This is an automatically translated article.
Venous thromboembolism is one of the familiar problems that often occur especially in special locations. Thromboembolic disease has a high risk of death once complications appear.1. What is hypercoagulability?
Hypercoagulable disease is the occurrence of blood clots as a result of some genetic defect or the patient has a certain disease. Hypercoagulability arises due to 3 main mechanisms:
Increase in blood levels of thromboplastin, thrombin factors; Reducing the activity of natural anticoagulants (heparin, antithrombin...), Inhibiting the fibrinolytic system.
Tăng đông máu có thể phát sinh do ức chế hệ tiêu fibrin.
2. What is the cause of increased blood clotting?
2.1 Being sick
Cancer. Inflammatory disorders: Ulcerative colitis. Myeloma proliferative disorders. After surgery. Estrogen, pregnancy. Lupus anticoagulant factor. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Anti-cardiolipin antibodies.
2.2 Congenital
Deficiency of antithrombin III. Factor VIII Leyden. Protein C deficiency. Protein S deficiency. Dysfibrinogenemia. Plasminogen abnormality.
Bệnh nhân ung thư có thể mắc tăng đông máu
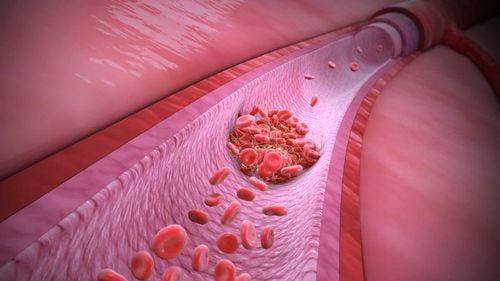
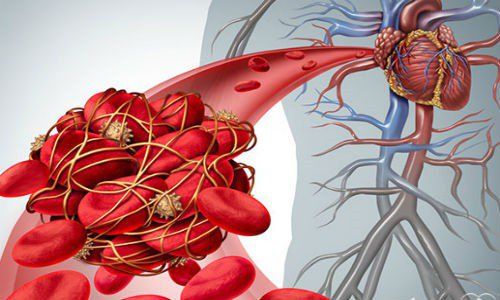
3. What is Thromboembolism?
Venous thrombosis is a condition in which a blood clot forms in a vein. Blocking blood flow (embolism) to the heart causes local symptoms and can cause many dangerous complications when the clot moves to other places. Patients can die if not diagnosed and treated promptly.4. Who is prone to thromboembolism?
The elderly, the elderly. The patient must lie motionless for a long time, especially after surgery or trauma. Pregnant women, after giving birth. Prolonged use of oral contraceptives. Malignant, autoimmune diseases. Smoke. Heart failure .

Bệnh nhân suy tim dễ bị huyết khối tắc mạch
5. How to prevent thromboembolic disease?
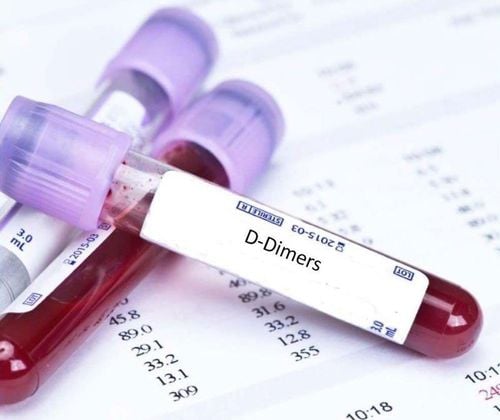
Positive lifestyle changes: Limit drinking alcohol, alcohol, stimulants, don't smoke. Control weight, exercise regularly to improve health. Avoid lying or sitting motionless for a long time, especially for elderly subjects. Light and moderate exercise after surgery under the guidance of the doctor. Diagnosis of venous thromboembolism depends on the patient's symptoms, location, and history of thrombosis. Your doctor will assign a risk group and order the necessary tests to evaluate the status of the blood clot. The most commonly used tools and tests are D-dimer in the blood, vascular ultrasound, and helical computed tomography (also known as CT scan).

Hạn chế rượu bia phòng ngừa bệnh huyết khối tắc mạch
6. How to treat venous thrombosis?
To treat hypercoagulability can be used with support and different drugs including: Anticoagulants, thrombolytics, endovascular interventions may be considered depending on the severity of the disease and the patient's condition. drug response status.Hypercoagulability in patients with thromboembolism is not a strange disease. It is necessary to prevent the disease, to avoid the "stagnation" of blood, especially in the lower extremities, causing thromboembolism. Making positive lifestyle changes is the most effective way to prevent disease.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as if you need to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website for the best service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.