This is an automatically translated article.
Non-gonococcal urethritis is a dangerous disease that, if not treated thoroughly, can lead to many complications affecting men's health and fertility.
1. What is non-gonococcal urethritis?
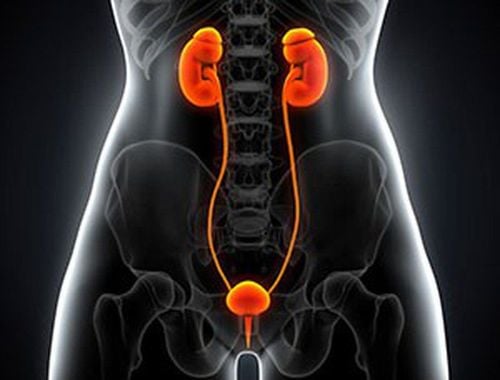
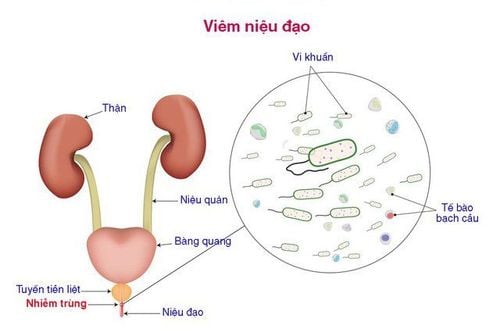
The urethra is the tube that extends from the bladder to the opening of the stoma that helps to pass urine out. In men, this organ also plays the role of carrying semen out. Urethritis is a urinary tract infection caused by bacteria and viruses. Non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU), also known as non-specific urethritis, is known to be a typical of urethritis not caused by gonorrhea but mainly by Chlamydia bacteria. This is a fairly common sexually transmitted disease but can be prevented by practicing safe sex. There are still cases of men with both gonococcal urethritis and non-gonococcal urethritis at the same time.
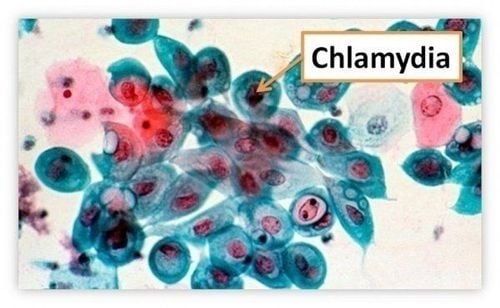
Vi khuẩn Chlamydia gây viêm niệu đạo
2. Causes of disease
Causes of the formation of non-gonococcal urethritis:
Due to the attack of bacteria on the urethra The foreskin is long and narrow. Men have liberal sex habits Improper genital hygiene way. Trauma, surgery on the bladder tube and the tip of the penis, narrowing of the urethra Men with social diseases Side effects of urinary catheterization after surgery Side effects of chemicals in soap, In particular, infection with Chlamydia Trachomatis (30-50%) and Ureaplasma Urealyticun (10-40%) account for about half of cases of non-gonococcal urethritis. Chlamydia is a bacteria that is usually found during unprotected sex with an infected person. Chlamydia can be transmitted during vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
In addition, other bacteria such as Herpes Simplex and Trichomonas Vaginalis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Candida albicans, Streptococcus, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Escherichia coli... are also potential pathogens.
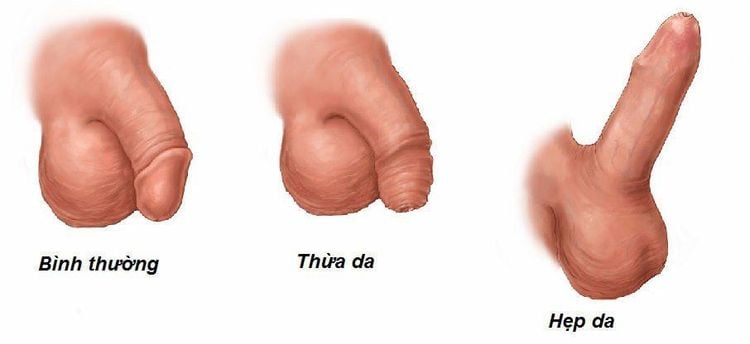
Bao quy đầu bị dài và hẹp có thể gây viêm niệu đạo
3. Symptoms to recognize the disease
The incubation period for non-gonococcal urethritis is usually 10-20 days after exposure. Although many cases do not experience any symptoms, most people will have typical symptoms such as:
Painful, swollen, red urethra, easily irritated Hot urine, sometimes mixed with pus, blood . Difficulty urinating Burning pain, discomfort during sex The urethral opening appears fluid but little and sparse, with an unpleasant odor. There may be fever, nausea, or vomiting. Most patients go to the hospital with some symptoms, but up to 50% of patients who have sex with a partner with Chlamydia do not show any symptoms.

