This is an automatically translated article.
How long you decide to breastfeed is up to you. There are many different opinions, experts have their own recommendations, others have their own opinions, but only you can make the decision that is right for your family's circumstances. Some women choose to breastfeed for just a few weeks, others for years. So how long is enough to breastfeed? There will always be people who think you're breastfeeding for too long or too short. However, there is no right or wrong way and no one should judge you for how long you decide to breastfeed. The following article will provide useful information to help parents and caregivers make early decisions about breastfeeding.
Breast milk is the best source of nutrition for the health of infants and children.

Trẻ nên được bú sữa mẹ hoàn toàn trong 6 tháng đầu đời
1. Breastfeeding recommendations from reputable organizations
Health experts around the world agree on how long mothers should breastfeed their babies. Here are some top expert recommendations:
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP): Recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months, then continued breastfeeding with complementary feeding. miles for at least a year. When a baby is over 1 year old, how long can continue to breastfeed depends on the mother and the baby's needs. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG): Advises to exclusively breastfeed infants for the first 6 months and then continue breastfeeding with complementary foods for the first year. After the first year, breastfeeding should be continued for as long as it is convenient for both mother and baby. World Health Organization (WHO): It is recommended that infants be exclusively breastfed for the first 6 months and then continue to breastfeed with complementary foods for 2 years or longer.
2. Benefits of breastfeeding by month of age
2.1. The first day
Experts recommend giving babies skin-to-skin contact with their mothers and breastfeeding in the first hours after birth. The benefits include that the baby can receive the warmth from the mother and remember them, while also having the effect of stimulating milk for the mother.
The milk that the baby sucks at this time is a pale yellow liquid called colostrum. Colostrum is the first stage of breast milk, containing important nutrients and antibodies for the infant. Your newborn baby's belly is very small. Babies don't need much milk with each feeding to stay full. Your baby may want to eat as often as every 1 to 3 hours. Breastfeeding regularly helps to increase milk supply and train the baby's sucking and swallowing reflex.
In the days that follow, more breast milk provides early nutrition and can help protect the baby from infections.
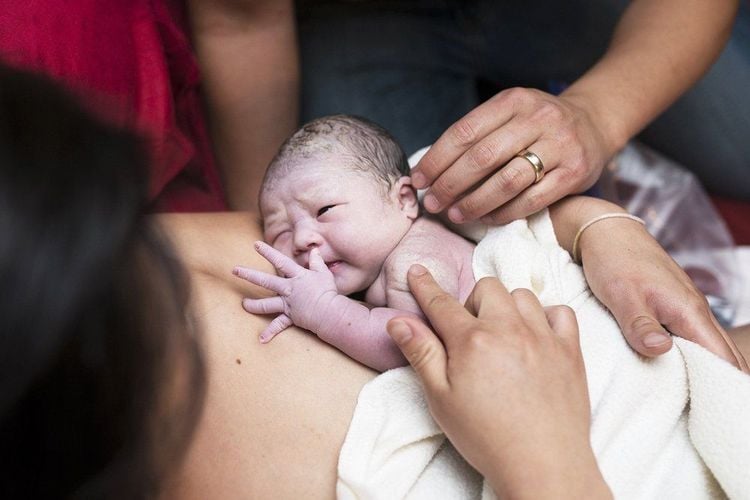

