This is an automatically translated article.
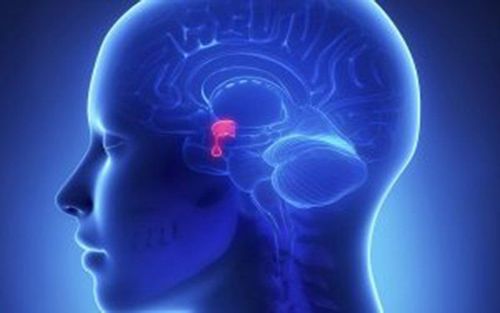
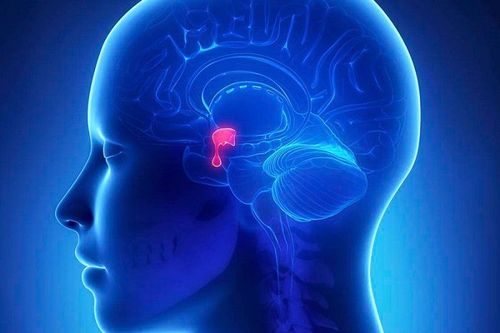
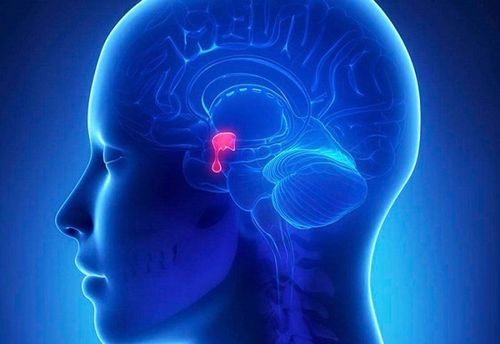
Pathological pituitary tumors usually account for about 10% of intracranial tumors. Most pituitary tumors are benign, arising from the anterior pituitary gland (posterior pituitary tumors are also present but are very rare).
1. Why need surgery for pituitary tumor?
Pituitary tumors are most common in the 30-40 years old and there is no difference in the sexes. Patients often feel the pressure of the tumor causing headaches, dizziness, nausea, temporal hemiparesis, drooping eyelids... or endocrine problems such as menstrual disorders, lactation in women and lactation. sexual dysfunction in men. There are also signs such as hypertension, acromegaly, diabetes insipidus...
Based on clinical signs combined with endocrine tests, observing tumor images on magnetic resonance.. .the doctor will consider the appropriate treatment for the patient. The treatment options available are pituitary surgery, radiation therapy, or medical therapy.
Currently, with the development of technology such as Navigator nerve positioning system, endoscopic system, microsurgery glass, the form of pituitary tumor surgery by craniotomy is more and more widely indicated and provide positive results for the patient.
Indications for surgery for pituitary tumor: The tumor of the pituitary gland is large, grows upward, posteriorly or laterally, and invades the cavernous sinus or the temporal base.

U tuyến yên có thể gây ra tăng huyết áp
2. Pre-operative preparation for pituitary tumor by craniotomy
Before surgery, the patient will be carefully examined clinically including:
Specialist assessment of eyes, endocrinology, otolaryngology... CT scan, brain magnetic resonance imaging to assess the structure skull base Perform preoperative anesthetic examination as prescribed. After that, the patient is shaved or washed, cleaned and disinfected the surgical area. The composition of the surgical team consists of 7-8 people including:
1 main surgeon and 2 assistant surgeons. 1 nurse serves equipment for the surgeon, 1 nurse runs outside. 1 anesthesiologist, 1 nurse anesthetist. Instruments and instruments used in surgery include:
System of equipment to conduct endotracheal anesthesia and monitor patients during and after surgery. The operating table has a Mayfield head mounting system. Drilling machine, Navigation system, microsurgery glasses, Sonopet ultrasound knife, cranial microsurgery kit. Consumables: gauze, skull cotton, skull wax, 4/0 or 5/0 prolene thread, 2/0 vicryl thread, Surgicel hemostatic gauze, spongel hemostatic sponge... Skull pin or maxillofacial screw, glue Floseal biological hemostasis, closed subcutaneous drainage.
3. Procedure for pituitary tumor surgery
At the beginning of surgery, depending on the tumor location, the patient is placed in the supine position, with the head straight or slightly tilted to the left. The patient's head is securely fixed to the Mayfield head mount. The anesthesiologist then administers endotracheal anesthesia.
