This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Department of Gastroenterology - Endoscopy, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Currently, the rate of people with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is increasing rapidly. If non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is not detected and treated promptly, it will cause serious consequences. There are many causes of nonalcoholic fatty liver.
1. Causes of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
When using a lot of foods containing high fat content that is not converted into energy by the liver or the metabolism is slowed down, it will lead to fat accumulation in liver cells, causing fatty liver. not by alcohol.
People with the following factors have a higher risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:
Overweight and obese Being middle-aged, higher rates in men than women High blood pressure Disorders Hereditary metabolic syndrome Polycystic ovary syndrome Dyslipidemia Type 2 diabetes Hypothyroidism, hypopituitarism, hypogonadism However, some people still have fatty liver disease without other factors. above risk.

2. Diagnosis
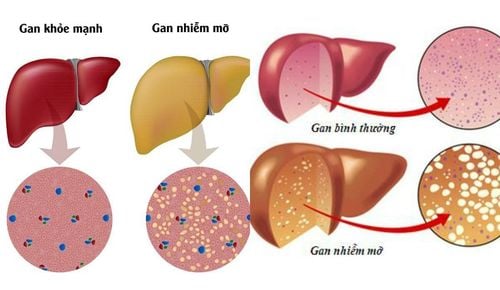
Nonalcoholic fatty liver is divided into 2 types:
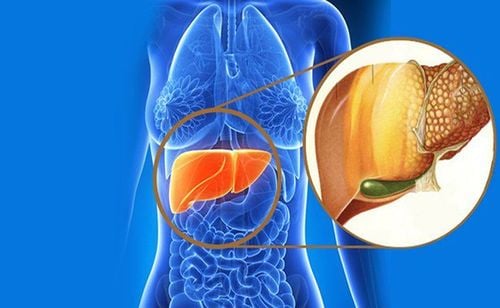
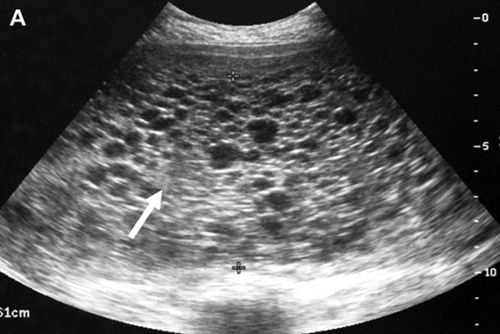
Fatty degeneration: a mild fatty liver disorder that does not cause damage to the liver. Over time it can lead to a progressive condition. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: it is inflammation in and around fatty liver cells that can progress to cirrhosis, liver failure, and primary liver cancer. 2.1.Assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver Fatty liver can be identified by abdominal ultrasound.
2.2. Evaluation of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis The scales to evaluate the degree of liver fibrosis include: Fibrotest
Evaluation of liver fibrosis by liver elastography technique.
Combination of biomarkers, liver fibrosis assessment index and liver elasticity measurement to monitor and evaluate liver fibrosis.

3. Progress
For patients who have progressed to hepatitis, especially cirrhosis, there is an increased risk of liver cancer and death.
4. Treatment
Maintain a healthy diet and exercise. Limit foods high in cholesterol and increase your intake of green vegetables and fruits. Use medication to lower high triglycerides and cholesterol Do not drink alcohol Control blood sugar

5. Those who need to be screened for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Subjects with persistent elevation of liver enzymes, obesity, type 2 diabetes, high blood lipids or metabolic disorders must periodically have a check-up to assess the degree of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Studies around the world show that the number of patients with liver cancer caused by non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is increasing. In the future it may be the cause of liver cancer. It is recommended to regularly visit specialists and combine with treatment methods to limit the risk of disease and progression of the disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
See also:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Non-alcoholic fatty liver: Progression and symptoms Non-alcoholic fatty liver: Diagnosis and treatment Who is susceptible to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease? Non-alcoholic fatty liver: Causes, symptoms, complications