This is an automatically translated article.
Thyroid plays a major role in regulating metabolism and ensuring good human health. If the body needs more energy in certain situations, it will produce more thyroid hormone.
1. What is the thyroid gland?
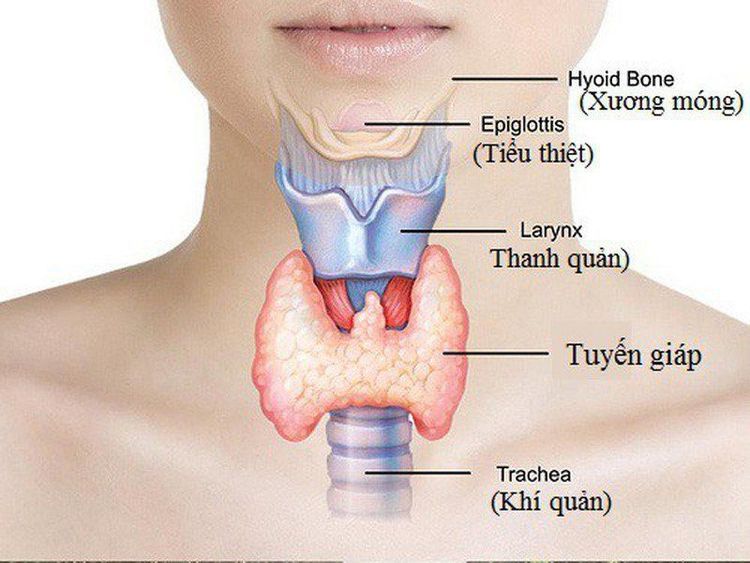
The thyroid gland is an important hormone gland, which plays a role in metabolism, growth and development of the human body. It helps regulate many body functions by continuously releasing a steady amount of thyroid hormones into the bloodstream. If the body needs more energy in certain situations (for example, cold or during pregnancy), the thyroid gland produces more hormones.This organ is found on the front of the neck, below the dialog box. It is butterfly-shaped, with two lateral lobes resting on and around the trachea, connected anteriorly by a narrow band of tissue.
The average thyroid weighs between 20 and 60 grams. It is surrounded by two fibrous capsules. The outer capsule is connected to the voice box muscles and many important blood vessels and nerves. There is loose connective tissue between the inside and outside of the cyst, so the thyroid can move and change its position when we swallow.
Thyroid tissue itself consists of many individual lobules enclosed in thin layers of connective tissue. These lobules contain a large number of small sacs (vesicles) called follicles that contain thyroid hormones in the form of droplets.
Một lượng ổn định các hormon tuyến giáp sẽ được giải phóng vào máu
2. What hormone does the thyroid gland secrete?
The thyroid gland produces the following three hormones:
- Triiodothyronine hormone (also known as T3)
- Tetraiodothyronine hormone (also known as thyroxine or T4)
- Calcitonin hormone
Strictly speaking, only T3 and T4 is the appropriate thyroid hormone. They are produced in the follicular epithelial cells of the thyroid gland.
Iodine is one of the main building blocks of both of these thyroid hormones. Our bodies cannot produce iodine, so we need to get enough in our diet. Iodine is absorbed into the bloodstream from food in the intestines. It is then taken to the thyroid gland, where it is ultimately used to make thyroid hormones.
Sometimes our body needs more or less thyroid hormone. To make the correct amount of hormone, the thyroid gland needs the help of another gland, the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland "notifies" the thyroid gland about how much or how little hormone to release into the bloodstream. Therefore, the pituitary gland is considered a thyroid-stimulating hormone. In addition, a certain amount of thyroid hormone is attached to transport proteins in the blood. If the body needs more hormones, T3 and T4 can be released from the proteins in the blood and do their job.
The third hormone produced by the thyroid gland is called calcitonin. Calcitonin is produced by C cells. It is involved in calcium and bone metabolism.
T3 and T4 increase basal metabolic rate. They make all the cells in the body work harder, so the cells also need more energy. This has the following effects, for example:
- Body temperature rises;
- Faster heart rate;
- Food is used up quickly because the energy stored in the liver and muscles is broken down;
- Adult brain (in children);
- Accelerated growth (in children);
- Activation of the nervous system leads to improved concentration and faster reflexes.
3. What is thyroid hormone function?
The function of thyroid hormone is to take iodine found in many foods and convert it into thyroid hormones such as: Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroid cells are the only cells in the body that can absorb iodine. These cells combine iodine and the amino acid tyrosine to make T3 and T4. T3 and T4 are then released into the bloodstream and transported throughout the body, where they control metabolism (converting oxygen and calories into energy).
Mất cân bằng hormon tuyến giáp có thể ảnh hưởng sâu đến hầu hết mọi khía cạnh sức khỏe của bạn
4. Thyroid hormone imbalance
An overactive thyroid (also known as hyperthyroidism) occurs if the thyroid gland makes too much hormone. This condition is an abnormal function of the thyroid gland. The hormones produced by the thyroid gland are T4 and T3, which play an important role in the functioning of the body. For this reason, when there's an imbalance, such as a high T4, it can profoundly affect almost every aspect of your health.If the thyroid gland is underactive (hypothyroidism) it means it is not producing enough hormones. Since the main purpose of thyroid hormone is to "regulate the body's metabolism", people with this condition will have symptoms related to a slow metabolism.
The thyroid gland can also grow in size. Sometimes the entire thyroid gland becomes enlarged (diffuse goiter) or individual lumps called nodules develop in the gland (nodular goiter). A special test called a thyroid scan can be used to see if the nodules are producing abnormal amounts of hormones. If they make more hormones than the rest of the thyroid tissue, they are called "hot" nodules. If they produce less, they are called "cold" notes.
In a nutshell, the thyroid gland helps regulate many body functions by continuously releasing a steady amount of hormones into the bloodstream. If the body needs more energy in certain situations, the thyroid gland produces more hormones. In most cases, an enlarged thyroid or nodules isn't caused by anything serious. But it's still best to see your doctor if you notice any changes in your thyroid.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.