This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thanh Nam - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.The most common way to diagnose gout is to test the joint fluid for urate crystals. However, this method does not always detect the disease. Computed tomography (CT) scan is an advanced method to detect gout in 1⁄3 of the cases where the joint fluid test is negative for the disease.
1. Causes of Gout
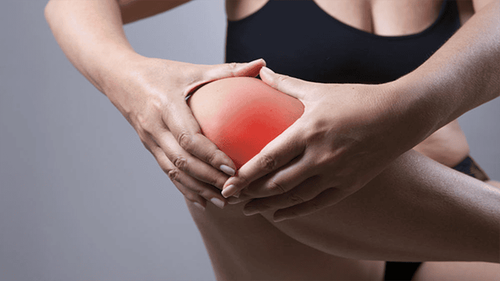
Gout is an inflammatory disease where monosodium urate (MSU) crystals accumulate in a joint, causing it to become red, hot, painful, and swollen within a few hours. The underlying cause is high levels of uric acid in the blood, which causes the deposition and formation of sharp, needle-like crystals in areas with slow blood flow such as joints, synovial membranes, and cartilage. bones, subcutaneous tissues, tendons, renal parenchyma, renal calyces and tubules...Over time, repeated attacks of gout can cause destruction of the tissues of the joints including Includes joints, cartilage, and bones.
Mechanism of uric acid production
Organic purines and pyrimidines are nitrogen-containing heterocyclic organic molecules that are very common in nature, which are the main constituents of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. When the cells and the nucleic acid chains within these cells are degraded, the purines are converted to uric acids that can be filtered out of the blood and excreted in the urine. But uric acid is only soluble to a limited extent in body fluids.
Hyperuricemia occurs when uric acid levels exceed the threshold of 6.8mg/dL. At a pH of 7.4, uric acid becomes the urate ion that binds with sodium to form monosodium urate crystals.
These crystals form due to consumption of purines such as when eating a lot of purine-rich foods like shrimp, crab, fish, red meat, animal organs or drinking a lot of drinks like syrup, corn sugar (corn). ..
Trắc nghiệm: Kiểm tra hiểu biết của bạn về bệnh gút
Bệnh gút là một dạng viêm khớp phổ biến, xảy ra chủ yếu do tình trạng tích tụ các axit uric trong cơ thể. Trả lời 15 câu hỏi trắc nghiệm sau sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về bệnh gút.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
Hyperuricemia can also occur as a result of chemotherapy or radiation therapy. These therapies cause cell death at a higher rate and at a faster rate than usual.
In addition, some people have a genetic predisposition to produce too much uric acid, and others have chronic kidney disease that makes it difficult to excrete uric acid.
Thiazide diuretics and aspirin can also increase uric acid levels and thus increase the risk of gout.
2. Signs of Gout
Gout usually first affects the joints of the foot or the innermost joint of the big toe. This condition is called an acute gout attack. It usually takes 20-30 years from the time of hyperuricemia to the first attack, and it is found that 10-40% of people with gout have renal colic even before they have arthritis.Often, when having an acute gout attack, the patient will wake up from sleep and feel like the big toe is on fire. The pain is most severe in the early hours, then subsides over time, but discomfort and joint swelling persist for days or weeks.
Gout can also affect other joints such as ankles, knees, wrists and elbows.
Gout is common in people with a high standard of living, the rate in some European countries is about 0.5% of the population, the rate of men is 10 times higher than that of women.
3. Diagnosis of Gout
To diagnose gout, doctors usually ask patients to examine one or more of the following: examination of joint fluid, blood tests, X-rays, and ultrasound.3.1. Blood test The cause of gout is the deposition of urate salt crystals in the joints due to high uric acid levels in the body. Blood test helps to evaluate uric acid index in the blood, if it exceeds the allowable threshold: 420 μmol/l for men or 380 μmol/l for women, it is considered high blood uric acid concentration. However, just raising uric acid in the blood is not enough to conclude gout, but this is also a factor that should be paid attention to in the diagnosis of the disease.
3.2. Checking joint fluid Aspiration of fluid from a painful joint to check for urate crystals will help confirm gout. However, this method is rarely used in clinical practice due to its invasiveness and low sensitivity.
3.3. X-ray At an early stage, joint damage is concentrated only in the joint capsule, cartilage tissue, so it is difficult to detect on radiographs with signs of joint effusion, soft tissue edema. In the late stages, bone damage may be evident with erosive bone loss at the joint surface. Therefore, X-ray can help identify bone and joint injuries, thereby giving an appropriate treatment plan.
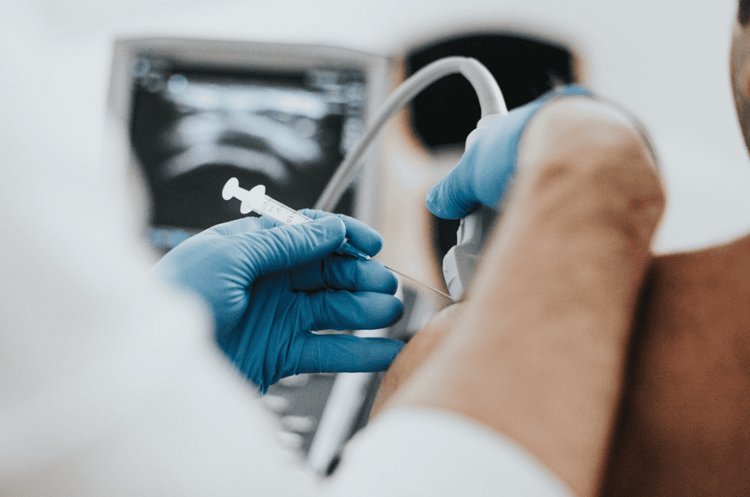
3.5. Computerized tomography helps diagnose gout According to a recent study, American scientists said that in addition to the usual methods of gout diagnosis, computed tomography (CT scan) is also an effective way to help diagnose gout. diagnose gout. A CT scan can help diagnose gout quickly by detecting urate crystals in the joints, even when the joints are not inflamed. Detecting gout as early as possible plays an important role in helping experts have appropriate treatment, and at the same time, patients also know how to actively change their diet and lifestyle to prevent it. gout attack.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. Gout examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.