This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Alcoholic hepatitis occurs in people who drink a lot of alcohol for many years in a row. Alcoholic hepatitis has a very complicated course, not all heavy drinkers develop hepatitis, and the disease can also occur in people with only moderate amounts of alcohol.
1. Overview
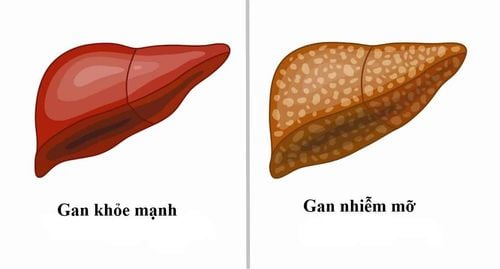
Alcoholic hepatitis is a medical condition caused by long-term alcohol consumption. The disease is aggravated by heavy drinking and continuous alcohol use.The main cause of alcoholic hepatitis is regular heavy use of alcohol, fat builds up in liver cells and can lead to inflammation and scarring of the liver.
If the sick person detects this condition, stop drinking alcohol immediately. Drinking too much alcohol can lead to other health problems, such as cirrhosis, excessive bleeding, or even liver failure.
Patients may need a liver transplant if they do not receive treatment or stop drinking alcohol in the early stages. Women have a higher risk of alcoholic hepatitis. This may be due to differences in how men's and women's bodies absorb and break down alcohol.
2. Why does alcohol cause hepatitis?

Ethyl alcohol or ethanol is an ingredient in beer, wine and liquor that causes intoxication. It affects every organ in the body and the central nervous system. Alcohol can damage and destroy liver cells. The liver breaks down alcohol for elimination from the body. The liver can only metabolize alcohol in small doses, with excess alcohol circulating throughout the body. Drinking more alcohol than the body can handle can cause serious injury or damage to the liver.
Alcoholic hepatitis occurs when a person drinking too much alcohol damages the liver. These chemicals trigger an inflammatory process that destroys liver cells. Over time, scarring replaces healthy liver tissue, interfering with liver function. This irreversible scarring (cirrhosis) is the end stage of alcoholic liver disease.
In addition, if a person has had hepatitis B, hepatitis C, hemochromatosis in the past, and alcohol use - even in moderation - is more likely to develop cirrhosis than if not drinking.
Malnutrition: Many people who drink heavily are malnourished because they eat poorly or because alcohol and its byproducts prevent the body from absorbing nutrients properly. Lack of nutrients contributes to liver cell damage.
Most people with alcoholic hepatitis have a history of drinking more than 3.5 ounces (100 grams) - the equivalent of seven glasses of wine, seven beers or seven spirits - daily for at least 20 years.
However, alcoholic hepatitis can occur in people who drink less and have other risk factors such as:
Patient's sex : Women are at higher risk for alcoholic hepatitis This is due to differences in how women metabolize alcohol. Obesity: Heavy drinkers who are overweight may be more likely to develop alcoholic hepatitis and progress from that condition to cirrhosis. Genetic factors: Studies suggest a genetic component in alcoholic liver disease although genetic and environmental factors are difficult to separate. Race and ethnicity: Blacks and Hispanics have a higher risk of alcoholic hepatitis. Complications of alcoholic hepatitis cause severe liver damage, involving scar tissue. Scar tissue can slow blood flow through your liver, increase pressure in a large blood vessel (portal vein) and build up toxins.
3. Prevention of alcoholic hepatitis

Protect the body from hepatitis C, because hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease caused by a virus that, when left untreated, can lead to cirrhosis. If you have hepatitis C and drink alcohol, you are more likely to get cirrhosis than if you don't drink.
Do not drink alcohol while taking medication, because it can cause complications when combined with alcohol - especially pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol, others). Consult your doctor if you are taking any medication and want to drink alcohol.
With nearly 10 years of experience in the field of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong has successfully performed many complicated endoscopic interventions, detecting many digestive cancer lesions at an advanced stage. early, bringing health and peace of mind to many patients. Doctor Phuong specializes in early cancer diagnosis in stomach and colon, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in the treatment of biliary tract stones, biliary atresia, cholangiocarcinoma, biliary fistula and treatment of cardiac spasms with technique of opening muscle through the mouth to treat cardiac spasms.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Mayoclinic.org