This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Pham Van Hung - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
High blood pressure is a disease that can lead to many dangerous complications such as angina, stroke, heart failure, kidney failure, etc. Patients can detect high blood pressure if their blood pressure is measured properly. The following is the standard blood pressure measurement procedure issued together with Decision No. 3192/QD-BYT dated August 31, 2010 of the Minister of Health.
1. Principle of measuring blood pressure
The principle of blood pressure measurement is to inflate a rubber armband, relieve the pulse of an artery, and then gradually deflate and record the response of the artery. Systolic and diastolic blood pressure values help doctors assess whether a patient has high blood pressure:Systolic blood pressure: equivalent to the time when blood begins to pass while the pressure at the ice is high su decreased. Diastolic pressure: corresponds to the time when blood is completely free to circulate in the artery when there is no pressure from the rubber band.
2. General rules when measuring blood pressure
Patients who need to rest for at least 15 minutes should take measurements at the same time of day. It is necessary to check the parts of the sphygmomanometer such as valves, cuffs, rubber pumps, manometers, etc. before measuring. In addition, the patient should use a sphygmomanometer for measurements. Location: usually measured in brachial artery. In case of necessity, when indicated by the doctor, the popliteal artery and other locations can be measured. When recording the results, the blood pressure measurement location must be recorded. When you want to measure blood pressure at any location, you need to find the artery there. Do not stop halfway and then continue to inflate as it will give false results. When releasing steam, it is necessary to continuously discharge until the mercury needle or column drops to the zero position. When the blood pressure readings are abnormal, such as the hypertensive crisis, the blood pressure is stuck, the patient has shock, pulse collapse. , ... should immediately notify the treating doctor.3. Prepare equipment before measuring blood pressure
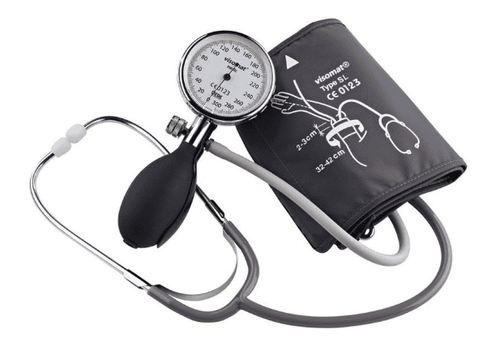
4. The process of measuring blood pressure properly according to the guidance of the Ministry of Health
When measuring blood pressure at the clinic or measuring blood pressure at home, patients need to follow the following procedure:Rest in a quiet room for at least 5-10 minutes before measuring blood pressure. Before 2 hours, do not use stimulants such as coffee, tobacco, alcohol. Standard measuring position: person having blood pressure measured is sitting on a recliner, arms stretched out on the table, elbow creases at heart level. In addition, the patient can also have blood pressure measured in lying and standing positions. The elderly or those with diabetes should have their blood pressure measured in an upright position to determine if orthostatic hypotension is present. Use sphygmomanometers and periodically calibrated measuring devices. The length of the cuff (in the cuff) must be at least 80% of the arm circumference, and the width should be at least 40% of the arm circumference. Then, the person performing the blood pressure measurement needs to wrap the bandage tightly enough, the lower edge of the cuff is 2cm above the elbow crease and place the device in a position that ensures that the device or the zero mark of the scale is level with the heart. In the case of not using an automatic sphygmomanometer, before measuring blood pressure, it is necessary to locate the brachial artery to place a stethoscope. After the pulse is no longer visible, it is necessary to inflate more 30mmHg and then deflate at a rate of 2-3mmHg/beat. The systolic blood pressure was obtained at the time of the first beat (Korotkoff phase I) and the diastolic blood pressure corresponding to the time of complete disappearance of the beat (Korotkoff phase V). Do not talk while taking your blood pressure. At the first measurement, blood pressure should be measured in both arms. The hand blood pressure measurement with the higher value will be used to monitor blood pressure later. Blood pressure should be measured at least 2 times, at least 1-2 minutes apart. If the blood pressure readings differ by more than 10 mm Hg between the two readings, the measurement should be repeated several times after resting the patient for more than 5 minutes. Blood pressure values are recorded as the average of the last 2 measurements. Repeated blood pressure measurements increase accuracy in patients with cardiac arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation. In case of doubt, blood pressure can be monitored with an automatic home meter or with a 24-hour automatic blood pressure monitor (also known as a blood pressure Holter). Record the blood pressure reading in mmHg as systolic/diastolic pressure (eg 126/82 mmHg). The person recording the blood pressure value should not round the number to more than one unit and should immediately notify the person being measured.
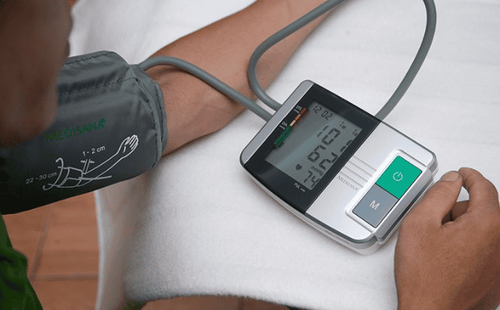
5. How to read blood pressure readings
5.1 Normal blood pressure readings Systolic blood pressure: 90 mmHg - 130 mmHg. Diastolic blood pressure: 60 mmHg - 85 mmHg. 5.2 Low blood pressure readings Systolic blood pressure <85 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure <60 mmHg indicates low blood pressure. Low blood pressure leads to insufficient blood supply for the functioning of organs, especially distant organs such as the brain, causing manifestations such as dizziness, lightheadedness, nausea,...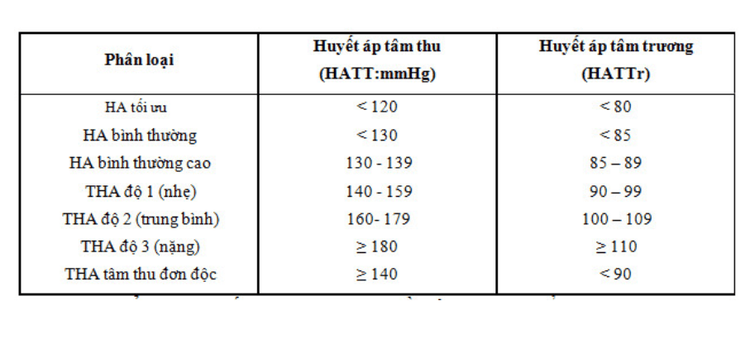
Prehypertension: systolic blood pressure 130-139 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure 85-90 mmHg. Grade 1 hypertension: systolic blood pressure 140-159 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure 90-99 mmHg. Grade 2 hypertension: systolic blood pressure 160-179 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure 100-109 mmHg. Grade 3 hypertension: systolic blood pressure ≥ 180 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 110 mmHg. Isolated systolic hypertension: systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure < 90 mmHg. Taking daily blood pressure measurement, especially for the elderly, helps to screen and treat many dangerous complications early such as heart attack, stroke, etc., contributing to maximum protection for the patient's health.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.














