This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by MSc Duong Van Sy - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Environmental pollution is increasing, leading to an increase in ENT diseases, including otitis media. The disease occurs at any age and is most common in young children. Because ear diseases have similar symptoms, many people are often subjective. The article will give you the most overview about otitis media, helping to prevent, detect, and treat the disease better.
1. What is otitis media?
Otitis media is a group of diseases in the middle ear, is the damage and inflammation that appears in the middle ear due to bacteria that multiply and grow in the ear or affected by external factors in the environment.
There are two main types: acute otitis media and exudative otitis media.
Acute otitis media is a persistent infection of the middle ear. This disease can be the cause of ongoing damage to the middle ear and eardrum, and prolonged damage can cause persistent fluid to leak through the hole in the eardrum. Otitis media with discharge is an infection in the middle ear that has not been infected for more than three months. The disease usually does not have obvious physical symptoms, sometimes the patient only has a feeling of fullness in the ears. All of the above types may be related to the patient's hearing loss. Hearing loss in exudative otitis media due to persistent disease, may affect learning ability in children with the disease. The phenomenon of acute otitis media can gradually turn into otitis media with purulent, purulent or purulent fluid if not handled properly.
2. Causes of otitis media
The most important cause of otitis media is the structural and functional immaturity of the eustachian tubes in their age and the immaturity of their immune system.
The eustachian tube dysfunction that can cause otitis media with effusion is tubal obstruction or abnormal opening. Tubular occlusion may be functional or mechanical, or both. Functional tubal occlusion is caused by prolonged collapse of the eustachian tube, too soft eustachian tube, abnormal opening mechanism, or both. Faucet obstruction is common in infants and young children because the softer cartilage of the faucet makes opening the faucet difficult. Furthermore, there seems to be a difference between the craniofacial base in children and adults that makes the dilatation of the pharynx less effective in children.
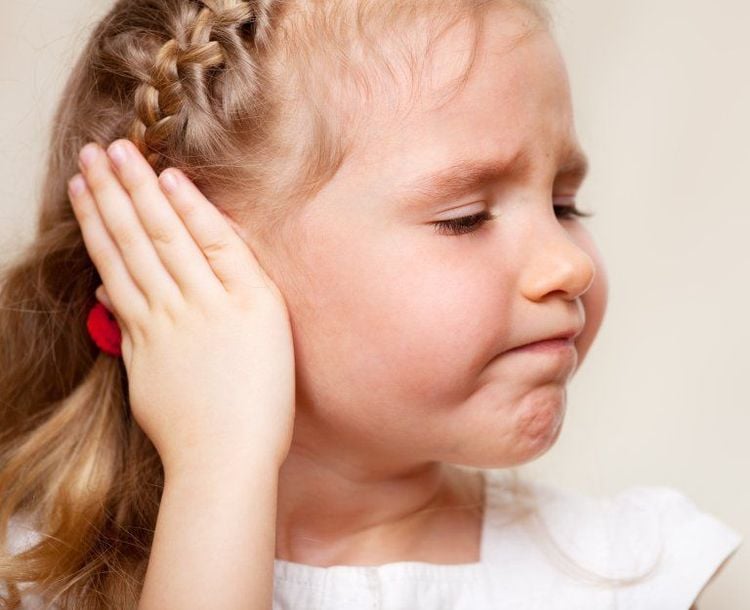

3. Symptoms of otitis media
Physical symptoms of acute otitis media include bulging or immobile eardrums when air is pumped into the ear, and fluid draining from the ear (not related to otitis externa).
Otitis media in young children often manifests with the following symptoms:
Children have a fever, usually a high fever of 39 - 40 degrees Celsius, crying a lot, refusing to breastfeed, poor appetite, vomiting, convulsions. If they are older children, they will complain of ear pain, while young children can only shake their heads and rub their ears with their hands. Gastrointestinal disorders: Children have loose stools, many times, appearing almost simultaneously with fever symptoms. Babies with unexplained fever, diarrhea and vomiting should have a thorough ENT examination so that acute otitis media can be detected early.
If not detected and treated promptly, a few days later (2-3 days) the disease will progress to the purulent rupture stage due to the perforated eardrum, pus draining out through the ear canal with the following symptoms:
Children reduce fever, cry less, eat and sleep. End of digestive disorders, bowel movements return to normal. No more ear pain. In fact, at this time, the disease did not improve, but began to turn into a chronic stage, with a very important sign of purulent ear discharge.
If left untreated, the disease will progress to chronic otitis media or chronic mastoiditis, with the risk of complications that can occur at any time.
4. How to treat otitis media?
The treatment of otitis media is aimed at restoring hearing, preventing the progression of irreversible chronic diseases such as otitis media with adhesions, atrial fibrillation, eardrum retraction bags or attrial collapse, and preventing otitis media. recurrence level.
For medical treatment, the drugs used to treat include antibiotics, antihistamines, anti-edema drugs, nasal drops, corticosteroids, eustachian tubes (helps improve hearing immediately but only in a short time), no more than 1 hour, frequent use, may damage the faucet speaker and cause infection upstream).
For surgical treatment, the patient is performed curettage of the VA; tonsillectomy in the presence of recurrent tonsillitis and nasopharyngitis; Ventilation is the most effective treatment solution available today.
Pediatrics Department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, bronchitis , pneumonia in children, ... With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.