This is an automatically translated article.
Brain cancer is a life-threatening disease. Brain cancer occurs in both adults and children. It can develop with many different types, including both malignant and benign tumors. Finding out and detecting it early will help patients have a good chance of being treated. This article will present some methods to help diagnose brain cancer early.1. What is brain cancer?
A brain tumor is a mass or growth of abnormal cells in the brain. Many different types of brain tumors exist: Some brain tumors are noncancerous (benign) and some brain tumors are cancerous (malignant). Brain tumors can start in your brain (primary brain tumor) or cancer can start in other parts of your body and spread to your brain (secondary or metastatic brain tumor).
How quickly a brain tumor grows can vary widely. Accordingly, the growth rate and location of the brain tumor determine how it will affect the function of the nervous system
Brain tumor treatment options depend on the type of brain tumor that the patient has. , as well as its size and location. Early detection of brain cancer makes treatment more effective.
2. How to identify brain cancer
How to detect brain cancer? Doctors use many tests to find or diagnose brain tumors and learn the type of brain tumor. They also do tests to see if it has spread to another part of the body from where it started. This is called metastasis and is relatively rare for primary brain tumors. Doctors may also do tests to see which treatments might work best.
For most types of tumors, taking a sample of the tumor may be the only sure way for a doctor to know if an area of the body has a tumor. This can be done in a procedure called a biopsy or by removing part or all of the tumor with surgery. During a biopsy, the doctor takes a small sample of tissue for laboratory testing. If this is not possible, your doctor may recommend other tests to help make a more accurate diagnosis.

Có nhiều cách để xác định ung thư não
Imaging tests can help your doctor find out if the tumor is a primary brain tumor or if it is cancer that has spread to the brain from elsewhere in the body. Imaging tests show pictures of the inside of the body. Your doctor may consider these factors when choosing a diagnostic test:
Suspected tumor type Your signs and symptoms Your age and general health Results of previous medical tests Most Brain tumors are not diagnosed until symptoms appear. Usually a brain tumor is initially diagnosed by an internist or a neurologist. In addition to taking a detailed medical history and physical exam, your doctor may recommend other tests. These tests are meant to help find the presence and sometimes the type or grade of a brain tumor.
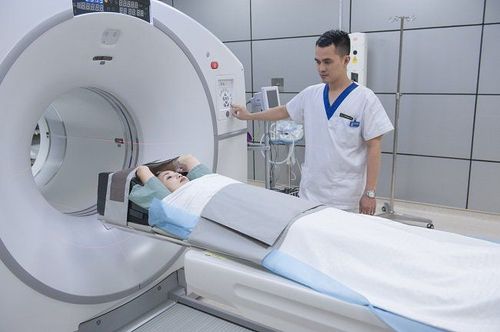
In general, the diagnosis of a brain tumor usually begins with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Once an MRI shows a tumor in the brain, the most common way to determine the type of brain tumor is to see results from a tissue sample after a biopsy or surgery.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI uses a magnetic field, not X-rays, to create detailed images of the body. An MRI can be used to measure the size of the tumor. A special dye called a contrast medium is used by the patient before the scan to create a clearer picture. This dye can be injected into a patient's vein or taken orally in pill or solution form. An MRI produces more detailed images than a CT scan and is the preferred way to diagnose brain tumors. An MRI can be of the brain, spinal cord, or both, depending on the type of tumor suspected and the likelihood that it will metastasize in the central nervous system. There are different types of MRIs. The results of the neurological exam, performed by an internist or neurologist, help determine which type of MRI to use. Intravenous (IV) gadolinium-enhanced MRI is often used to help create a clearer picture of a brain tumor. This is the first time the patient has had a conventional MRI scan and then a special contrast agent called gadolinium is injected through an IV. Then a second MRI is done to take another series of images using dye. An MRI technique called "diffuse weighted imaging" helps to show the cellular structure of the brain. Or another technique called "perfusion imaging" shows the amount of blood reaching the tumor. These methods can help your doctor predict how well treatment will work. MRI of the spine can be used to diagnose tumors on or near the spine. Functional MRI (fMRI) provides information about the location of specific areas of the brain responsible for muscle movement and speech. During the fMRI test, the patient is asked to do some work that causes changes in the brain that can be seen on the fMRI image. This test is used to help plan surgery, so the surgeon can avoid damaging functional parts of the brain while removing the tumor. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) is a test that uses MRI to provide information about the chemical composition of the brain. It can help tell the difference between any dead tissue caused by previous rounds of radiation and new tumor cells in the brain.
MRI cột sống có thể được sử dụng để chẩn đoán khối u trên hoặc gần cột sống
The health care team may also recommend other tests to help make a diagnosis or find effective treatment. However, not all of the tests listed below will be used for everyone.
