This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Master, Doctor Hoang Van Lan Duc - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
For the prognosis and treatment of pleural fluid, the assessment of the fluid is very important. We must assess whether the fluid is free or localized, exudates or exudates, pus or blood, fluid in a bedridden patient, fluid in a person with lung-pleural cancer, etc. From there, assess the degree of influence on respiratory function. In the following article, we will introduce a few ways to measure the amount of free pleural fluid on ultrasound.
1. Formulas for measuring in supine position: Balik and Eisenberger's formulas
Measurement is as follows:
The patient lies on his back, the ultrasound probe is perpendicular to the lateral chest wall (usually placed in the middle or posterior axillary line). At the position of the intercostal space, the most fluid can be seen (the transducer can be placed in the frontal plane position, scanned from top to bottom, to the position with the most fluid, rotate the transducer perpendicular to the chest wall and then carry out measured), measured at maximum inspiration.
Measure the thickness of the pleural fluid from the parietal (thoracic wall) to the visceral (lung surface) at the largest point, the unit is mm.

Balik's formula: V (ml)= fluid thickness (mm) x 20 Eibenberger's formula: V (ml) = 47.6 x fluid thickness (mm) – 837 Eibenberger's formula is commonly used when the measured fluid thickness is 20mm or more.
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để có một lá phổi khỏe mạnh?
Để nhận biết phổi của bạn có thật sự khỏe mạnh hay không và làm cách nào để có một lá phổi khỏe mạnh, bạn có thể thực hiện bài trắc nghiệm sau đây.2. Measurement formulas in sitting or standing position: Goecke formula 1 and Goecke 2
How to measure: The patient is in a sitting or standing position, placing the probe along the body at the posterior axillary line in the coronal plane as shown in the illustration. Next, measure at the end, then exhale.
H: height of pleural fluid from the lowest point of the costophrenic angle to the highest point of the fluid (cm). D: thickness of fluid from the dome of the diaphragm to the base of the lung (cm). Goecke Formula 1: V (ml) = H x 90 Goecke formula 2: V (ml) = (H + D) x 70

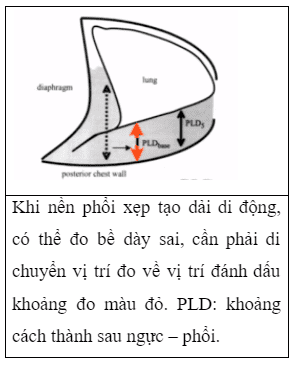
Note that the volume estimation is not accurate when the volume is small. Cross-probe placement will result in an overestimation of the fluid volume. Tall patients have a large thoracic cavity, the fluid spreads over a larger area, leading to a lower estimate of the fluid volume by measuring the measured fluid thickness than it actually is. In cases where the collapsed lung base forms a moving band during breathing, when the thickness of the fluid may be mistakenly measured, it is necessary to move the measurement site to the area where the lung parenchyma is present (as shown below).
According to Roch [1], the thickness of fluid measured in the intercostal space 5 > 5cm, the amount of fluid is definitely greater than 500ml with a sensitivity of 90%, positive predictive value 91%, negative predictive value 82% . Some authors have also shown that estimates of fluid volume in the right and left pleural spaces may differ slightly.
Currently, hospitals in Vinmec Health System have the most advanced ultrasound system, with the latest ultrasound machines such as GE's for general ultrasound, machines with high resolution transducers , small probes or small probes, can be spliced between the intercostal spaces for pleural ultrasound, detailed assessment of structures as well as abnormalities of the pleura, pleural fluid, making a diagnosis fast and accurate.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:Roch A., Bojan M., Michelet P., et al. (2005). Usefulness of ultrasonography in predicting pleural effusions > 500 mL in patients receiving mechanical ventilation. Chest , 127 ( 1 ), 224–232. Eibenberger K.L., Dock W.I., Ammann M.E., et al. (1994). Quantification of pleural effusions: sonography versus radiography. Radiology , 191 ( 3 ), 681–684. Hassan M., Rizk R., Essam H., et al. (2017). Validation of equations for pleural effusion volume estimation by ultrasonography. J Ultrasound , 20 ( 4 ), 267–271. Ibitoye B.O., Idowu B.M., Ogunrombi A.B., et al. (2018). Ultrasonographic quantification of pleural effusion: comparison of four formulae. Ultrason Seoul Korea , 37 ( 3 ), 254–260.