This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by resident Doctor Nguyen Quynh Giang - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. Dr. Giang has many years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging, especially in the field of multi-segment computed tomography, magnetic resonance.Esophageal cancer is common in elderly patients, who use a lot of alcohol, beer, and tobacco. To diagnose esophageal cancer, doctors can use many techniques such as pet imaging for esophageal cancer, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, biopsy,...
1. An overview of esophageal cancer
The esophagus is part of the upper digestive system, connecting the throat and stomach, and helps carry food and liquids from the throat to the stomach. In an adult, the esophagus is about 25cm long. Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells grow in the esophagus. There are 2 main types of esophageal cancer:Squamous cell carcinoma: Cancer that develops in the thin, flat cells (squamous) that form the inner lining of the esophagus. Squamous cell carcinoma usually starts in the upper and middle parts of the esophagus. Adenocarcinoma: A cancer that develops in the glandular cells in the lining of the esophagus. In the early stages of esophageal cancer, people may have no symptoms. In more advanced stages of esophageal cancer, symptoms may include:
Difficulty swallowing, pain when swallowing Frequent coughing and regurgitation, possible vomiting blood Hoarseness, chest pain Eating indigestion, often frequent heartburn, thin people, weight loss, fatigue stools with mucus or blood in the stool Esophageal cancer is often detected when the disease is at an advanced stage. The disease usually occurs in people over 50 years old, the rate of men is twice as high as that of women. In addition to gender and age, another risk factor for esophageal cancer is smoking, regular alcohol consumption, and having gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).

2. Imaging techniques used in the diagnosis of esophageal cancer
To diagnose esophageal cancer, your doctor will ask about your medical history, clinical symptoms, and risk factors. The doctor will also do a general health check to assess the overall health of the patient. To determine whether or not esophageal cancer has spread and has spread, the doctor may order one or more of the following imaging techniques:2.1. Chest X-ray X-ray- Chest radiograph is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses a very small amount of radiation to create images of the inside of the chest. X-ray images help the doctor see abnormalities in the shape of the esophagus, if any.
2.2. Computed tomography of the chest Computerized tomography (CT)-chest: is a technique that uses many X-rays to scan the chest in a cross-section, along with computer processing technology to create images 2- 3D. Compared to a conventional chest X-ray, a computed tomography scan gives more detailed information.
2.3. Contrast upper gastrointestinal tract The patient will be given oral contrast before the X-ray, which can be a barium solution or a water-soluble contrast agent. The esophagus, stomach, and duodenum will be visualized on X-ray with contrast medium.
2.3. Esophageal endoscopy Your doctor will insert an endoscope (a thin tube with a light and lens) into your esophagus to get a direct view of the inside of your esophagus. The endoscope can be inserted through the mouth or nose and down the throat into the esophagus. Some esophagoscopes can be equipped with instruments to biopsy samples from the damaged esophagus. This specimen is taken out for anatomical examination to determine whether it is cancerous or not.
2.4. Esophageal cancer pet ct scan Esophageal cancer pet ct scan (also known as Positron tomography) is a technique that uses a special camera and a tracer (radioactive substance) to look at the muscles organs in the body. The tracer, when injected into the body, emits small positively charged particles (positrons). The camera records the positrons and turns the recordings into computerized images. Positron emission tomography images when combined with CT scan to get more detailed information about the location of the tracer. By identifying changes in the body at the cellular level, esophageal cancer can detect early onset of the disease before it becomes apparent on other imaging techniques. Esophageal PET scans also help determine if the cancer has spread, evaluate the effectiveness of a treatment plan, and determine if the cancer will return after treatment.
After performing the above imaging techniques, if it is not certain that the abnormality in the esophagus is benign, the doctor will order an esophageal biopsy. A biopsy is the removal of tissue samples from the affected area, followed by histopathological examination to determine the presence, extent, or stage of esophageal cancer. Depending on the specific injury condition in the patient, the doctor will choose the appropriate form of biopsy. Biopsy can be performed concurrently during esophagoscopy.
If after performing imaging techniques, the doctor excludes the possibility that the patient has esophageal cancer, no further diagnostic steps are needed. Patients will be focused on treating diseases that cause damage to the esophagus detected by the doctor. Patients need periodic follow-up visits so that the doctor can monitor the response to treatment and the level of recovery of the esophagus.
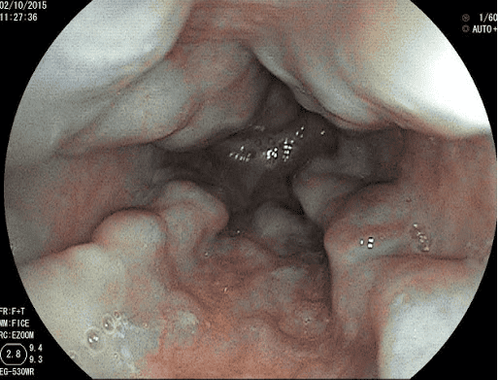
When screening for gastrointestinal cancer at Vinmec, you will receive:
Gastrointestinal specialty examination with an oncologist (by appointment). Gastroscopy and colonoscopy with an NBI endoscope with anesthesia. Peripheral blood count (laser counter). Automated prothrombin time test. Automated thrombin time test. Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT) test using an automated machine. General abdominal ultrasound.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: radiologyinfo.org
SEE MORE
10 ENT diseases related to gastroesophageal reflux How long should I fast before gastroscopy? Danger from gastroesophageal reflux