This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.According to the Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America, Crohn's disease affects more than half a million Americans. Most are diagnosed with the disease in their 20s and 30s, but some begin to show symptoms during childhood and adolescence. About 20% of cases of Crohn's disease occur in children. So, how to treat Crohn's disease in children?
1. What is Crohn's disease?
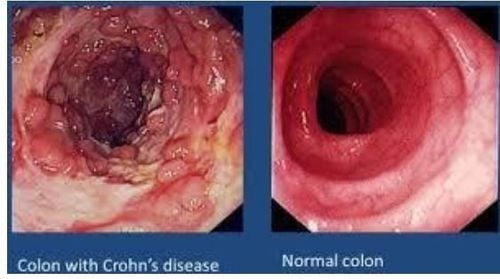
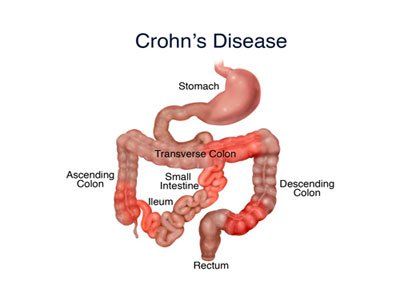
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease. According to the Crohn's & Colitis Foundation (CCF), about 780,000 Americans have the condition.Crohn's disease usually occurs in the small intestine and colon. It can affect any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus. The severity of Crohn's ranges from mild to debilitating. Symptoms vary and can change over time. In severe cases, the disease can lead to flare-ups and life-threatening complications.
Crohn's disease is an inflammatory bowel disease that causes swelling of the lining of the digestive tract, affecting the ability to properly digest food. Inflammation can lead to symptoms, including:
Abdominal cramps. Excessive diarrhea. Rectal bleeding. Fever. Tired. Anorexia. Many children are still going through puberty when they are diagnosed. This disease can slow growth and weaken bones.
Trying to combine school chores and daily activities with sudden flare-ups of Crohn's can be challenging for children. However, there are treatments that can help your child manage symptoms and deal with the effects of the disease.
2. Crohn's disease in children
Most people with Crohn's disease are diagnosed in their 20s and 30s, but IBD can also develop in children. Approximately 1 in 4 people with IBD show symptoms before age 20 (according to a 2016 review).Crohn's disease involving only the colon is common in children and adolescents. This means that it can be difficult to tell the difference between Crohn's and ulcerative colitis until the child begins to show other symptoms.
Proper treatment for Crohn's disease in children is important because untreated Crohn's disease can lead to growth retardation and weak bones. It can also cause significant psychological problems during this stage of life. The treatment of Crohn's includes:
Antibiotics. Aminosalicylates. Biological. Immune conditioning. Steroids. Change your diet. Crohn's drugs can have some significant side effects in children. Therefore, you must work closely with your child's doctor to find the right treatment plan.

3. Treatment of Crohn's Disease in Children
For young people dealing with Crohn's disease, it's important to find treatments that relieve symptoms without causing harmful side effects. Some medications may be more dangerous for children. One example is infliximab (Remicade), which is commonly used to treat Crohn's disease in adults.Infliximab may be effective in treating adults, but it has been found to cause hepatocellular T-cell carcinoma in some children, especially in children who are taking certain Crohn's medications. is different. This is a rare type of cancer that can be life-threatening. However, Remicade was recently approved by the FDA to treat children with moderate to severe Crohn's disease who have not responded well to other treatments. Your doctor will help you weigh the risks and benefits of this or any other treatment.
Ask your doctor what medicine is best to ease your child's symptoms. There are different medications that can help your child without causing serious negative effects. Sometimes, when medical treatments don't control your child's symptoms, surgery may need to be considered.
3.1. Conventional Medical Treatments Aminosalicylate: The preferred drug to treat Crohn's disease in children is aminosalicylate (5-ASAs). This is a group of drugs that can reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. Because inflammation often triggers Crohn's disease symptoms, 5-ASA can help prevent flare-ups.
However, these drugs have potential side effects; including headaches, stomach cramps, and bloating. In rare cases, children taking 5-ASAs may experience hair loss and skin rashes. The drug can also increase the risk of swelling around the heart, lungs, and pancreas.
Antibiotics: Antibiotics are also a type of medicine that can be used to treat Crohn's disease in children. Common antibiotics for Crohn's include metronidazole and ciprofloxacin (Cipro), both of which are prescribed in milder doses for children. These drugs work by suppressing inflammation in the digestive tract, helping to reduce the recurrence of symptoms.
Steroids: Steroid medications in the form of corticosteroids may also be prescribed for some children with Crohn's disease.
These drugs can cause unpleasant side effects, so they are rarely the preferred choice for long-term treatment. Corticosteroids can cause the following side effects in children:
Acne. Face swelling. Weight gain. Hair growth, hair in an unwanted position. Mood swings. Personality changes. High Blood Pressure . These side effects usually go away when the doctor lowers the dose or stops the child from using the corticosteroid.
Immunosuppressants: Immunosuppressants or drugs that suppress the immune system (such as azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine), may be used to help wean or reduce corticosteroid use.
These drugs can cause side effects such as:
Nausea. Fever. Rash. Inflammation of the liver or pancreas. Decrease in white blood cells and platelets in the blood. Immunosuppressants may increase the risk of developing lymphoma.
3.2. Treatment of Crohn's in Children Through Nutrition Diet: If you are alert to the potential side effects of these medications, manage your child's symptoms through diet and nutrition. may be the best choice. To help prevent flare-ups, you should avoid giving your child certain foods that can worsen symptoms, such as spicy foods, beans, and possibly dairy products.
Although many cases of Crohn's disease are too severe to be treated with diet alone, ensuring that your child has a balanced diet can help reduce symptoms. Make sure they eat enough lean protein, fruits and vegetables. Besides, you should give your child foods that contain soluble fiber; such as apple sauce, blueberries, and oatmeal. They may also need calcium supplements if they have weak bones due to Crohn's disease. Other vitamin and mineral supplements are also often recommended.

While this is a safe method of combating the effects of Crohn's disease, it can take a significant amount of time, causing inconvenience to many families. Talk to your child's doctor to see if EEN might be a good option for your family.
4. Outlook for Children with Crohn's Disease
Because Crohn's disease is a chronic disease, it's important to maintain a doctor's follow-up throughout your child's life. Your child will likely have periods of remission and flare-ups, which are often unpredictable. However, by working with your doctor, you can find a treatment plan that will help control your child's symptoms and limit negative effects. Studies are underway to look at new treatments that are more effective, safer, and can produce long-term or even permanent remissions.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.