This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Interventional Cardiologists, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
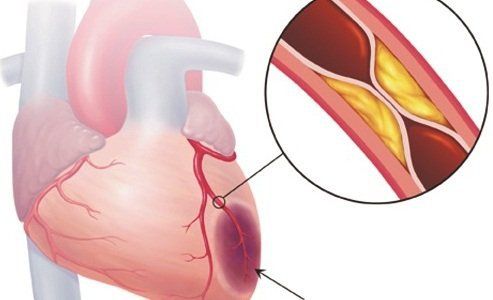
When the coronary arteries are damaged to a certain extent, the blood flow to the heart will not be enough, leading to myocardial ischemia. Therefore, patients with coronary artery disease need to be diagnosed early to have timely intervention methods. The diagnostic method by measuring the fraction of coronary flow reserve (FFR) is an invasive measure to assess myocardial ischemia accurately and effectively.
1. Ischemic heart disease caused by damage to coronary arteries
Myocardial ischemia (also known as myocardial ischemia) is a disease that occurs when blood flow to the heart is reduced, causing the heart to not receive enough oxygen needed for the contraction and ejection of the blood.
Decreased blood flow to the heart is the result of partial or complete blockage of the branches of the coronary arteries. Myocardial ischemia reduces the pumping ability of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle, in many cases leading to arrhythmias and myocardial infarction. Coronary artery stenosis can cause a heart attack.
2. Effects of coronary artery damage
Damage to the coronary arteries will cause myocardial ischemia, which can last for a long time. Patients will have chest pain, heart failure, arrhythmia and the risk of acute myocardial infarction is very high.
When the atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary arteries burst, they will completely block the coronary arteries and cause acute myocardial ischemia, myocardial necrosis (also known as acute myocardial infarction). The mortality rate from acute myocardial infarction is very high. Patients who survive acute myocardial infarction may continue to have heart failure and arrhythmias after myocardial infarction.
Complications of coronary artery disease can lead to:
Angina: When the coronary arteries are narrow, the heart may not receive enough blood when the need is greatest, especially during physical activity. This can cause angina or difficulty breathing; Heart attack: Broken and clotted cholesterol plaques that completely block a heart artery can trigger a heart attack. The lack of blood flow to the heart can damage the heart muscle. This damage depends in part on how it is treated; Heart failure: Usually occurs immediately after a myocardial infarction due to myocardial necrosis or as a result of prolonged myocardial ischemia. Manifestations of heart failure are frequent coughing, shortness of breath, fatigue; Irregular heartbeat, arrhythmia: Lack of blood to supply the heart or damage to heart tissues can interfere with the heart's electrical impulses, causing an irregular heartbeat.
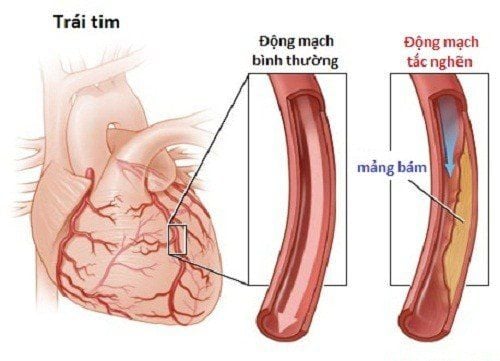
3. Evaluation of coronary artery damage by FFR . method
3.1 What is the FFR method? Although percutaneous coronary angiography is considered the standard of care in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease, this method merely helps the physician assess the degree of narrowing of the lumen without answering the question of whether the lesion is present. Does the injury cause myocardial ischemia?
Therefore, Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) is a parameter measured during coronary angiography, which helps the physician answer the question of whether the narrow lesion is present. affect coronary artery hemodynamics and require reperfusion intervention or not.
Many studies around the world have shown that the advantages of FFR method will give better long-term effectiveness than patients who do not apply FFR method. In other words, FFR is an accurate and effective invasive measure of myocardial ischemia, which is of great significance to patients with stable ischemic heart disease who have clinical chest pain symptoms. atypical.
3.2 In what cases is the FFR method indicated? This method is indicated for:
Patients with moderate coronary artery stenosis (narrowing from 40-70%) on catheter angiography images, including cases of restenosis in old coronary artery stents; Patients with multivessel coronary artery stenosis that cannot be identified as the culprit causing myocardial ischemia; Patients with diffuse stenosis at multiple sites on the same coronary artery, to determine which site is the most significant stenosis; The patient has narrowing at the bifurcation site and a decision should be made whether to intervene in the lateral branch; Follow-up after coronary angioplasty/stent intervention to evaluate outcomes and assess side effects. This method has no absolute contraindications, relative contraindications should be considered in the following cases:
Narrow lesions on the distal side are too distal unsuitable anatomically for FFR measurement; Acute myocardial infarction, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, with multiple collateral circulation, coronary artery muscle bridge... because it is difficult to accurately assess the degree of hemodynamic impact.

4. Where is the FFR fractional flow reserve measurement technique performed?
At Vinmec Hai Phong International Hospital, the coronary flow reserve fraction measurement technique is performed using an international standard coronary flow reserve fraction meter system; Modern and optimized equipment. Especially, the technique is performed by a team of highly qualified and skilled cardiologists of Vinmec Hai Phong such as:
Master. Dr. Bui Tien Dat: He received intensive training in the field of cardiology and cardiovascular resuscitation at Hanoi Medical University and Bach Mai Hospital. The doctor has more than 12 years of experience in the field of emergency resuscitation - cardiology. In addition, at Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital, Professor, Dr. Do Doan Loi comes to visit regularly. Professor, Dr. Do Doan Loi has nearly 40 years of experience in the field of examination and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, having held many important positions at major hospitals such as: Deputy Director of Bach Mai Hospital; Director of the Vietnam Heart Institute and currently a senior consultant at Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.
The strength in the examination and treatment of cardiovascular diseases of Professor, Dr. Do Doan Loi is examination, diagnosis, treatment and emergency of Cardiovascular diseases and Internal Medicine; echocardiography; directing the organization of cardiovascular intervention.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.