This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by MSc Vu Tan Phuc - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital. The doctor has nearly 10 years of experience in the field of gastroenterology with strengths in diagnostic and therapeutic Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.Hepatitis E virus does not lead to long-term illness or liver damage like some other forms of hepatitis such as hepatitis B, C or D. However, hepatitis E can be dangerous for pregnant women or anyone have weak immune systems, including the elderly and sick people.
1. What is Hepatitis E?
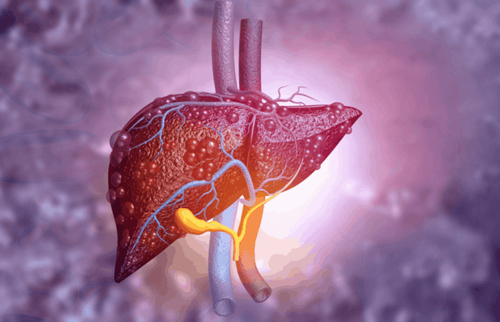
Hepatitis E is caused by the hepatitis E virus (HEV). It can cause the patient's liver to swell. The hepatitis E virus has at least four different types: genotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4. Genotypes 1 and 2 are found only in humans. Genotypes 3 and 4 circulate in some animals (wild boars and deer) without causing any disease and sometimes infect humans.The virus is shed in the feces of an infected person and enters the human body through the intestines. It is transmitted mainly through contaminated drinking water. Usually, the infection is self-limited and resolves on its own within 2 to 6 weeks. Most people with hepatitis E get better within a few months.
Usually, hepatitis E does not lead to long-term disease or liver damage like some other forms of hepatitis but hepatitis E can be dangerous for pregnant women or anyone with a weakened immune system, including the elderly and the sick.
You can also get hepatitis E if you eat undercooked meat from an infected animal such as a pig or deer.
Hepatitis E is found worldwide, but the disease is most common in East and South Asia. There is currently a vaccine to prevent hepatitis E virus infection that has been developed and licensed in China, but is not yet available in other countries.
Mild fever Feeling very tired Less hunger Abdominal pain Light-colored stools Skin rash or itching Joint pain Yellow skin or eyes.
2. Diagnosis of hepatitis E virus
To diagnose hepatitis E, your doctor will first ask about your medical history and detailed symptoms. The patient should clearly state the most recent travel, because the doctor may think that the patient has been exposed to contaminated water.The doctor will order a blood test or a stool test to get an accurate diagnosis of hepatitis E.
Cases of hepatitis E are not clinically differentiated from other types of acute viral hepatitis. However, the diagnosis can often be strongly suspected in appropriate epidemiological settings.
A definitive diagnosis of hepatitis E infection is usually based on the detection of IgM antibodies specific to the virus in a person's blood. Additional tests include reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to detect hepatitis E virus RNA in blood and stool. This test requires specialized laboratory facilities.

3. Treatment of hepatitis E . virus
There is no specific treatment capable of altering the course of acute hepatitis E. In most cases, hepatitis E clears up on its own in about 4 to 6 weeks, so hospitalization is usually not required. The following measures can reduce the symptoms of the disease such as:Rest Eat healthy foods Drink lots of water Avoid alcohol Inform your doctor before the patient takes any medicine that may cause problems. liver damage, such as acetaminophen. If the patient is pregnant, the doctor may require hospitalization for monitoring. In severe cases, the patient may be given medication to fight the infection.
Prevention is the most effective method against this disease. Here are some steps to help prevent hepatitis E virus infection:
Maintain hygiene measures Avoid consumption of water and ice of unknown origin Do not eat blood pudding, undercooked meat, venison, shellfish. life Wash your hands with soap after using the bathroom, changing diapers, and before you prepare or eat food.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Source: webmd.com & who.int