This is an automatically translated article.
In the event of an accident that injures or breaks a blood vessel, blood clotting and hemostasis occur rapidly to respond and closely control the damaged area.1. East, what is hemostasis?
Coagulation and hemostasis is a condition in which a soluble protein in the blood is converted into a solid gene fibrin to fill the damaged vessel wall, in order to limit blood loss, prevent bleeding, and at the same time , which helps maintain blood in a liquid state.In the event of an accident that injures or breaks a blood vessel, blood clotting and hemostasis take place quickly to respond and closely control the damaged area.

Khi xảy ra tai nạn làm tổn thương hoặc đứt mạch máu, quá trình đông máu và cầm máu diễn ra nhanh chóng để đáp ứng và kiểm soát chặt chẽ vùng bị tổn thương
2. How does blood clotting take place?
The process of coagulation and hemostasis is an interaction between three factors including: vessel wall, blood cells and plasma proteins. The process takes place under the regulation of nerves and humors, and at the same time ensures the balance of the two systems, that is:Coagulation: Protects the body from bleeding and blood loss. Anti-clotting: Ensures blood vessel circulation and circulation, helping the body maintain life. In order to seal the damaged area and stop bleeding, the process of blood clotting and hemostasis in the body takes place in four main stages:
Vasoconstriction (also known as primary hemostasis) Formation of a urinary plug platelets Coagulation Hemolysis (also called fibrinolysis) 2.1 Vasoconstriction Hemostasis occurs as soon as the blood vessel wall is damaged. Under the influence of the nerve mechanism that indicates pain and endothelial cells release fluid, the vasoconstrictor reflex takes place first to reduce the flow rate of blood flow, temporarily stopping bleeding to avoid injury. injury to the vessel wall, and at the same time facilitates the adhesion of platelets to the vessel wall.
For small blood vessels as well as capillaries, the vasoconstrictor reflex is important for hemostasis. If the vessel wall is severely damaged, the vasoconstriction reflex will be stronger, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. During vasoconstriction, the body also immediately begins the process of platelet plug formation and blood clotting.
2.2 Formation of platelet plugs When the vessel wall is damaged, platelet aggregation immediately occurs. With a rough surface and electrostatic attraction, the submucosa is exposed when the vessel wall is damaged, facilitating easy platelet adhesion. After adhesion, platelets are reshaped and activated, releasing platelet-aggregating substances and forming a platelet plug. Within minutes, the platelet plug has grown in size so that it can quickly fill the damaged blood vessel.
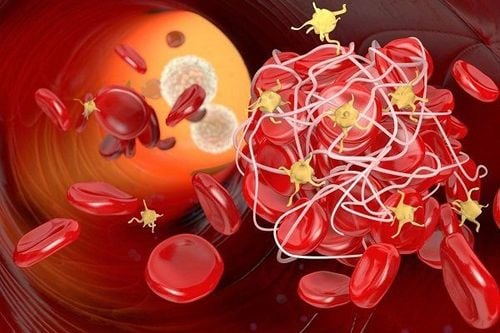
Khi tổn thương lớn thì cần phải có cục máu đông hình thành
2.3 Coagulation Coagulation is the process by which blood changes from liquid to solid when blood vessels are damaged. Coagulation is influenced by more than 50 substances and consists of a sequence of reactions that occur in succession in the following order:
Formation of a prothrombinase complex (activated thromboplastin) via endogenous and exogenous pathways Formation thrombin Formation of fibrin Coagulation is initiated through two routes: endogenous - plasma in contact with the negatively charged subendothelial layer (when the vessel wall is damaged and exposing the subendothelial layer) and exogenous - organizational factors involved in direct activation. The result is a prothrombinase complex.
The process of thrombin formation after the prothrombinase complex is established takes place rapidly. Thrombin plays a very important role in coagulation and hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and activating fibrinolytic factors. When thrombin is formed, positive upregulation also occurs to produce more thrombin, allowing clotting to continue until a blocking mechanism occurs.
When thrombin is formed, it hydrolyzes fibrinogen to produce fibrin monomer, the fibrin monomers polymerize together to form fibrin filaments to lead to the formation of a blood clot network. The clot network is a stable gel-like mass that holds red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
A blood clot is formed to prevent bleeding and help stop bleeding. However, it then shrinks under the action of platelets, and at the same time it produces serum. Unlike plasma, serum does not contain clotting factors. The clot shrinks to help seal the wound more tightly and stabilize blood flow.
2.4 Hemolysis After a blood clot fills the damaged blood vessel area, it will be scarified, then dissolve to allow the vessel lumen to open, blood vessels to continue circulating to ensure the nourishment of the tissues. function below the injured area.
3. Common coagulation and hemostasis disorders
Bệnh ưa chảy máu - Hemophilia là một trong những rối loạn đông máu thường gặp
Vitamin K deficiency: Vitamin K plays an important role in the synthesis of clotting factors in the liver. Therefore, if vitamin K deficiency will cause bleeding. Hemophilia: This is an inherited chromosomal disease caused by a lack of clotting factors, usually discovered after an injury. Primary thrombocytopenia: Symptoms of the disease are the appearance of many red, bleeding spots all over the body. Thrombosis: When there is atherosclerosis, slow blood flow, trauma, or infection, blood clots will cause a blood vessel embolism. Intravascular coagulation: Inability to maintain hemostasis due to deficiency of coagulation factors. Physiology of hemostasis in the body is very important, helping to stop bleeding and heal damaged blood vessels.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE ALSO:
Mistakes in first aid for nosebleeds Treatment of hemophilia Tests to help assess the ability to clot, stop bleeding