This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Nguyen Hong Tram - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the examination and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases, especially gastrointestinal - hepatobiliary diseases, gastrointestinal endoscopy and general internal diseases.Hepato-renal syndrome (HRS) occurs mainly in patients with advanced cirrhosis, but can also be seen in acute liver failure. HRS can occur spontaneously or after a precipitating factor. The mortality rate of patients with hepatorenal syndrome is about 80-95%. Median survival is 2 weeks.
1. Classification of hepatorenal syndrome
Hepatorenal syndrome is divided into 2 types:Type 1:
HRS type 1 is characterized by rapidly progressive renal failure, i.e., within 2 weeks doubling of baseline serum creatinine to levels above 226 umol /L.
HRS type 1 usually occurs after predisposing factors, especially infection with ascites. The prognosis of HRS type 1 is very poor.
Type 2:
This type is characterized by moderately progressive renal failure. The disease usually progresses spontaneously but may also appear after precipitating factors. Serum creatinine concentration from 133 to 226mcmol/L.
Typical HRS type 2 is often accompanied by persistent ascites. The prognosis of type 2 HRS is better than type 1 HRS.
2. Causes of liver and kidney failure syndrome
Predisposing factors:Excessive drainage of ascites without albumin replacement, usually causes HRS type 1 to 15%. Infection with ascites causes HRS type 1 to 30%. Gastrointestinal bleeding. Major surgery. Nephrotoxic drugs: Anti-inflammatory analgesics, diuretics overdose. Patients at high risk of renal failure:
Pre-existing ascites. Severe liver failure. The liver is not big. Pre-existing mild renal impairment (Cr >1.5mg/dl, MLCT <50ml/min). Malnutrition . Low blood sodium. Increased urinary osmotic pressure. Reduce blood colloidal pressure. Increased blood potassium. Esophageal varices.
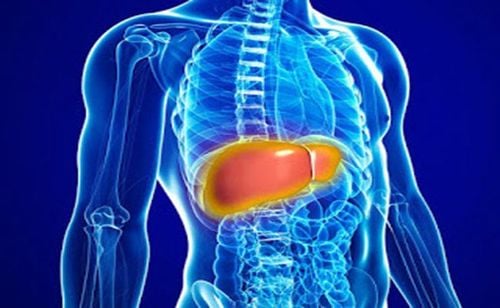
3. Symptoms of hepatorenal syndrome
3.1 Clinical
Manifestations of liver failure: Jaundice, malnutrition, coagulopathy, hepatic coma. Oliguria, anuria, urine output < 500 ml/24 h, and condition not improving with diuretics or albumin replacement. Circulatory failure with a decrease in arterial blood pressure.3.2 Subclinical
Increased blood creatinine, blood electrolytes, urine electrolytes: Manifestations of prerenal acute renal failure (decreased urinary Na concentration, increased urinary osmolality and increased urinary osmolality/blood osmolality ratio) . Biochemical tests: Manifestations of liver dysfunction. Tests help rule out other causes of kidney failure. Abdominal ultrasound: Normal renal parenchyma and calyx, normal kidney size.4. Treatment of hepatorenal syndrome
4.1 Prevention of hepatorenal syndrome
Use of antibiotics and albumin infusion in patients with infectious cirrhosis with ascites can prevent HRS. Do not use nephrotoxic drugs such as aminoglycoside antibiotics, NSAIDs. Avoid excessive use of diuretics that cause fluid loss.4.2 Treatment of hepatorenal syndrome type 1
Initial treatment for type 1 HRS is with vasopressors and albumin.The most widely used vasoconstrictor is Terlipressin. Midodrine plus octreotide and dopamine are two other treatments that require further clinical evaluation. Dopamine can be used as low as 1.5-2mcg/kg body weight/hour in combination with albumin infusion.
4.3 Treatment of hepatorenal syndrome type 2
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.