This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vo Thien Ngon - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital
A man's body is constantly making sperm, but this regeneration is not instantaneous, it takes a certain process. On average, it takes a man about 74 days to fully produce sperm. This process of sperm formation is called spermatogenesis.
1. Where is sperm produced?
In humans, sperm are male gametes, carrying a haploid set of 23 chromosomes. During fertilization, the 23 chromosomes of the sperm combine with the 23 chromosomes of the egg to form a zygote with 46 chromosomes and develop into a complete individual. Sperm are highly differentiated to perform its reproductive function, which is to travel in the female reproductive tract, to recognize and fertilize an egg.Sperm are produced in the testicles, in small tightly coiled tubes called seminiferous tubules. The total length of these pipes is up to 250m. Located between the seminiferous tubules are Leydig cells that produce the male sex hormone testosterone.
2. How is sperm formed?
The process of spermatogenesis begins with stem cells, called spermatocytes. As males enter puberty, the spermatozoa will begin to divide many times and differentiate to produce sperm cells.Sperm are born from spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules, then move into the epididymis to undergo maturation before ejaculation.
When a man is sexually aroused, the process of ejaculation begins. From the epididymis, sperm are released along the vas deferens, then mixed with secretions of the prostate gland (accounting for 30%), seminal vesicles (accounting for 60%), and urethral bulbous glands (accounting for 10%). and finally expelled through the urethra. If ejaculation does not occur, the sperm dies and is absorbed by the epididymis of the epididymis.
The process of spermatogenesis begins at puberty and continues continuously until death. This is a very efficient process with several tens to several hundred million sperms being produced in each testicle. However, fertilization is an ineffective process, when dozens or hundreds of sperm are released into the female reproductive tract, but in the end, only 1 sperm is actually fertilized with an egg. Therefore, the risk of male infertility will increase if spermatogenesis is impaired, leading to a decrease in sperm quality and quantity.
3. What is the structure of sperm?
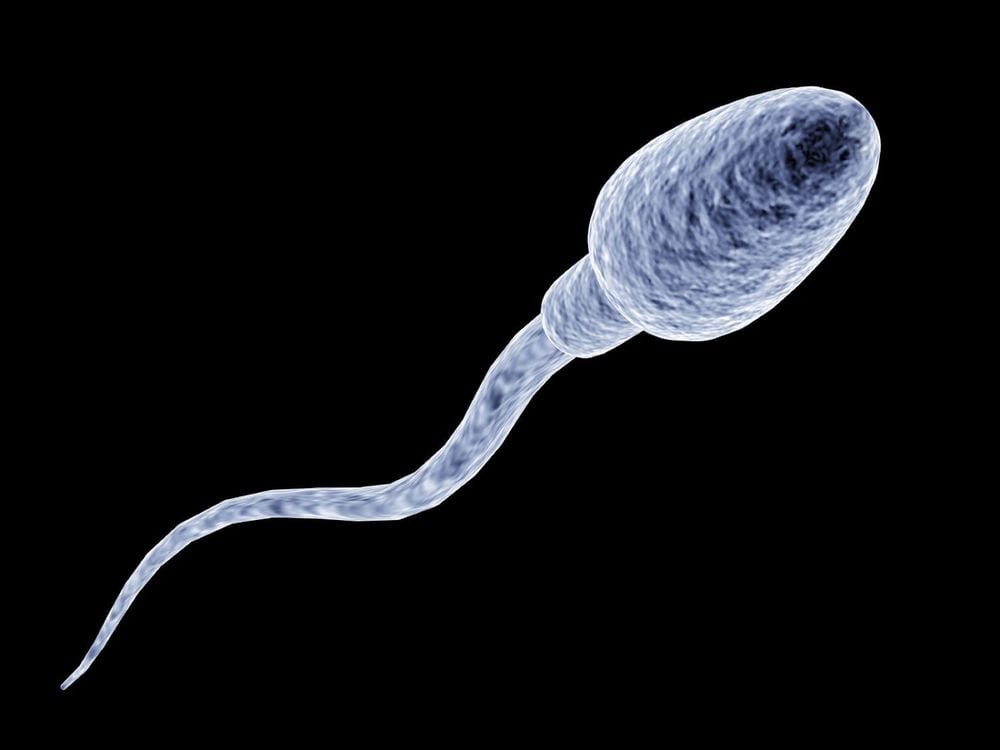
Mature sperm are about 50 - 60 μm long and have 3 parts: head, neck and tail.Sperm head The head of the sperm is shaped like a flat teardrop, inside contains a nucleus carrying a haploid set of chromosomes (1n), 23 chromosomes including 1 sex chromosome (X or Y) ). Each sperm has a unique set of genes.
Above the nucleus, there is a cap-shaped polar bag, containing enzymes that destroy obstacles around the egg and the outer membrane of the egg, helping sperm penetrate inside to fertilize the egg.
