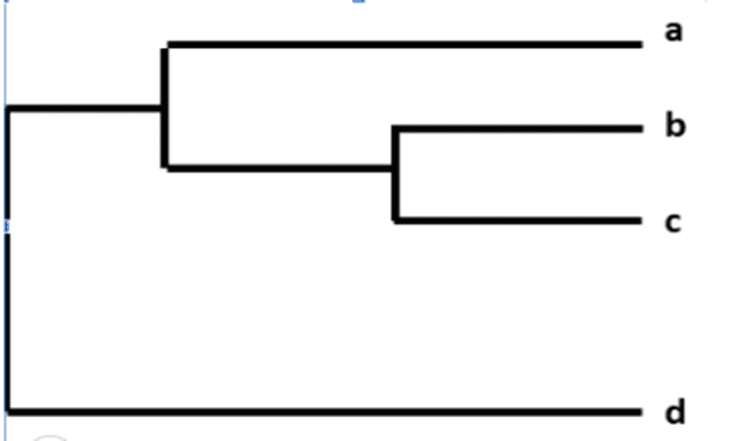
Cây phả hệ
For example, after CDC sequences the influenza A (H3N2) virus, it will be classified with other viral sequences with similar HA (H3) and NA (N2) genes. Next, the CDC compares sequences between the viruses and looks for differences. The family tree was then used to visually represent the genetic differences of influenza A (H3N2) viruses.
Comparative work on the genetics of influenza viruses is done year-round. This genetic data, combined with virus antigenic characterization data, helps determine which vaccine should be selected for the upcoming Northern or Southern Hemisphere flu season. Prior to the WHO vaccine consultation meeting in February and September, CDC collected seasonal influenza viruses to compare HA and NA gene sequences with circulating influenza strains. This helps assess the relationship between circulating influenza viruses and the viruses that the seasonal flu vaccine is resistant to.
For example, sometimes during a season, circulating viruses will change genetically, making them different from the virus used to make vaccines. This is an indication that a different vaccine is needed to prevent flu for the next season.
Besides, factors such as antigenic properties also greatly influence the vaccine decision. The HA and NA surface proteins of seasonal influenza viruses are antigens, recognized by the human immune system. After they enter the body, an immune response is activated, the body produces antibodies that block the infection. The process of analyzing the virus's response to antibodies, which help assess the relevance of a virus, is called antigenic characterization.
Các đặc điểm di truyền của virus cúm mùa có ảnh hưởng lớn đến quyết định vắc-xin
3. Influenza Genome Sequencing Method
A sample containing many influenza virus particles cultured in a test tube often has small genetic differences compared with the entire virus population of the same strain.
Previously, scientists used a genome sequencing technique called the Sanger Reaction, to track the evolution of influenza. The Sanger reaction identifies the dominant genetic sequence in a strain of multiple seasonal influenza viruses. As such, small variations in the overall viral population sample are not reflected in the final results. This method only partially sequenced the influenza virus genome, rather than the entire genome sequence.
Over the past five years, CDC has used Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) methodologies, to expand the amount of information and granularity that sequence analysis gathers. This method uses advanced molecular (AMD) to determine the genetic sequence of each virus in a sample. Thus, it is possible to reveal genetic variations between the various seasonal influenza virus particles in the sample and the entire coding region of the genome. Such a level of detail would directly benefit public health, but data must be carefully interpreted by highly trained experts, combined with real-world context. In summary, annual influenza gene mapping using NGS and AMD will improve the effectiveness of seasonal influenza vaccines.

Phương pháp giải trình tự bộ gen cúm giúp cải thiện hiệu quả vắc-xin cúm mùa
Based on the recommendations of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (U.S. CDC), Vinmec International General Hospital has implemented influenza vaccination in the entire hospital system across the country. for all customers 6 months and older.
Customers who choose to get vaccinated at Vinmec will be completely assured of the quality of the vaccine as well as the implementation process, because:
Children will be examined and screened by pediatricians - vaccines. Full screening of health and fitness problems, advice on preventive vaccines and injection regimens, how to monitor and care for children after vaccination before ordering vaccination according to the latest recommendations of the Ministry of Health & World Health Organization to ensure the best effectiveness and safety for children. A team of experienced and professional pediatric doctors and nurses, understand children's psychology and apply effective pain relief methods for children during the vaccination process. 100% of vaccinated children were monitored for 30 minutes after vaccination and reassessed before leaving. Underwent general supervision before, during and after vaccination at Vinmec Health System and always have an emergency team ready to coordinate with the vaccination department to handle cases of anaphylaxis, respiratory failure - circulatory arrest, ensuring Ensure timely and correct handling when incidents occur. The vaccination room is airy, with a play area, helping children feel comfortable as if they are walking and have a good mentality before and after vaccination. Vaccines are imported and stored in a modern cold storage system, with a cold chain that meets GSP standards, keeping vaccines in the best conditions to ensure quality. Parents will receive a reminder message before the vaccination date and their child's vaccination information will be synchronized with the national immunization information system. Vinmec International General Hospital is currently providing a Package Immunization Program with a variety of vaccines for different audiences, from infants, young children, adults, and women before and during pregnancy pregnant.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the nationwide health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: cdc.gov