CT scan . A CT scan takes pictures of the inside of the body using X-rays taken from different angles. A computer combines these images into a detailed 3-D image that shows any abnormalities or tumors. A CT scan can help find bleeding and enlargement of fluid-filled spaces in the brain, called ventricles. Changes to the bones in the skull can also be seen on a CT scan and it can be used to measure tumor size. A CT scan may also be used if the patient cannot have an MRI, such as if the patient has a pacemaker. Sometimes a contrast medium is given before scanning to provide finer detail on the image. This dye can be injected into a patient's vein or taken orally as a pill or liquid to swallow. Positron emission tomography (PET) or PET-CT scan. First, a PET scan is used to learn more about the tumor while the patient is undergoing treatment. It may also be used if the tumor recurs after treatment. A PET scan is often combined with a CT scan, known as a PET-CT scan. However, you may hear your doctor refer to the procedure as a PET scan. A PET scan is a way to create images of organs and tissues inside the body using different substances, such as sugars or proteins. A small amount of radioactive material is injected into the patient's body. This substance is taken up by actively dividing cells. Because tumor cells are more likely to be dividing actively, they absorb more radioactive material. A scanner then detects the substance to create images of the inside of the body. Cerebral angiogram: A cerebral angiogram is an X-ray picture, or series of X-rays, of the head that shows the arteries in the brain. X-rays are taken after a special dye called contrast medium is injected into the main arteries of the patient's head. Lumbar puncture or spinal tap: Lumbar puncture is a procedure in which a needle is used to obtain a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to look for tumor cells, blood, or tumor markers. . Tumor markers or biomarkers are substances found in higher than normal amounts in the blood, urine, spinal fluid, plasma, or other body fluids of people with certain types of tumors . Usually, a local anesthetic is given to numb the patient's lower back before the procedure.
Điện não đồ là một xét nghiệm không xâm lấn, trong đó các điện cực được gắn vào bên ngoài đầu của một người để đo hoạt động điện của não
Take bone marrow . Your doctor may recommend a myelogram to find out if the tumor has spread to the spinal fluid, other parts of the brain, or the spinal cord. Myelograms use dye that is injected into the cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds the spinal cord. The dye shows up on X-rays and can outline the spinal cord to help your doctor find a tumor. This is rarely done; lumbar puncture is more common. Molecular testing of the tumor: Your doctor may recommend that you perform laboratory tests on a tumor sample to identify genes, proteins, and other factors, such as tumor markers, tumor only. Certain biomarkers can help doctors determine a patient's prognosis, which is the chance of recovery. Researchers are examining biomarkers to find ways to diagnose brain tumors before symptoms begin. The results of these tests can help determine treatment options. Signs commonly considered for brain tumors include: For oligodendrogliomas, loss of the p arm of chromosome 1 and loss of the q arm of chromosome 19. This is called a 1p/19q co-loss. It is associated with more successful treatment, especially with chemotherapy. It can be used to help plan treatment, especially for non-productive lipomas. A mutation in the isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) gene, found in about 70% to 80% of low-grade gliomas in adults. Higher grade tumors may also have mutations in the IDH gene, which suggests that these start as lower grade tumors becoming higher grade. This mutation is associated with a better prognosis in both low-grade and high-grade tumors. In glioblastoma, whether a gene called methyl guanine methyl transferase (MGMT) is changed can help doctors understand a patient's prognosis and how effective treatment will be. Its role in determining the benefit of a treatment is being tested in clinical trials.

Các xét nghiệm hình ảnh chẩn đoán u não
Nerve, vision and hearing tests: These tests help determine if the tumor is affecting brain function. An eye exam can detect changes to the optic nerve, as well as changes to a person's field of vision. Neurocognitive Assessment: This includes a detailed assessment of all major brain functions, such as memory storage and retrieval, expressive and receptive language abilities, computation, dexterity and overall condition of the patient. These tests are performed by a licensed clinical neuropsychologist. This specialist will write a formal report to compare with future assessments or identify specific problems that can be helped through treatment. Electroencephalogram (EEG): An electroencephalogram is a noninvasive test in which electrodes are attached to the outside of a person's head to measure the brain's electrical activity. It is used to monitor possible seizures. Induced Potentials: Evoked potentials involve the use of electrodes to measure the electrical activity of nerves and can often detect acoustic cell tumor, a noncancerous brain tumor. . This test can be used as a guide when removing a growing tumor around important nerves. After diagnostic tests for a brain tumor are done, your doctor will review all test results with you. If the diagnosis is a brain tumor, additional tests will be done to learn more about the tumor. The results help your doctor describe the tumor and plan your treatment.
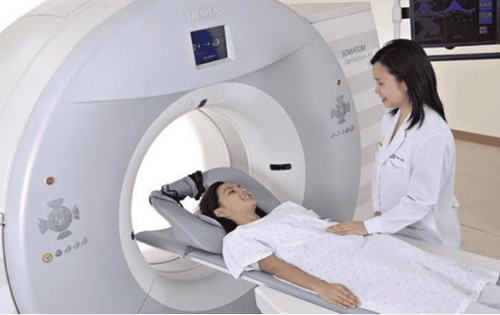
Tại Bệnh viện Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec trang bị đầy đủ hệ thống máy móc y tế chẩn đoán ung thư não
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has been and continues to be fully equipped with modern diagnostic facilities such as: PET/CT, SPECT/CT, MRI... biology, immunohistochemistry, genetic testing, molecular biology testing, as well as a full range of targeted drugs, the most advanced immunotherapy drugs in cancer treatment.
After having an accurate diagnosis of the disease, the stage, the patient will be consulted to choose the most appropriate and effective treatment methods. The treatment process is always closely coordinated with many specialties: Diagnostic Imaging, Biochemistry, Immunology, Cardiology, Stem Cell and Gene Technology; Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Department of Endocrinology, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Psychology, Department of Nutrition... to bring the highest efficiency and comfort to patients. After undergoing the treatment phase, the patient will also be monitored and re-examined to determine whether the cancer treatment is effective or not.
Especially, now to improve service quality, Vinmec also deploys many cancer screening packages that can help customers detect cancer early before there are no symptoms, bringing a better prognosis. treatment and a high chance of recovery.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: mayoclinic.org, cancer.net
MORE:
Glioblastoma: What you need to know Brain cancer: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Brain tumor: What you need to know