Most cases of gonorrhea are chronic, lacking typical symptoms and causing many complications for patients. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are essential to minimize the complications of the disease.
1. What is Chronic Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium. It is a sexually transmitted infection commonly found in sexually active individuals and can sometimes be seen in newborns infected by their mothers.
The disease is classified into two types: acute gonorrhea and chronic gonorrhea. Acute gonorrhea typically presents with symptoms such as painful urination and pus discharge. However, if diagnosed and treated early, gonorrhea can be easily managed.
If acute gonorrhea is not diagnosed and treated early, it can progress to chronic gonorrhea. The symptoms of chronic gonorrhea are often unclear and can recur multiple times. During this stage, the gonorrhea bacteria have proliferated significantly, making treatment more challenging and causing damage to the reproductive organs and fertility in both men and women.
For patients with chronic gonorrhea, samples need to be cultured in a CO2-enriched blood agar environment for accurate diagnosis. The only source of infection is individuals with gonorrhea. Sexual contact, sharing towels, or washing underwear with infected individuals can significantly increase the risk of contracting gonorrhea.
2. Is Chronic Gonorrhea Contagious?
Many people are unaware of whether chronic gonorrhea is contagious, but in reality, gonorrhea, whether acute or chronic, is indeed contagious. Approximately 90% of gonorrhea transmission occurs through sexual contact. After engaging in sexual activity with an infected partner, the gonorrhea bacteria adhere to the columnar epithelial cells of the healthy person's genitourinary tract, leading to rapid infection immediately after sexual contact.
Chronic gonorrhea can also be transmitted from mother to child. This occurs when a mother with gonorrhea is not diagnosed and treated early during pregnancy. During childbirth, the baby passes through the birth canal and can come into contact with gonorrheal pus, leading to gonococcal conjunctivitis in the newborn.
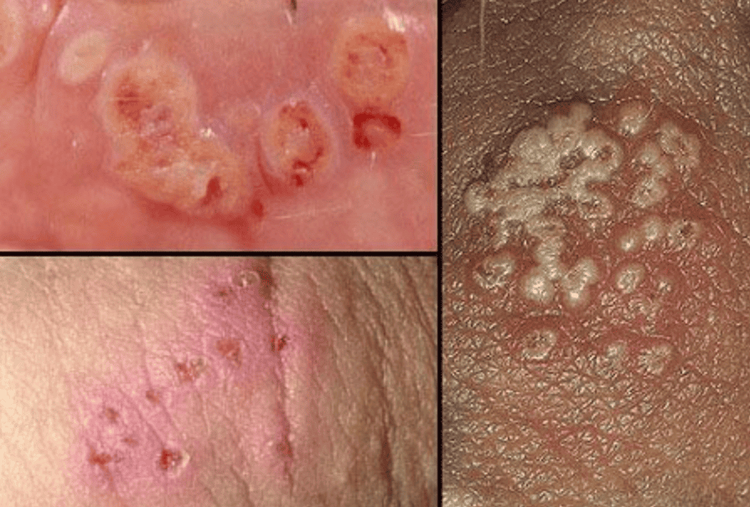
3. Symptoms of Chronic Gonorrhea
"How long does it take for gonorrhea to become chronic?" is a question that many people are concerned about. According to specialists, if acute gonorrhea is not treated or not treated properly, it will become chronic after 1 month.
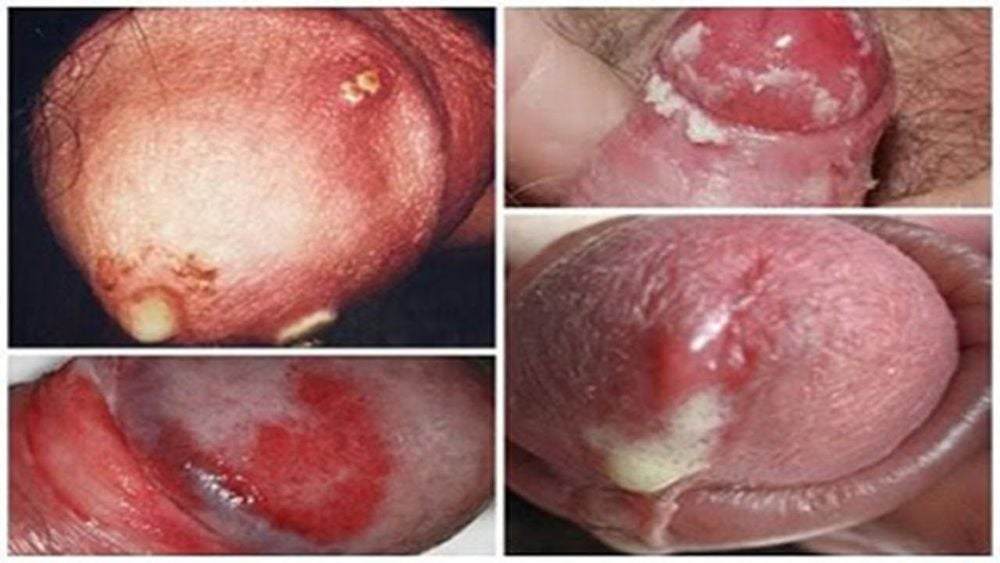
Symptoms of gonorrhea in men include:
Mild burning sensation during urination, difficulty urinating, frequent urination, or swollen lymph nodes in the groin are common symptoms in men with chronic gonorrhea. Patients often feel a burning sensation when urinating, accompanied by thick white or yellow pus on the glans penis.
