This is an automatically translated article.
Currently, Vietnam is a country with the highest rate of people using antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in the world, due to ignorance and abuse in daily life. Therefore, adults, especially parents, need to be equipped with more knowledge about the principles of antibiotic use for themselves and children in the family.
1. What are antibiotics?
Antibiotics are two types, which can be synthetic or semi-synthetic substances or secreted by microorganisms at very low concentrations, so they have the ability to specific, inhibit the growth or kill bacteria without cause serious toxicity to the human body. There are many different groups of antibiotics, which have specific effects on each type of bacteria, such as some antibiotics are able to kill bacteria, while some can only prevent the growth of bacteria. growth of a single bacterium. Antibiotics can be divided into 9 groups as follows:
Beta-lactam Aminoglycoside Macrolide Lincosamide Tetracycline Phenicol Peptid Quinolone Other antibiotic groups: Sulfonamide, Oxazolidinone, 5-nitro imidazole
2. Principles of using antibiotics for children
General principles when using antibiotics for children include:
Use only when there is an infection Use the right dose, at the right time according to the specific regimen Only combine antibiotics when absolutely necessary Choose the right antibiotic criteria: high efficacy, few complications and reasonable price Application of pharmacokinetics in drug use Choosing a reasonable route of antibiotic administration: oral, intramuscular, intravenous
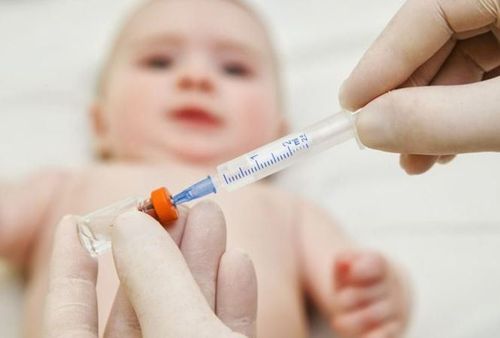
Bác sĩ sẽ lựa chọn đường dùng kháng sinh hợp lý với tình trạng bệnh lý của trẻ
Dosage will be based on body weight in mg/kg, age or body surface area Estimated dose for children = surface area body (m2) x adult dose/1.8 In all cases should avoid intramuscular injection for children When using long-term drugs should use sugar-free drugs. With liquid drugs with a volume of less than 5ml, it is necessary to pump and divide the liquid Keep medicine out of reach of children Do not put medicine in baby's bottle Arrange medication times for children to avoid periods of sleep, study or playtime,...
3. Which antibiotic is good for children?
The antibiotics on the market today are mainly broad-spectrum antibiotics, that is, can treat bacterial infections in many different sites. However, there are still priority options for each antibiotic in each common pediatric disease such as:
Upper respiratory tract infections: upper respiratory tract bacteria are mainly gram-positive bacteria, so antibiotics The first choice is usually a new generation cephalosporin. However, gram-positive bacteria causing upper respiratory infections are still sensitive to amoxicillin and 1st and 2nd generation cephalosporins. Lower respiratory tract infections: can use amoxicillin or amoxicillin, clavulanic, cefdinir, cefpodoxime, cefixime is not recommended. . For children over 5 years old with pneumonia or under 5 years old but after 2 days of slow response to the drug, azithromycin can be added. Gastrointestinal infections: antibiotics are indicated when the child has bloody stools, diarrhea that is suspected of cholera. The antibiotics that can be used include: ciprofloxacin, trimethoprim, cefixime, azithromycin, metronidazole, ... Soft tissue skin infections: the causative agent is usually Staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus should choose one of the following antibiotics: amoxicillin - Clavulanic, cefdinir, erythromycin, topical fucidin can be applied. Urinary tract infections: biseptol, ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin-clavulanic, cefuroxime or cefpodoxime, cefixime can be used.

Hiện nay trên thị trường có rất nhiều loại kháng sinh khác nhau dành cho trẻ em
4. Some antibiotics are contraindicated in children
Some groups of antibiotics can cause harm when used for children, including:
Aminoglycoside group: can cause nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity leading to deafness in infants Phenicol group: May cause bone marrow suppression, optic neuritis and “Blue-gray syndrome” in infants and children under 6 months Lincosamide group: can cause pseudomembranous colitis in children under 2 years Tetracycline group : used for children under 8 years old can cause permanent tooth discoloration, enamel dysplasia, bone growth inhibition Quinolone group: use for children under 16 years old can affect the development of synaptic cartilage leading to Children with dwarfism Sulfamid group: can cause nausea, diarrhea, disorders of the hematopoietic system, allergies, risk of stones, hematuria for infants Basically, before using antibiotics for children Parents need to carefully read the medicine before taking it and it is important to consult the doctor and pharmacist. Self-medication can have many health risks.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, the above antibiotics are fully supplied, quality assurance, response to infection treatment. In addition, the hospital has also implemented an antibiotic use management program since 2017, with the close cooperation of doctors and clinical pharmacists to make a reasonable antibiotic choice, ensuring treatment effectiveness. , minimize drug side effects and limit the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.