Ngay sau khi chào đời, trẻ cần được thực hiện da kề da
2.2. First month
As the baby grows, the baby's belly also grows. Your baby will gradually be able to take in more breast milk with each feeding. During the first few weeks and months, the time between feeds will be about 2 to 4 hours longer than average. Your baby's feeding frequency can change depending on the time of day and the baby's needs, when the baby is too full to eat more or when you feed the baby when the baby is too sleepy, the quality of the feed will not be. Guaranteed, the baby will sleep without having enough time to feed. Your baby will feed about 8 to 12 times in 24 hours.
United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) describes breast milk as the baby's first immunization. Breast milk provides protective antibodies for at least the first year of a baby's life. These antibodies protect against:
Diarrhea Ear infections Pneumonia Other health problems like viral fever, ... Mothers receive the hormones prolactin and oxytocin both of which work together to create Feeling good for the mood and facilitating the contraction of the uterus after childbirth.
2.3. From 3 to 4 months
When babies enter the 3rd month, breast milk continues to maintain its ability to support the digestive system. It also provides children with protection against allergens found in other foods and supplements. At the same time, breastfeeding helps mothers burn 400-500 extra calories per day, which helps you quickly recover in shape after giving birth.
In addition, breastfeeding helps the mother's internal health. Some studies show that exclusive breastfeeding may reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and metabolic heart disease.
Trẻ được bú bằng sữa mẹ giảm nguy cơ mắc viêm khớp dạng thấp
2.4. 6 months
The benefits of breast milk remain even when you give your baby solid foods as recommended by the World Health Organization WHO. Breast milk continues to provide energy, protein, as well as vitamin A, iron and other important nutrients, and helps strengthen the baby's resistance to disease.
For mothers, breastfeeding up to this point reduces the risk of breast cancer and other cancers, such as ovarian, endometrial and uterine cancers. In fact, according to a report published by the World Cancer Research Fund and the American Institute for Cancer Research in 2017, for every 5 months a woman breastfeeds, a woman can reduce her risk of breast cancer by 2%. . In addition, exclusive breastfeeding is also one of the natural methods of contraception that some mothers apply when they do not want to have more children.
2.5. 9 - 12 months
Breast milk is still the most important source of nutrition, even after you give your baby solid foods. Breastfeeding frequency at this time may decrease as your baby is still eating a variety of complementary foods, but the amount of milk per feeding is still increasing, make sure your baby is not drinking less than 560ml/day.
An undeniable benefit of breastfeeding is cost savings. You can save a lot of money buying formula milk for other purposes such as choosing a preschool with a good quality of education.
Also, babies who are breastfed for a year are less likely to get sick and may need less speech or dental interventions.

Trẻ khi được 1 tuổi hoàn toàn có thể ăn thức ăn đặc
2.6. More than a year old
Feeding recommendations for one year onward include breastfeeding on demand and introducing other solids at least three times a day. You can also introduce formula at this time if you want to stop breastfeeding.
Some older studies suggest that longer periods of breastfeeding may benefit babies in terms of IQ and social development. But newer studies suggest that this is only a temporary benefit.
3. How long is enough to breastfeed?
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) there isn't any limit to how long you can breastfeed as long as it's convenient for both you and your baby and there's also no evidence of psychological harm or development. develop from breastfeeding to the third year of life or longer. Even the longer you breastfeed, the greater and lasting the benefits. Some of the positive effects are that children are healthy, happy, love life, and can use the safest milk for their health.

Thời gian cho trẻ bú tùy thuộc vào mỗi mẹ
4. Decision to wean
Actively extending feedings during the day for babies is the first step of the weaning process when weaning meals have gradually become routine.
The World Health Organization suggests continuing breastfeeding with complementary foods until the baby's second birthday or beyond. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends continuing to breastfeed babies along with foods until their baby's first birthday or for as long as desired by both mother and baby.
Some signs that your baby may be ready to wean include:
One year younger Get more nutrition from solid food Drink well from a cup Gradually cut down on unnecessary meals How to wean:
Work Weaning begins with the baby getting used to different foods and when mealtimes are better established, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Some tips:
Cut the feeding time smaller to avoid engorgement problems. Feed your baby expressed breast milk in a cup or bottle. Your baby will still get the benefits of breast milk, just from a different source. Relieve discomfort by applying cold or even cabbage leaves to your chest. If you feel your baby wants to suckle, feed them. In the meantime, use distractions with meals, toys or stuffed animals, and other activities. And make sure your child has close contact and cuddles during the change.
For children to be healthy and develop well, it is necessary to have a nutritious diet in terms of quantity and quality balance. If children are not provided with adequate and balanced nutrients, it will lead to diseases of excess or lack of nutrients, which adversely affect the comprehensive development of children in terms of physical, mental and motor skills.
Children who do not eat properly are at risk of micro-mineral deficiency causing anorexia, growth retardation, malabsorption,... If they notice the above signs, parents should supplement their children with products. The supplement contains lysine, essential micro-minerals and vitamins such as zinc, chromium, selenium, and B vitamins to help fully meet the nutritional needs of children. At the same time, these essential vitamins also support digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, help improve anorexia, and help children eat well.
Parents can learn more:
Signs of zinc deficiency in children
Micronutrient deficiency and failure to gain weight in children
Please regularly visit Vinmec.com website and update useful information to take care of your child. Take care of the baby and the whole family.
References: cdc.gov, verywellfamily.com, healthline.com













