This is an automatically translated article.
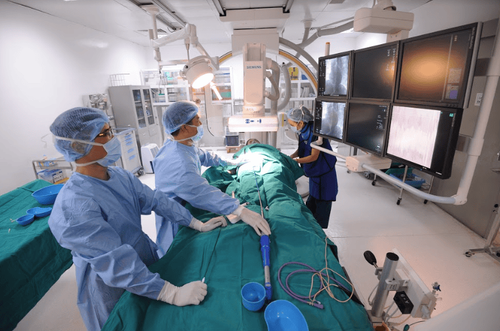
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Nguyen Van Duong - Interventional Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Coronary stenting is also known as an interventional coronary procedure. This is a minimally invasive, relatively safe and highly effective procedure in the treatment of coronary artery disease.
1. In case of coronary artery stenting
Coronary artery disease is one of the cardiovascular diseases with high incidence in Vietnam. Coronary artery disease occurs when one or more branches of the coronary arteries are narrowed/obstructed due to various causes (usually atherosclerotic plaques) resulting in the coronary arteries not being able to meet the myocardial oxygen demand. angina pectoris, even a heart attack.Angioplasty and stenting of coronary arteries are indicated in the treatment of coronary artery disease, specifically:
Stable angina unresponsive to optimal drug therapy Stable angina, but with myocardial ischemia (positive stress test or positive myocardial perfusion scintigraphy) and lesions in the coronary arteries that supply large areas of myocardium on noninvasive imaging. Unstable chest pain/acute myocardial infarction without ST elevation but high risk stratification.

Injuries not suitable for intervention (eg, unsuitable coronary anatomy, common body damage or diffuse multiple coronary arteries... ). Patients may bleed easily (low platelet count, coagulopathy, etc.) Non-adherence to treatment before and after interventional procedures. Coronary re-stenosis in many locations after intervention...
2. How does coronary stenting work?
Percutaneous coronary intervention is conducted with the following steps:The patient is explained by the doctor about the procedure, possible complications and signed a commitment to perform the procedure. Before the procedure, the patient was given antiplatelet drugs (aspirin, clopidogrel). Re-check the comorbid conditions, kidney function, medical history such as history of gastrointestinal bleeding, coagulation disorders, allergy to contrast agents..., perform some common tests. This usually includes a chest X-ray, an electrocardiogram, and blood tests.
3. Care after coronary intervention
If the procedure is successful, the patient will be asked to rest in bed for the doctor to monitor and adjust the medication. Patients can usually return to work or normal routine 1 week after coronary stenting. When going home, the patient should drink more water to prevent hypotension and kidney disease due to the effect of contrast. Avoid heavy exercise and heavy lifting for at least a day afterward. Contact your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following:Swelling or bleeding in the area where the needle was inserted and the catheter is inserted into the blood vessel. You have signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, discharge, or fever There is a change in the temperature or color of the leg or arm on the side of the procedure You have chest pain or difficulty breathing Most people who have undergone a coronary intervention will need to take dual antiplatelet drugs for at least 1 year. After 1 year, some patients will be re-evaluated by their physician and asked to continue this dual therapy or to receive aspirin or clopidogrel alone. You need to adhere to the medication prescribed by the doctor, do not change or stop the medication on your own.

4. Possible complications after coronary intervention
Although coronary stenting is a less invasive procedure than bypass surgery, it still carries certain risks:4.1 Re-stenosis in the stent During coronary intervention with drug-eluting stents, There is a small risk that the treated coronary artery may become blocked again (less than 5%). The risk of restenosis in the stent is about 10% to 20% with conventional stents.
4.2 Stent occlusion due to blood clot Blood clots can form in the stent even after the procedure. These blood clots can close an artery, causing a heart attack. That's why you need to use antiplatelet drugs after the intervention as directed by your doctor.
4.3 Bleeding You may experience bleeding in the thigh or arm area where the catheter was inserted. Usually, this simply results in a bruise, but sometimes severe bleeding occurs and blood transfusions or surgical procedures to stop the bleeding may be required.
In addition, other rare risks of angioplasty include:
Aortic dissection Coronary artery dissection: Your coronary artery may tear or burst during the procedure. If this complication occurs, your doctor may order emergency bypass surgery. Contrast-induced nephropathy: Contrast used during angioplasty and stenting can cause kidney damage, especially in people who already have kidney problems. If you're at high risk, your doctor may take steps to try to protect your kidneys, such as limiting the amount of contrast dye and making sure you're well-hydrated during treatment. Stroke: This is an extremely rare complication of angioplasty Arrhythmia: During the procedure, the heart may beat too fast or too slow. These heart rhythm problems are usually short-lived, but sometimes medication or a temporary pacemaker is needed. In summary, successful coronary intervention will help relieve symptoms and improve prognosis, but it also has certain risks. As a result, you'll need to continue with healthy lifestyle habits and take medications as prescribed by your doctor.
In April & May 2021, when there is a need for cardiovascular examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, customers will enjoy double incentives:
- Free specialist examination and 50% discount many cardiology packages such as:
+ Basic Cardiovascular Screening Package
+ Hypertension Checkup Package
+ Heart Failure Checkup Package
+ Coronary Cardiovascular Examination Package
+ Comprehensive Cardiovascular Checkup Package
- 50% off cost Fees for customers with post-examination treatment indications. The program is limited to the corresponding technique of each hospital and to customers who perform this treatment technique for the first time at Vinmec.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.