Men often experience nocturnal emissions and pain when the penis is erect.
The urethra becomes swollen and often has banana-like pus discharge from the urethral opening, especially in the early morning.
Other accompanying symptoms include back pain, loss of sensation in the genital area, and blood in the semen.
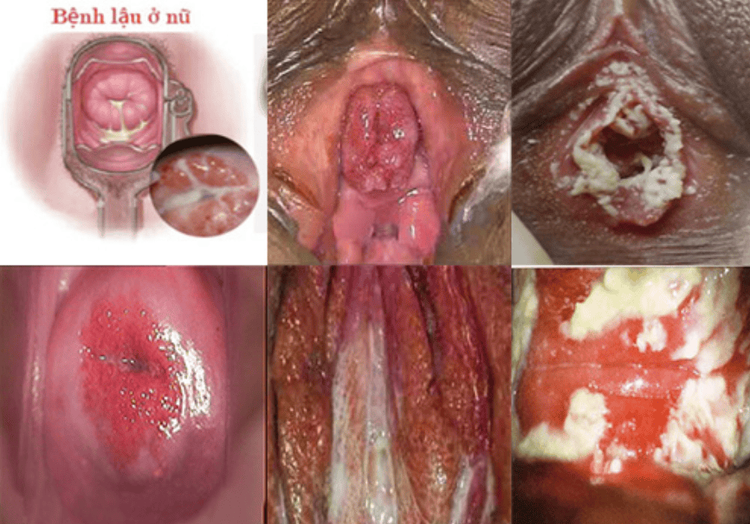
In women: Symptoms of gonorrhea in women are often unclear, and most do not have any unusual symptoms. Only a few patients experience yellow vaginal discharge or loss of sensation in the genital area. Therefore, women need to pay attention to their health to detect, diagnose, and treat gonorrhea early. Some symptoms of chronic gonorrhea in women include:
Abnormal vaginal discharge that is white or pale yellow
Painful urination or pain during sexual intercourse
Frequent abdominal and back pain, with some severe cases showing signs of high fever
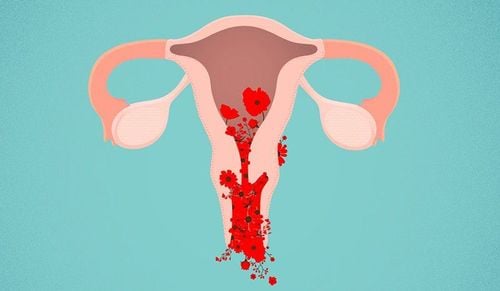
Abnormal vaginal bleeding when not menstruating
Chronic gonorrhea in women, if not diagnosed and treated early, can cause many dangerous complications affecting the patient's health and fertility, such as cervicitis, endometritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility.
4. Can Chronic Gonorrhea Be Cured?
Chronic gonorrhea is often not completely curable and has a high risk of recurrence if not properly cared for and treated. Therefore, it is essential to adhere to the following treatment principles:
Follow the prescribed treatment regimen and choose antibiotics based on the patient's antibiotic sensitivity test results.
When one partner is infected with gonorrhea, both partners need to be treated.
Patients with chronic gonorrhea often have damage to the genitourinary organs, so during treatment, they should rest and avoid activities like cycling, horseback riding, or running to prevent further injury to the genitourinary organs.
Combine treatment for post-gonorrhea infections caused by C. trachomatis, streptococci, and other bacteria.
Regular clinical examinations and retesting are necessary.
Medication Treatment: The primary treatment for gonorrhea is antibiotics. However, this method is most effective for patients with acute gonorrhea. When gonorrhea becomes chronic, antibiotic treatment is often less effective, and patients need to combine various methods to enhance treatment effectiveness.
Medication treatment for chronic gonorrhea only helps to stop the growth of the bacteria and cannot heal the damage caused by the disease. Therefore, patients need to be persistent and strictly follow the doctor's treatment regimen to achieve positive results.

Important Notes for Treating Chronic Gonorrhea:
Choose a reputable and quality healthcare facility with experienced specialists to ensure safety during treatment.
Opt for advanced and modern treatment methods and techniques to quickly and safely eliminate the infection, minimizing potential complications.
Early detection, diagnosis, and treatment are crucial to avoid affecting health and fertility. Follow the doctor's instructions precisely.
Ensure adequate nutrition, engage in regular physical exercise to boost the immune system, and enhance the body's resistance to harmful bacteria.
Use condoms during sexual intercourse to minimize the risk of transmitting gonorrhea to others.
If you suspect an infection, seek medical attention early to minimize potential complications from gonorrhea.
To arrange an appointment, please call … or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.