This is an automatically translated article.
Citrates containing the citrate salts of potassium or sodium are used to alkalinize the blood or urine. To ensure that no side effects are caused, there are a few things to keep in mind before, during and after using Citrate.
1. What is the use of Citrate?
Citrate is a drug that can only be used with a doctor's prescription. This medicine is available in the following dosage forms: Tablet, solution, powder, syrup.
Commonly used brand names of Citrate in the United States such as: Citra pH, Cytra-K, Cytra-K Crystals, Liqui-DualCitra, Polycitra-K, Polycitra-K Crystals, Urocit-K 10, Urocit-K 15, Urocit-K 5; in Canada: Pms-Dicitrate.
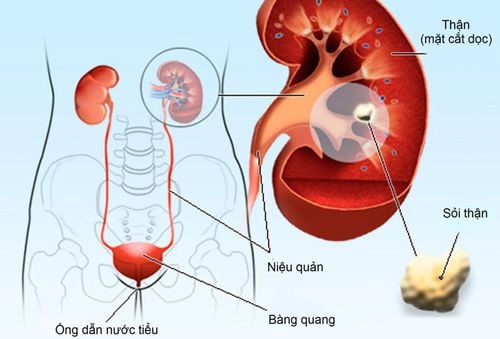
Citrate is used to make urine more alkaline (less acidic), which in turn helps prevent certain types of kidney stones. Sometimes Citrate is used with other medicines to help treat kidney stones that can occur with gout. In addition, the drug is also used to make the blood more alkaline in certain conditions.
2. How to use Citrate?
2.1. Some people need to be careful when using Citrate Tell your doctor if you have a history of allergic reactions to drugs in this class. There are no studies on the effects of Citrate during pregnancy. Scientists do not yet know if Citrate passes into breast milk, but Citrate has not been reported to cause problems in a nursing infant. Some special medical problems may affect the use of medicines in this class, don't forget to tell your doctor if you have any of the following: Addison's disease, type 2 diabetes, kidney disease , diarrhea (chronic), edema (swelling of the feet or legs), high blood pressure, blood poisoning during pregnancy, heart disease (potassium in citrates can make heart disease worse), bowel or intestinal obstruction esophagus, stomach ulcers or other stomach problems, urinary tract infections. 2.2. Correct use of Citrate For patients taking Citrate tablets:
Swallow the tablet whole, do not crush, chew or suck. Drink with a full glass of water. If you find it difficult to swallow pills or the medicine appears to be stuck in your throat, see your doctor right away. Citrate can cause serious irritation if not swallowed completely and not properly dissolved. For Liquid Citrate users:
Dilute with 1 full glass of water or juice and drink. For patients taking powdered forms of Citrate:
Put one sachet in at least 1 full glass of water or juice. Stir well to make sure the powder is completely dissolved. Drink all of the mixture to make sure you get the right dose. Take each dose immediately after a meal or within 30 minutes after eating. This keeps you from having an upset stomach or has a laxative effect. Take Citrate only as directed by your doctor. Do not use more or more often. This is very important, especially if you are also taking diuretics or Digitalis.
Dosage of Citrate is different for each patient. The following information is the average dose of these drugs.
