This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Trinh Le Hong Minh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging.Traumatic brain injury is the leading cause of death among all types of trauma, especially in developing countries like Vietnam. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment contribute significantly to limiting complications and mortality of the disease. Currently, computed tomography is an effective tool for doctors in the diagnosis and treatment of traumatic brain injury.
1. What is computed tomography?
Computed tomography is an imaging method that uses many X-rays to scan an area of the body in a cross-section, in collaboration with a computer to produce 2-D or 3-D images of a part of the body. body. Thanks to its high resolution and cross-sectional view, computed tomography is very popular for indications for brain lesions such as: intracranial hematoma, traumatic brain injury, foci. infarction, brain tumor, brain abscess, blockage of cerebrospinal fluid circulation.Computed tomography in traumatic brain injury usually has 3 imaging methods including:
2. How does traumatic brain injury produce computed tomography images?
Patients with traumatic brain injury may have some corresponding images on computed tomography as follows:2.1. Image of bone lesions Image of bone lesions showing fractures, fractures, subsidence of skull bones and facial mass
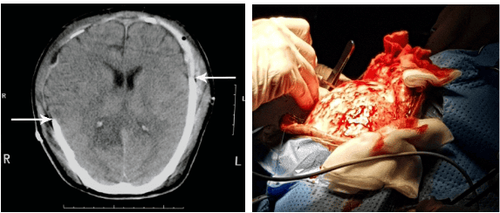
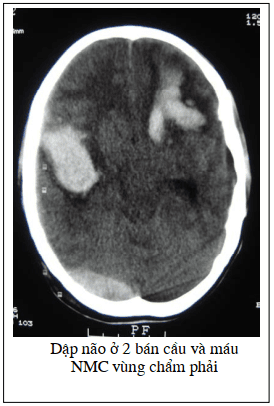
Epidural hematoma: manifested by an area of increased density located close to the plate in the skull, with a penetrating form. double-convex glass. One side is convex close to the inner surface of the skull, the other face towards the brain parenchyma. The hematoma is often clearly seen in the early days, if left untreated for a long time, it can be liquefied, causing the density to become homogenous or lower than that of brain tissue. Small-sized hematomas can be absorbed. Subdural hematoma: manifested by increased density in the shape of a crescent, the convex side is close to the plate in the skull, the concave side is towards the brain tissue. The subdural hematoma initially has the same density as the epidural hematoma, but is later absorbed and degraded to form an area of co-densification or hypoattenuation with brain tissue called a chronic hematoma. 2.3. Image of brain contusion in trauma Image of brain contusion in trauma is an image between an area of brain tissue that is reduced in density due to edema, with nodules that increase density in the form of hemorrhagic type, and the lesions have a space-occupying effect due to cerebral edema . The cause is usually brain tissue hemorrhage in trauma in the area of the brain adjacent to the skull corresponding to the area of the skull being impacted. However, in a few cases, the damaged brain area is opposite to the impact site according to the mechanism of force feedback in traumatic brain injury.
2.5. Image of pneumothorax in the brain Image of pneumothorax in the brain caused by a skull fracture accompanied by a tear in the dura, allowing air to enter the brain.
Brain CT scan allows to detect and diagnose traumatic brain injury as well as different brain pathologies.
Vinmec International General Hospital is proud to be one of the hospital systems in the country that has invested in modern CT scanners with a team of doctors who are leading experts who can conduct imaging and diagnosis. , detect cranial pathologies and brain injury images are sharp and effective, providing the highest chance of treatment for patients.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.