This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor I Huynh Kim Long - Emergency Resuscitation Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.The principle of treatment of vascular wounds is to give first aid to the wound properly and quickly to maintain the patient's vital function. First aid for vascular wounds needs to be urgently because the longer, the delay, a volume of blood is lost, over time will lose a lot of blood and lead to shock and death for the injured person.
1. What is a vascular wound?
Vascular wounds are wounds with cuts, tears, and loss of major blood vessels in different parts of the body, causing massive bleeding, which can lead to rapid death if not treated promptly. . A soft wound with a large area, crushing the tissue causing bleeding, losing a lot of blood, and quickly should be considered as a vascular wound.Vascular wounds are a common surgical emergency in life, at work, in daily life,... The immediate application of first aid measures to vascular wounds to temporarily stop bleeding is necessary to save lives. injured person's life.
Vascular wounds are classified according to the following types:
Causes: Found in daily life and activities due to trauma, sharp objects such as knives, scissors, glass fragments; due to bullets or metal fragments, infections caused by injections that cause rupture of blood vessels,...

Properties: Simple vascular wound; combined vascular injury (with nerve, bone, muscle damage,...)
2. How dangerous is a vascular wound?
Vascular wounds can cause rapid death from causes such as hemorrhagic shock due to not providing timely first aid; toxic shock due to anaerobic metabolism; cause specific infections (bacteremia, gas gangrene; tetanus). Therefore, it is very important to recognize the symptoms for timely intervention.Vascular wounds do not have to bleed, because there are many types of vascular wounds that have stopped bleeding. Therefore, the clinical examination can detect vascular wounds thanks to signs such as:
There are white or gaseous wounds in the right path of the blood vessels; when the patient is injured, there is red bleeding through the wound; Hematoma around the wound, typically when the hematoma is widespread and pulsating with the heart rate, local murmurs are heard and palpation is palpable.
Peripheral ischemic signs appear ( by careful examination and comparison with the contralateral limb): Cold extremities, decreased movement and sensation; Peripheral pulse decreased or lost; Oxygen saturation in the proximal limb decreased (SaO2).
3. First aid for vascular wounds
Accordingly, the principle of treatment of vascular wounds is to give first aid to vascular wounds properly and quickly to maintain vital functions for the patient.3.1. Principles when giving first aid to vascular wounds First aid for vascular wounds should be urgent and quick: This principle is aimed at stopping bleeding, because the longer it takes, the more it is delayed, a volume of blood is lost. Over time, it will lose a lot of blood and lead to shock and death for the injured person.
First aid for vascular wounds requires proper hemostasis according to the nature of the wound: Depending on the bleeding nature of each wound, give appropriate first aid measures to stop bleeding such as: Bandage for puncture wounds, cuts deep blood vessels; compression bandages for wounds that crush large muscle blocks...

When placing the tourniquet, loosen the tourniquet every hour for a few minutes to allow blood to flow down to nourish the lower part of the wound, then re-tie the tourniquet when the blood starts to flow again.
The tourniquet should only be placed in the following cases: The limb is crushed and cannot be preserved; place the tourniquet at the site of the accident, but near a hospital, where the patient transport time to the hospital is less than one hour; temporarily placed for a short time in preparation for surgery.
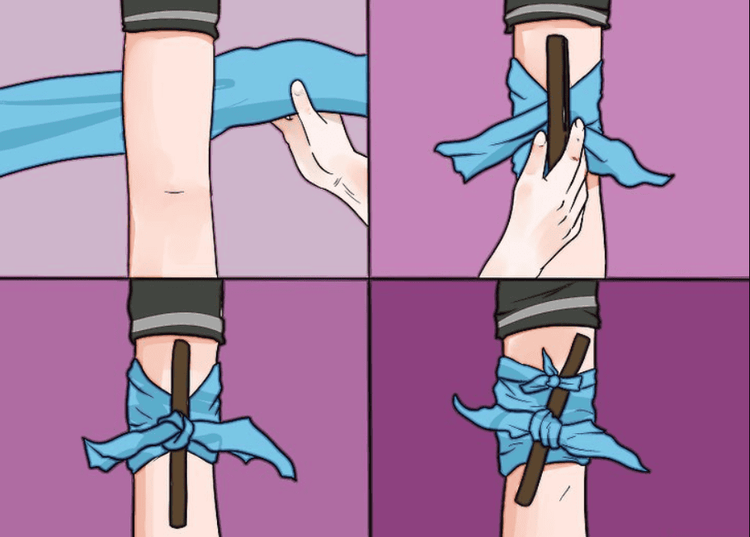
Pressure bandage to stop bleeding: This method uses a bandage or a towel folded into a small lump to place on the wound. wound and apply pressure on top to stop bleeding, wrap the bandage tightly around the limb until no blood seeps into the bandage.
The best hemostatic dressing is to use an elastic bandage. This method is simple and easy to perform, has a good hemostatic effect and does not cause bad consequences for the injured area.
This method is fast, easy to do, good hemostasis. However, it will cause pain for the victim, can not be done for a long time, and cannot be applied in cases of accompanying fractures.
Vascular wound is a surgical emergency. After giving proper first aid to a vascular wound, the patient must be promptly taken to a qualified emergency center.
Surgical ligation of the great peripheral blood vessels is one of the necessary indications to promptly prevent the consequences of acute peripheral vascular injury, including arterial wounds, vascular trauma. peripheral blood and limb artery occlusion. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in diagnosing and treating large peripheral blood vessels effectively best.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.