The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Nguyen Thi Tam Ly, MSc - Clinical Doctor at Reproductive Support Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.
Thick uterine lining can be a physiological sign in pregnant women; however, in women of reproductive age, if the uterine lining is too thick, it can lead to difficulty conceiving.
1. What is a thick endometrium?
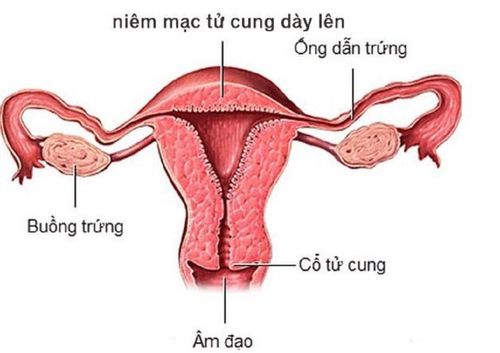
The endometrium is a layer of cells lining the inside of the uterus, this layer of mucosa is soft and spongy. The thickness of the endometrium changes with age and menstrual cycle.
Before puberty and after menopause, the endometrium is thin, during reproductive age, the endometrium changes with the menstrual cycle and the endometrium thickens during pregnancy.
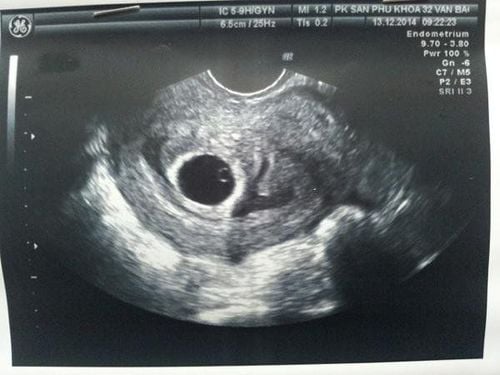
After menstruation, the endometrium remains a thin layer, this is when the endometrium is thinnest. Under the influence of estrogen, epithelial cells proliferate rapidly, the mucosa gradually thickens, blood vessels develop strongly, the glands of the cervix secrete a layer of mucus to facilitate sperm movement into the uterus. The endometrium is about 12-15mm thick in the middle and end of the menstrual cycle, the endometrium at this stage proliferates waiting for the implantation of the fertilized egg. If conception occurs, the uterine lining continues to grow to nourish the fetus. If conception does not occur, the uterine lining will peel off and cause menstruation.
When the uterine lining is over 20mm and is not a case of pregnancy, it is called endometrial hyperplasia or thickened uterine lining.
2. Causes of thickened uterine lining
The main cause of thickened uterine lining is an imbalance between estrogen and progesterone hormones, which is caused by the following factors:
Excessive estrogen production in the body or the use of exogenous estrogen stimulates the uterine lining to grow thicker.
Overweight and obesity are risk factors for thickened uterine lining.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Continuous use of estrogen-containing drugs without progesterone
The body lacks progesterone hormone.
Common signs of a thick uterine lining:
A thick uterine lining causes prolonged bleeding called menorrhagia (menstruation lasting more than 7 days) or hypermenorrhea (menstrual flow exceeding 80ml per menstrual cycle).
A thick uterine lining in women of reproductive age can delay pregnancy by preventing conception. In postmenopausal women, a thick uterine lining (>5mm) is a dangerous sign that requires treatment to screen for the risk of endometrial cancer.
3. Solutions to treat a thick uterine lining
The treatment for a thick uterine lining depends on each individual:
In women of childbearing age, the main cause is an imbalance between the hormones estrogen and progesterone. The doctor will prescribe hormone therapy to restore the balance between these two hormones in the body, thereby increasing the chance of pregnancy.
For postmenopausal women, an abnormally thick uterine lining is a warning sign of endometrial cancer. The doctor will order a biopsy of the uterine lining for pathological examination to see if there are any abnormal cells.
In addition to medical treatment or gynecological intervention, applying a regimen of exercise and diet can help improve the condition of uterine lining thickening.
Limit eating red meat and animal fat because they increase the risk of hyperplasia and cancer of the uterine lining.
Limit foods rich in vitamin C, some foods rich in vitamin C such as guava, oranges, tangerines, grapefruit, ...
Limit foods rich in vitamin E, vitamin E is abundant in nuts such as almonds, and sunflower seeds ...
Limit products made from soybeans such as soy milk, and tofu ... Because soybeans have components with a structure and effects similar to estrogen.
Reduce eating foods high in sugar because it can lead to hormonal imbalance.
Note that foods should only be limited, not completely avoided, to ensure that the body still receives enough diverse nutrients.
Exercise regimen: regular exercise, reasonable sports such as walking, swimming, yoga... It can reduce the amount of estrogen in the body; estrogen is the leading cause of thickening of the uterine lining. In addition, reasonable exercise also helps limit overweight and obesity or helps lose weight in overweight people, which is a risk factor leading to the thickening of the uterine lining.
Balance time between rest and work; avoid staying up late and getting enough sleep to help the body secrete balanced hormones.
In addition, after treatment and combining a reasonable diet, it is necessary to have a follow-up examination to monitor the condition of the thickened uterine lining.
To overcome the condition of the thickened uterine lining, it is necessary to re-establish hormonal imbalance with medication and diet. Because this condition can lead to difficulty conceiving, women who suspect they have the disease should go to the hospital for early consultation and treatment.

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.