This is an automatically translated article.
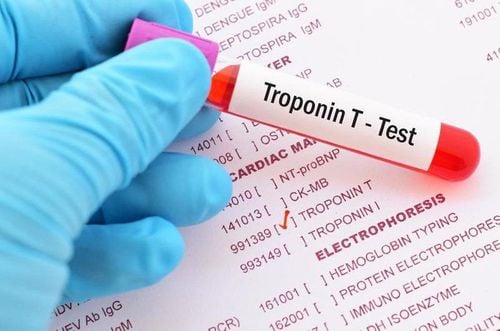
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Nguyen Van Duong - Interventional Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Elevated serum troponin has been observed in patients admitted to the hospital with chest pain. Often it can be caused by acute myocardial infarction with myocardial necrosis. However, there are also cases of increased troponin not due to myocardial infarction.
1. Overview of acute coronary syndromes and myocardial infarction
Coronary artery disease is one of the main causes of death globally today. In particular, acute coronary syndrome is a condition in which atherosclerotic plaques in the artery lumen are dislodged, forming blood clots, reducing blood flow to the heart or causing arterial blockage, threatening the patient's life. Acute coronary syndrome can occur in two forms as unstable angina and acute myocardial infarction.When the heart muscle is damaged, the body releases troponin - a substance involved in the regulation of heart muscle contraction into the blood. This substance rises slowly in the blood after 4-6 hours and stays high for several days. Therefore, the troponin test is considered an early diagnostic method of cardiac damage along with other cardiac markers.
However, when chest pain occurs, it is difficult to make a diagnosis based on the results of elevated serum troponin because the typical symptoms of myocardial infarction must be combined with other tests such as electrocardiogram. thing.

2. Elevated serum troponin associated with acute coronary syndrome
The troponin test is usually indicated for patients with suspected acute coronary syndromes, that is, when unstable angina occurs, the patient undergoes an electrocardiogram and a myocardial infarction is detected. ECG with or without ST segment elevation.Currently, the high-sensitivity 2 troponin hsTnT and hsTnI tests have helped doctors diagnose and detect acute coronary syndromes early and provide prognosis. However, further differential diagnosis of causes of elevated serum troponin beyond acute coronary syndromes and noncardiac syndromes should be continued.
3. Elevated serum troponin associated with cardiovascular disease, in addition to acute coronary syndrome
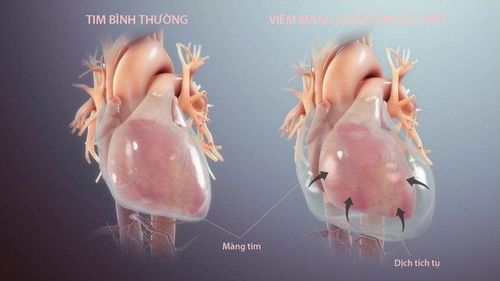
Elevated serum troponin in addition to acute coronary syndrome can be caused by the following:Heart failure: The patient does not present with typical chest pain, only shortness of breath. Test results showed a moderate increase in troponin levels. Until now, the mechanism of increased troponin due to heart failure is not clear. Some studies have suggested that it may be due to damaged heart muscle cells that degrade the proteins. Besides, there are many factors involved in the process of promoting myocardial cell death such as hormones, nerves, cytokines, ... thereby releasing and increasing serum troponin. Pulmonary embolism due to thrombosis: Patients with pulmonary embolism due to thrombosis who present with hypotension and shock will face a high risk of death. When shortness of breath or acute chest pain occurs, the patient is hospitalized and a troponin test is indicated. The mechanism of elevation of serum troponin in patients with pulmonary embolism is thought to be a sudden increase in pulmonary vascular resistance causing right ventricular distension. Ultrasound showing dysfunction of right ventricular function is the basis for predicting mortality in patients. Aortic dissection: Increased serum troponin (troponin I) occurs in patients with type A acute aortic dissection.
4. Increased troponin not related to cardiovascular
Increased cardiac troponin not due to myocardial infarction can be caused by the following:Shock, hypotension: Hypotension reduces perfusion pressure in the myocardium. Renal disease (advanced or end-stage): In patients with advanced or end-stage renal disease may present with diffuse cardiovascular obstruction, left ventricular hypertrophy. Stroke, cerebral hemorrhage: Increased serum troponin has been observed in patients with stroke or cerebral hemorrhage due to an imbalance in the autonomic nervous system. After a stroke, patients may experience complications of myocardial or coronary injury. Exercise: After exercise or strenuous exercise, the body releases troponin into the heart muscle cells. Drug use: Certain sympathomimetic drugs such as acetaminophen, antidepressants, benzodiazepines, opioids, sympathomimetic may increase serum troponin (troponin I).

Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment and prevention of diseases. When performing the examination process at Vinmec, customers will be welcomed and used modern facilities and machinery along with perfect medical services under the guidance and advice of doctors. Good doctors, well-trained both at home and abroad.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline for support.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.