Steps of surgery for pituitary tumor
Step 1: Registering the nerve positioning system (Neuronavigation) Step 2: Thoroughly disinfect the surgical area, numb the skin incision area (on the right eyebrow or hairline on the right forehead) ). Step 3: Make skin incision, separate muscle fascia, periosteum to reveal skull bone. Step 4: Open the skull cap with a machine drill (through the forehead or the right keyhole) Step 5: Open the arcuate dura, the subarachnoid space to aspirate less cerebrospinal fluid so that the brain collapses. Place the brain valve (if necessary), put in the microsurgery. Step 6: Identify the optic nerve, ipsilateral carotid artery area, dissect the arachnoid toward the midline to determine the optic interference. Step 7: Use a drill to grind the bone at the top of the eye socket, expand it with the trigger. Step 8: Surgically separate the tumor from the nerves and blood vessels (if necessary). Partial removal of the tumor with microsurgery scissors or ultrasound knife. Send a portion of the tumor sample for immediate biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and give appropriate treatment. Step 9: During surgery, use Navigation to determine the position of the correlation between the tumor and the nerves and blood vessels. Hemostasis with bipolar electric knife, Surgicel gauze or Floseal glue Step 10: Close the dura with 5/0 prolene suture, suspend the dura, and reset the bone. Place surgical drainage if necessary, secure the skull cap with pins or maxillofacial screws. Close the incision and end the operation.
4. Monitoring and treatment after surgery
Monitor vital signs: Monitor the patient's respiratory, pulse, blood pressure, circulation, endocrine, temperature, liver and kidney function... to assess vital signs. . Nerve signal monitoring: Assess the patient's nerve signals based on the following criteria: Assessment of consciousness: based on the Glasgow coma scale Assessment of arm and leg mobility Observe pupil size , round or distorted shape, reflexes to light Function assessment of other cranial nerves: VIII nerve palsy (hearing loss, tinnitus, deafness), peripheral VII nerve palsy (face distortion), aspiration swallowing , choking, hoarse speech (IX cord paralysis)
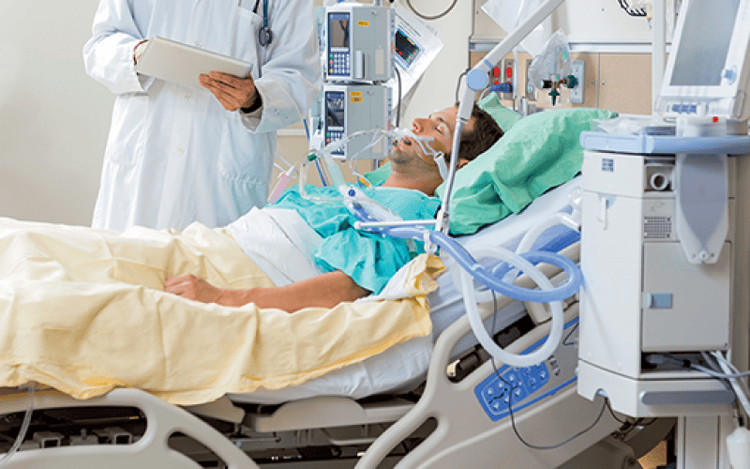
Sau phẫu thuật người bệnh cần được theo dõi cẩn thận để tránh các tai biến
5. Complications and post-operative treatment
After surgery for pituitary tumor by opening the skull cap, some risks can still occur leading to complications. Some common complications after surgery may include:
Postoperative cerebral hemorrhage: The surgical process may inadvertently affect large arteries or small blood vessels... leading to post-operative bleeding. surgery. In this case, it is possible to manage according to the bleeding lesion and consider surgical removal of the hematoma if necessary. Ventricular dilation: A condition in which cerebrospinal fluid is blocked and accumulates too much (possibly due to bleeding or hemorrhage). The solution is to drain the ventricles out or into the abdomen. Infection, brain abscess, meningitis: For this infection, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics according to the antibiotic chart if blood cultures, cerebrospinal fluid show bacteria. In the case of the test, there is no bacteria but there is evidence of bacteria using the 3rd or 4th generation in combination with Vancomycin or Glycoside groups. Diabetes insipidus or adrenal insufficiency : The doctor may prescribe medication (hormone replacement), extra water, electrolytes. Cerebrospinal fluid leak: is a complication that occurs when cerebrospinal fluid flows from the skull to the outside through the patient's nostrils or ears. To treat, it is necessary to drain the lumbar spinal cord from 4-5 days until the leak is gone, and the incision is enhanced with stitches. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely rest in peace. examination and treatment center at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Pituitary tumors: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Pituitary tumors: When is hormone replacement therapy needed? Measures to treat pituitary tumors