This is an automatically translated article.
Post by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalBased on how the cancer cells look under the microscope, the doctor divides them into 2 types of lung cancer, which are small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. If you think you have symptoms of lung cancer, see your health care provider. Your doctor will diagnose lung cancer using the following methods.
1. Diagnosis of lung cancer by clinical examination
Your doctor will check your vital signs such as oxygen saturation, heart rate and blood pressure, listen to your breathing, and check your liver or swollen lymph nodes. They may send you for additional testing if they see anything unusual or problematic.
2. CT Scan A CT scan is an X-ray beam that takes several pictures of the inside as it rotates around your body, providing more detailed pictures of your internal organs. This method of diagnosing lung cancer can help doctors identify early cancers or tumors better than with a standard X-ray.
3. Bronchoscopy
A thin, lighted tube called a bronchoscope will be passed through your mouth or nose and down into your lungs to examine your bronchi and lungs. They may take a sample of cells to test.
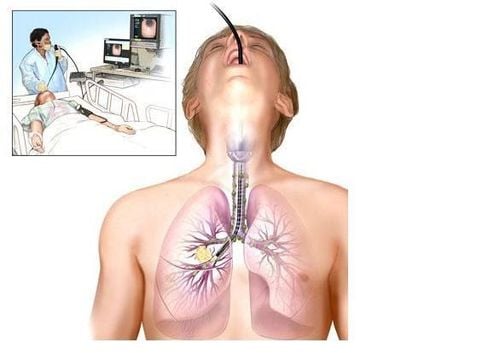
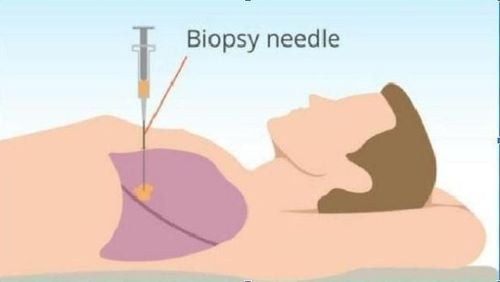
5. Lung biopsy Imaging tests can help your doctor detect masses and tumors. Some tumors may have suspicious features, but radiologists cannot be sure whether they are benign or malignant. Only a biopsy can help a doctor determine if suspicious lung lesions are cancerous. A biopsy will also help your doctor determine the type of cancer and help guide treatment. Some lung biopsy methods include:
During a thoracotomy, your doctor inserts a long needle to take a sample of fluid, called a pleural effusion, between the layers of tissue lining your lungs . During fine-needle aspiration, your doctor will use a thin needle to remove cells from your lungs or lymph nodes. Core biopsy is similar to fine-needle aspiration. Your doctor uses a needle to take a larger sample called a "core". During a thoracoscopy, your doctor will make a small incision in your chest and back to examine lung tissue with a thin tube. During mediastinoscopy, your doctor will thread a thin lighted tube through a small incision at the top of your breastbone to visualize and take a sample of tissue and lymph nodes. During an endobronchial ultrasound, your doctor uses sound waves to guide the bronchoscope down your windpipe or “windpipe” to look for tumors and take pictures if they appear. They will also take samples from the areas mentioned. During a thoracotomy, your surgeon will make a long incision in your chest to remove lymph node tissue and other tissues for examination.
Other tests may be needed to determine if the cancer has spread or metastasized anywhere in the body:
Doctors may order an MRI when they suspect lung cancer may have spread spread to the brain or spinal cord. Positron emission tomography involves the injection of a radioactive drug or tracer, which collects in cancer cells, allowing your doctor to see areas of cancer. Doctors only order bone scans when they suspect that cancer has spread to the bones. It involves injecting radioactive material into your vein, which builds up in abnormal or cancerous areas of the bone. Then they can see it on the picture. In short, you should see your doctor immediately if you suspect you may have lung cancer. Many tests are available to determine what stage a lung cancer diagnosis is in if you have cancer. Detecting cancer early can help doctors treat it more effectively. Whatever stage the cancer is in, treatment is available.
In particular, lung cancer screening is the most effective measure for you to detect and promptly treat lung cancer, protect your health and life. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has a Lung Cancer Screening Package with many outstanding advantages such as:
A team of highly qualified and experienced doctors. Comprehensive professional cooperation with domestic and international hospitals: Singapore, Japan, USA,... Comprehensive patient care and treatment, multi-specialty coordination towards individualizing each patient. Having a full range of specialized facilities to diagnose the disease and stage it before treatment: Endoscopy, CT scan, PET-CT scan, MRI, histopathological diagnosis, gene-cell testing, .. Full range of main cancer treatment methods: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplant... When registering for the Lung Cancer Screening Package at Vinmec, customers will receive:
Examination respiratory specialist Low-dose computed tomography lung cancer screening
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:Lung cancer fact sheet. (2016) lung.org/lung-health-and-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/lung-cancer/learn-about-lung-cancer/lung-cancer-fact-sheet.html?referrer=https://www .google.com/ Lung cancer (small cell) (2016, February 26). Retrieved from cancer.org/cancer/lungcancer-smallcell/detailedguide/small-cell-lung-cancer-diagnosis Lung cancer – patient version. (n.d.) cancer.gov/types/lung Mayo Clinic Staff. (2015, September 25). Lung cancer: definition mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/lung-cancer/basics/definition/con-20025531