For Potassium Citrate:
Oral tablet form to make urine more alkaline (less acidic) and prevent kidney stones: Adults take an initial dose of 1.08 to 2.16 grams, 3 times a day, drink during meals. Some people can take 1.62 grams, 4 times a day with food or 30 minutes after eating or a snack before going to bed. Usually no more than 10.8 grams per day would be taken. Children take the dose as directed by the doctor. For Potassium Citrate and Citric Acid:
Oral solution form
To make urine or blood more alkaline (less acidic) and prevent kidney stones: Adults take 2 to 3 teaspoons of solution initially , mixed with water or juice, 4 times a day, after meals and before going to bed. Children take the dose prescribed by the doctor. Make urine more alkaline: Children initial dose of 1 to 3 teaspoons of solution, mixed with water or juice, 4 times a day after meals and at bedtime. Powder for oral administration:
To make urine or blood more alkaline (less acidic) and prevent kidney stones: Adults initially take 3.3 grams of Potassium Citrate, mixed with water or juice, four times a day, after meals and before going to bed. Not recommended for use by children. For Potassium Citrate and Sodium Citrate:
Oral tablet form:
To make urine more alkaline (less acidic) and prevent kidney stones: Adults you should first take 1 to 4 tablets after meals and before go to sleep. Children: Dosage prescribed by the doctor. For Sodium Citrate and citric acid:
Oral solution form:
To make urine and blood more alkaline (less acidic) and prevent kidney stones: Adults take 2 to 6 teaspoons of solution 4 times/day, after meals and before going to bed. The solution should be mixed in 30 to 90ml of water. To make blood more alkaline (less acidic): Adults take 1 to 2 tablespoons as a single dose, possibly mixing it with one to 2 tablespoons of water. To make stomach contents less acidic before surgery: Children take 1 to 3 teaspoons of solution 4 times a day at first, after meals and at bedtime. The solution should be mixed in 30-90ml of water. For Tricitrates:
Oral solution form:
To make urine and blood more alkaline (less acidic) and prevent kidney stones: Adults take 1 to 2 tablespoons of solution 4 times a day at first: , after meals and before going to bed. To make stomach contents less acidic before surgery: Adults taking 1 tablespoon of a single dose should mix the solution with one tablespoon of water. To make urine or blood more alkaline (less acidic): Children take 5 to 10ml at first, 4 times a day after meals and at bedtime. If you miss a dose of Citrate, take it as soon as possible. However, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular dosing schedule if it is almost time for your next dose.
Keep your medicine in a cool place, away from moisture, away from heat and direct light.
2.3. Precautions while using Citrate Do not eat salty foods or use extra table salt while taking Citrate . This will help prevent kidney stones and unwanted side effects from occurring.
For people taking medicines containing Potassium Citrate:
Salt substitutes and low-salt milk may contain potassium, do not use them unless directed to do so by your doctor. If you are taking the tablet form and notice black, tarry stools or other signs of gastrointestinal bleeding, tell your doctor. If you are on a potassium-rich or potassium-restricted diet, check with your doctor as this medicine contains a large amount of potassium. For patients taking drugs containing Sodium Citrate:
If you are on a sodium-restricted diet, tell your doctor because Sodium Citrate-containing medicines contain a large amount of sodium.
3. Citrate drug interactions
Atropine Chlorpheniramine Diphenhydramine Isopropamide Flavoxate Homatropine Hydroxyzine Hyoscyamine Imipramine Ipratropium Isopropamide Loxapine Olanzapine Scopolamine Propantheline Propiverine Protriptyline is not recommended. Using drugs in this class with any of the drugs below is generally not recommended, but in some cases it can still be used, depending on the dose and frequency of dosing that can be changed:
Aceclofenac Acemetacin Aliskiren Aspirin Azilsartan Captopril Celecoxib Diclofenac Etoricoxib Enalapril Ibuprofen Losartan Naproxen Olmesartan Meloxicam Piroxicam Quinapril Ramipril Rofecoxib Salicylic Acid Salsalate Sodium Salicylate Valsartan
4. Citrate side effects
Stop using Citrate and get medical help right away if any of the following effects occur:
Very rare
Abdominal pain, stomach pain (severe) Black stools Vomiting (severe), sometimes there is blood. Seek medical advice as soon as possible if any of the following side effects occur:
Seizures Dizziness High blood pressure Irregular heartbeat or fast heartbeat Irritability Mood/mental changes Pain Muscles Anxiety, restlessness Numbness, tingling in feet, hands, lips Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing or slow breathing Swelling of feet, legs Fatigue Weakness or heaviness in legs. The above is not a complete list of Citrate interactions, side effects, each drug in this group may have its own caveat, ask your doctor if you have any questions. Note, Citrate is a prescription drug, patients need to use the drug as prescribed by the doctor, absolutely do not self-treat at home.