This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master. BSCK II Phan Thi Minh Huong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General HospitalAmong viral hepatitis, hepatitis E and hepatitis B stand out prominently. However, most people only know about hepatitis B and lack knowledge about hepatitis E. So hepatitis E is a disease. What, is it different from hepatitis B?
1. What is Hepatitis E?
Hepatitis E is a disease caused by the HEV virus, a single-stranded, positive, non-enveloped RNA virus with poor tolerance.Every year, around the world it is estimated that about 20 million people have this disease and about 3.5 million people have obvious signs and symptoms. Areas that are considered to have high infection rates include countries in the east and south of Asia, including Vietnam. The disease often occurs and can break out into epidemics in the rainy season, when the water source is heavily polluted.
The incubation period after exposure to the hepatitis E virus is about 3-8 weeks, with an average of 40 days. The stages of infection time are unclear. The disease shows symptoms most often in young people aged 15-40 years, in children often there are no symptoms or the disease is only very mild, without jaundice, so it is difficult to diagnose.
In rare cases, the disease can be transmitted through blood, from mother to child; The disease can also lead to fatal fulminant hepatitis, which is common in pregnant women.
The disease usually goes away on its own without leaving any complications. Patients are generally advised to rest, eat nutritious meals and fluids, avoid alcohol, and consult their doctor before taking any medication that can cause liver damage, especially acetaminophen. . In the case of chronic disease, the drugs indicated are ribavirin, peginterferon or a combination of peginterferon and ribavirin. The type of drug, dose and duration of use depend on the health status of each patient.
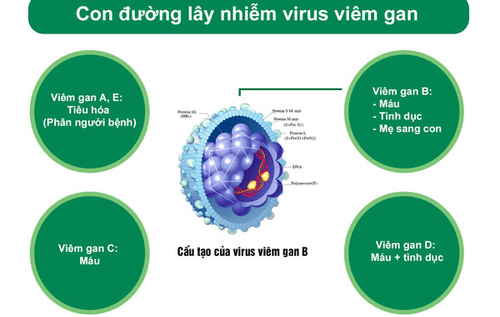
2. How is hepatitis E different from hepatitis B?
Transmission route: Hepatitis E is a disease transmitted through the gastrointestinal tract, hepatitis E virus lives in feces, garbage, dirty sewage through food (unhygienic vegetables) into the human body. Unlike hepatitis E, hepatitis B is transmitted through blood (sexual contact, mother to child, contact with secretions of an infected person).Progression of hepatitis E : The disease develops acutely causing jaundice, fatigue, loss of appetite, diarrhea,... After 7-10 days, the disease usually resolves on its own, does not become a chronic disease, so it does not cause any danger. In contrast, hepatitis B is a chronic disease, which can cause complications such as cirrhosis, liver cancer. Only drugs can be used to reduce the toxin of the liver. Viruses can't be cured. The disease often has no symptoms when the patient is healthy, when there are favorable factors, there will be typical manifestations of liver disease such as hepatitis E.
Viêm gan E khác gì viêm gan B?
Currently, there is no vaccine for hepatitis E. Patients also do not have long-term immunity to the disease, so there is still a risk of recurrence if they eat food and drink contaminated with hepatitis E virus.
To meet the demand for examination and treatment of liver diseases - Bile - Pancreas, Vinmec International General Hospital has launched standard liver - bile screening packages, comprehensive liver - bile screening packages and advanced liver - bile screening packages to help customers: liver function through liver enzyme tests Assess bile function; intravascular nutrition Early screening for liver cancer Perform tests such as Total blood cell analysis, blood clotting ability, screening for hepatitis B, C Assess hepatobiliary status through ultrasound images and other diseases risk of liver disease effects/exacerbation of liver disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.