Sperm neck This is the part between the head and tail. The neck of the sperm is very soft, making it easy for the head to turn from side to side like a swimming motion.
Sperm tail Sperm tail is divided into 3 segments: middle, main and terminal. The middle segment is the largest part of the tail containing mitochondria, which use glucose and fructose to generate energy for sperm to move. At the end, the dense filaments and caudal sheath become thinner, leaving only a thin layer of cells covering the end of the tail. The tail is thin and tapered so that the sperm can wag their tail and swim smoothly.
4. How long does spermatogenesis take?
The entire development from spermatozoa to spermatozoa is about 70 days. After that, sperm must spend an additional 12-21 days in the epididymis to mature functionally. Thus, the total time for a complete spermatogenesis process is from 10-12 weeks.5. Number of sperms produced per day
As noted above, spermatogenesis is a very efficient process. Every day, several hundred million sperm are produced from each testicle. When pushed out of the penis through the urethra (ejaculation), the number of sperm in semen can be as high as 500 million.6. Factors affecting spermatogenesis
Based on clinical practice, in most cases it is difficult to determine the exact cause of the decrease in sperm count and quality, leading to difficulties in treating infertility. However, being aware of the spermatogenesis process as well as the factors affecting it has also been of great help to increase the effectiveness of treatment.6.1 Diet A diet lacking in substances such as vitamin A, vitamin E, some amino acids, fatty acids and zinc can directly affect sperm formation, leading to a decrease in sperm count and In addition, recently there are many views that today's food often contains chemical radicals with weak estrogenic properties, which accumulate for a long time and inhibit spermatogenesis.

6.3 Temperature The temperature in the scrotum is usually about 2 degrees Celsius lower than the body, which is an ideal condition for normal spermatogenesis. In men with undescended testicles, if surgery is not performed early between the ages of 1-3 years to bring the testicles down to the scrotum, the histological structure of the testicles will be changed, even the seminiferous tubules will be atrophied. slap. At this time, spermatogenesis will be stopped or completely lost.
Many studies also show that increased temperature can reduce spermatogenesis and increase the rate of malformed sperm. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), men with a fever above 38.5 degrees Celsius can inhibit spermatogenesis for 6 months, resulting in low sperm count and poor quality. In addition, high temperature also damages the DNA of sperm. A 1988 study by Thonneau et al. reported that increasing temperature reduced spermatogenesis and increased the likelihood of sperm malformations. Research suggests that drivers who drive long distances are at risk of reduced spermatogenesis and infertility due to working conditions that require prolonged sitting in a position that causes the temperature in the scrotum to rise.
Another study in Vietnam also shows that the group of patients who are long-distance drivers have the highest percentage of immobilized sperm compared to other risk groups. In addition, professions that have to work in hot environments such as chefs, welders, masons, etc. also have reduced sperm quality.
6.4 Bacterial infections Men with inflammation of the genital organs, eg orchitis due to complications from mumps or bacteria; epididymitis, genital tract infection caused by gonorrhea, syphilis, etc., the process of increasing temperature or the formation of anti-sperm antibodies can cause the spermatogenic epithelium to be destroyed, leading to testicular failure. atrophy, the end result is infertility.
6.5 Radiation and Magnetic Field Sperm cells are very sensitive to radiation. When exposed to high-intensity radiation sources, spermatozoa are destroyed leading to irreversible infertility. In addition, radiation also damages chromosomes, causing malformations in later generations.
Magnetic fields generated by household electrical appliances, industrial electricity,... Low frequency and high intensity magnetic fields can adversely affect spermatogenesis.
6.6 Diseases and certain medications Systemic diseases affect sperm production. Specifically:
Acute diseases such as burns, injuries, surgical emergencies requiring surgery to inhibit spermatogenesis; Chronic diseases such as kidney failure, liver failure, endocrine disease,... reduce spermatogenesis; Cancer: Treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy lead to decreased spermatogenesis or completely stopped. In addition, some drugs are recommended to affect spermatogenesis, for example hormonal drugs, cimetidine, sulphasalazine, spironolactone, spironolactone, colchichine, chemicals in cancer treatment,. ..
Spermogenesis is a complex multi-step process that is regulated by a variety of local and systemic mechanisms. This process is very sensitive to the effects of biological, physical, and chemical factors inside and outside the body. Understanding the spermatogenesis process in men not only helps in the treatment of male infertility, but also forms the basis for research into effective methods of birth control.
Doctor Vo Thien Ngon has over 7 years of experience working as a urologist and surgeon at Hospitals: Hue Central Hospital, Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital, Tam Tri Da Nang General Hospital .
Doctor Ngon with the ability to specialize in the field of examination and treatment of diseases of the Urology and Andrology system, Urology surgery, endoscopic urological surgery, Laparo urinary tract surgery, endoscopy Urinary. Currently, Dr. Vo Thien Ngon is a Urology - Orthopedic Surgery Doctor, Department of General Surgery, Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com; medicalnewstoday.com