Người bệnh có thể xuất hiện sốt
4. Diagnostic measures
To diagnose a patient with non-gonococcal urethritis, doctors will rely on some information from the patient such as:
History of sexual intercourse (safe or unsafe, level of risk) muscle..) Is there any pus discharge, urethral fluid or not? Condition when urinating (burning or painful)? In addition, the doctor can perform an endoscopy and culture of the urethral fluid to identify the type of bacteria and fungus causing the disease so that appropriate treatment can be prescribed.
Urethroscopy: assess white blood cell density, identify bacteria and fungi. Culture of urethral fluid or urine at the beginning of the field: identification of bacteria and fungi. For Chlamydia bacteria, the diagnosis can be based on a positive serological test because culture is often difficult.
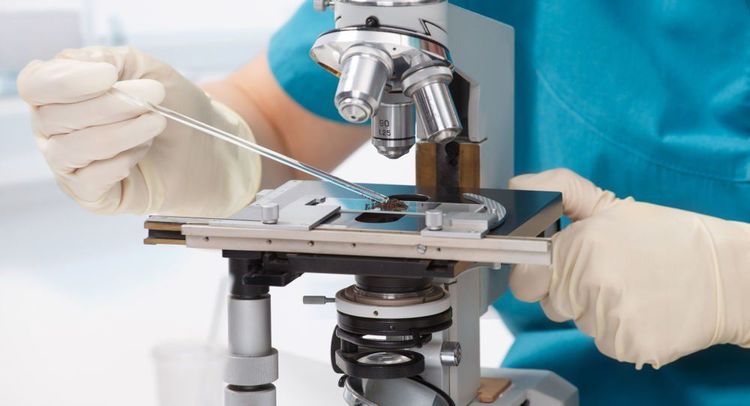

Soi dịch niệu đạo giúp chẩn đoán bệnh
5. Treatment of urethritis not caused by gonorrhea
Depending on the causative agent, the doctor will prescribe different treatment drugs. Usually, people with non-gonococcal urethritis will be prescribed antibiotics by doctors to treat them.
5.1 Cases of Chlamydia and Mycoplasma infections
Choose to use one of the drugs Azithromycin, Doxycycline, Ofloxacin, Erythromycin. Prefer Doxycycline and Azithromycin. Treat both the patient and the sexual partner. 5.2 In case of Trichomonas infection
Metronidazol 500mg / time, taken 2 times / day, used continuously for 7 days. Treat both the patient and the sexual partner. 5.3 Cases of fungal urethritis
Fungal urethritis is uncommon (caused by Candida Albicans commonly found in vaginitis). However, if you have it, you can choose Fluconazole or Itraconazole and pay attention to monitor liver and kidney function when using it. 5.4 In case of common bacterial urethritis
Choose one of the drugs in the antibiotic group Fluoroquinolone, Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole, Beta Lactam with a short course of 3-5 days. Maintain genital hygiene and coordinate treatment of vaginitis. In general, when treating non-gonococcal urethritis, men need to pay attention to the following:
Should use a single prescription Take medication for the cause of the disease Let your partner treat the same Stop using aphrodisiacs enjoy and have sex Follow appropriate therapy

Nên sử dụng một đơn thuốc duy nhất theo phác đồ của bác sĩ
Urethritis in general, if left untreated for a long time, will have unpredictable complications such as chronic kidney failure, prostatitis, orchitis, epididymitis, cystitis, infertility.. Therefore, the risks of urethritis should not be underestimated. It is necessary to detect early, treat early, once the body has abnormal signs, it is necessary to immediately go to the hospital for verification, to avoid missing the best time for treatment.
6. The secret to effective disease prevention
Drink enough water to flush the bladder: Drinking enough water (2-2.5l/day) can help the urinary system enhance urine excretion, thereby eliminating bacteria in the bladder, urinary tract, reduce the risk of urethritis. In addition, diuretics such as tea, acidic juices are also good choices to help increase urination. Improve resistance: Live in moderation, eat and sleep on time, exercise regularly, eat lots of green vegetables and supplement vitamins for the body. Aim to improve self-resistance from the invasion of foreign bacteria. Safe sex, faithful: the best way to prevent disease as well as reduce the risk of recurrence is to practice safe sex, use condoms, and be monogamous. At the same time, proactively check your health periodically so that diseases can be detected as early as possible. Attention to personal hygiene: Personal hygiene should be done, bathing regularly. Limit bathing to avoid bacteria in dirty water from entering the urethra. Do not share underwear, use separate towels and basins when cleaning the genitals. Choose dry cotton underwear: Synthetic fiber underwear, mixed with nylon often makes the genitals in a hot and humid state, secreting air, creating conditions for bacteria to grow, so change underwear to ingredients made of Cotton fibers are drier.
Recommended video:
Periodic health check at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
READ MORE
Urethral discharge syndrome in men What is the function of the urethra? Signs and treatment of urinary tract infections in women